Political Landscapes: Barriers and Walls in the 20th and 21st Century
advertisement

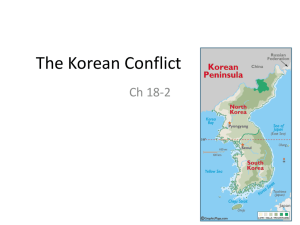
Political Landscapes: Barriers and Walls in the 20th and 21st Century AP Human Geography Directions • Use the graphic organizer provided to document information about important barriers/walls built by countries to establish their borders. • This graphic organizer will help you answer one of the FRQ’s found on the Unit Exam. THE MEXICO/US BORDER The Border • The Mexico–United States border is an international border running from Imperial Beach, California, and Tijuana, Baja California, in the west to Matamoros, Tamaulipas, and Brownsville, Texas, in the east. • 1,969 miles long Purpose • to slow/control the flow of illegal immigrants/goods from Mexico Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y9Pm8q8 OExM THE BERLIN WALL Another Cold War crisis • Background • East – West rivalry • Berlin divided – contrast the two halves. WEST: Prosperous, helped by US, attracted people from the East. Seen by USSR as ‘infection’ in the heart of Communist East Germany. EAST: Much less prosperous and under Communist control What they wanted The West • Prevent USSR from gaining control of East Germany • To see a united, democratic Germany The East • Maintain control over E Germany • Make the West recognise it as an independent state • Stop the flood of refugees especially the skilled and professional ones – much needed in E Germany Purpose of Wall • to prevent East Germans from fleeing to the West Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=szjFKADu6 9U NORTH KOREA/SOUTH KOREA DEMILITARIZED ZONE NORTH SOUTH PER CAPITA GDP $1,800 Many still suffering from lack of food PER CAPITA GDP $32,020 ECOMONY GROWING RAPIDLY Leadership in N. and S. Korea • Kim Jong-un is the supreme leader of North Korea. He is the son of Kim Jong-il. • Park Geun-hye is the eleventh and current President of South Korea. She is the first woman to be elected as President in South Korea • The two countries are separated by the DMZ (demilitarized zone) at the 38th parallel. • 38th Parallel - line of latitude (38 degrees North) that separates communist North Korea from democratic South Korea. • DMZ – Demilitarized Zone- a weapons-free zone between North Korea and South Korea; no weapons or troops are permitted in this zone, although each side is heavily guarded to prevent invasion by the other; it has also been made into a wildlife sanctuary in hopes that might deter either side from becoming aggressive Purpose of the DMZ • to act as a buffer zone in order to reduce the likelihood of violence between North and South Korea North Korea Population: 24.5 million 57% urban SATELLITE IMAGES AT NIGHT South Korea Population: 50 million 80% urban Video: Escape from North Korea • http://www.nytimes.com/2013/06/06/opinio n/escape-from-north-korea.html?_r=0 Social/Political Consequences • Increased tension between neighboring countries or among citizens within a “walled” country (e.g., East Berlin) • Increased isolation (reduction in the diffusion of culture) • Stigmatizing of excluded population (either internally or externally) • Promotes nationalism, reduces foreign influences, increases xenophobia • Illegal crossing of the border becomes more dangerous • Separation of families, friends, relatives, cultural groups • Increased protection/security from either real or perceived threat • Reduced face-to-face interaction between people of neighboring countries • Increased virtual communication between people of neighboring countries • Reduced migration Economic Consequences • • • • • • • • Cost of construction, maintenance, staffing Creates jobs: construction, maintenance, staffing Reduction in flow of illegal goods Reduction in flow of illegal labor and potential savings in social costs Loss of job opportunities for those excluded, less money earned/sent home, reverse remittances Loss of cheap labor Increased cost of smuggling (humans, drugs, other goods) Reduced seasonal migration Now work with a partner to answer this FRQ: • a. Identify 2 examples of walls or other barriers built by countries in the 20th and 21st centuries. (5 pts) • b. Explain the purpose of one of the examples you identified in part a. (10 pts) • c. For each of the categories listed below, discuss one consequence (positive or negative) faced by countries as a result of walls or other barriers established along their borders. (10 pts) – social or political – economic