lecture_7
advertisement
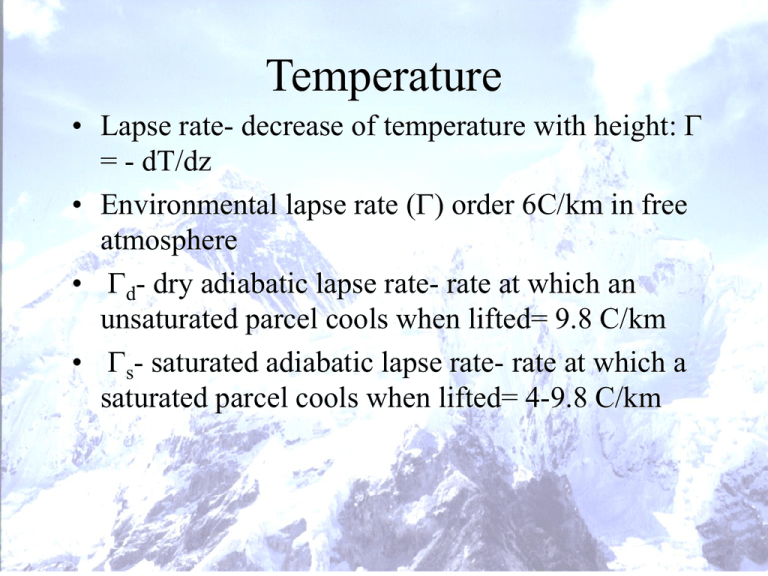
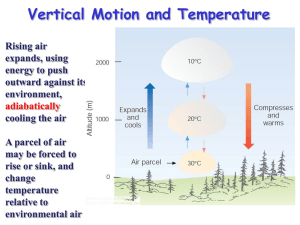
Temperature • Lapse rate- decrease of temperature with height: G = - dT/dz • Environmental lapse rate (G) order 6C/km in free atmosphere • Gd- dry adiabatic lapse rate- rate at which an unsaturated parcel cools when lifted= 9.8 C/km • Gs- saturated adiabatic lapse rate- rate at which a saturated parcel cools when lifted= 4-9.8 C/km Stability • Vertical momentum equation – vertical accelerations due to imbalance between downward directed gravitational force and upward directed pressure gradient force • Stable- adiabatic parcel displaced from original altitude accelerated back towards original altitude • Neutral- adiabatic parcel displaced from original altitude. continues to move at a constant speed • Unstable- adiabatic parcel displaced from original altitude continues to accelerate away from original altitude Stability • Absolutely Stable: G< Gd • Absolutely Unstable: G> Gd • Conditionally Unstable: Gs < G< Gd Lapse Rate Whiteman (2000) Parcel Theory Whiteman (2000) Skew-T log P diagrams • Plot vertical profile of temperature, moisture, wind as a function of elevation • Skewed to draw attention to vertical variations in temperature that deviate from typical 6C/km decrease with height • Dew point temperature- absolute measure of water vapor = f(e) Stability • Adiabatic parcel conserves potential temperature q as it rises or sinks • Stable atmosphere: d q /dz > 0 • Neutral atmosphere: d q /dz =0 • Unstable atmosphere d q /dz <0 Stable atm z q Planetary Boundary Layer • PBL-Layer in atmosphere affected by interaction with the surface • Free atmosphere- atmospheric layer above the PBL in which state variables largely unaffected by the surface PBL • Daytime convective boundary layer – – – – Neutral lapse rate above surface Parcels move freely vertically Strong mixing Can be several thousand meters deep over western U.S. • Nocturnal stable layer – Temperature usually increases with height away from the surface – inversion – Parcels flow horizontally – Little mixing – Usually few hundred meters deep Diurnal PBL Evolution Whiteman (2000) Diurnal Change in Temperature Whiteman (2000) Surface based temperature inversion Whiteman (2000) Elevated Inversion Whiteman (2000) Diurnal changes in stability Whiteman (2000) Whiteman(2000) Mountain/Valley PBL Mountain PBL Barry (1992) Free Air vs. Mountain Barry (1992) Valley vs. Summit Barry (1992) Influence of Wind Speed Barry (1992) Influence of cloud cover Barry (1992) Diurnal Temperature Range Barry (1992) Diurnal Temperature Range: Western U.S. A. Reinecke Wind Speed • Terrain controls wind speed and direction • However, some general characteristics of wind speed vs. altitude • Mid-latitudes: – Wind speed increases with height – Mt. Washington 1915 m: 23m/s in winter;12m/s in summer averages • Tropics – Wind speed decreases with height – New Guinea 4250 m: 2 m/s DJF average – El Misti Peru 4760 m 5 m/s average Wind Speed over Summit • Vertical compression of airflow over mountain accelerates air • Friction retards flow – Small scale roughness effects (<10 m dimension) – Form drag (10m<topography<1km) • Dynamical pressure perturbations created • Proportional to slope2 • Influences atmosphere through considerable depth Vertical compression • Consider case first of steady state, incompressible fluid flowing through constriction: Bernoulli effect Conservation of energy: Kinetic Energy + work down by pressure force + potential energy = 0 Vertical compression • (U22 – U12)/2 + (p2 – p1)/r + g(z2 – z1) = 0 1 U2 > U1 z2 = z1 so p2 < p1 2 Lower pressure in constriction Vertical compression • (U22 – U12)/2 + (p2 – p1)/r + g(z2 – z1) = 0 2 1 U2 > U1 z2 = z1 so p2 < p1 Lower pressure over summit Wind over Hill Barry 1992 Free Air vs. Summit Wind speed less at the summit than in the nearby free air Barry (1992) Roughness Effects • For well-mixed conditions (near neutral lapse rate) • U2 = u1 ln (z2/zo)/ln(z1/z0) • Roughness length zo=.5 h A/S where h height of obstacle, A- silhouette area, S surface area A/S< .1 • Zo- height where wind approaches 0 Terrain Roughness Zo (m) Classification Description .0002 Very smooth Water,pavement .03 open Prairie or farm .25 Rough High crops .5 Very rough >2 Chaotic Scattered bldgs/orchards Towns/forests