Maximum Distance to Oil vs Average Price
advertisement
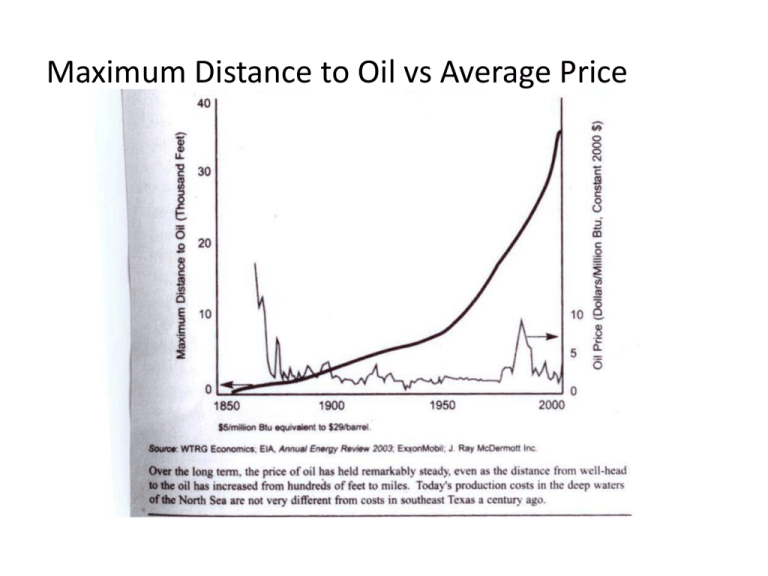
Maximum Distance to Oil vs Average Price Maximum Efficiency of Prime Movers Energy Density of Primary Fuels Power Density Crude Oil Production Natural Gas Production Annual Energy Consumption in England and Wales per capita by type Annual Energy Consumption in England and Wales per capita by type Energy Consumption in England and Wales (petajoules) 900 1800 1600 coal is 92% of the total by 1859 700 1400 600 1200 500 1000 400 800 300 600 200 400 coal is 10% of the 100 200 0 0 1560's Draft Animals 1700-09 Population 1750-59 1800-09 Firewood Wind 1850-59 Water Coal Petajoules (Coal) Petajoules 800 Energy Consumption in England and Wales (percent shares) 100.0% 90.0% 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% 1560's 1700-09 Draft Animals Population 1750-59 Firewood 1800-09 Wind Water 1850-59 Coal Real Prices of Coal and Charcoal in the Midlands Stationary Power Sources in Great Britain 100.0% 90.0% 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% 1760 1800 1830 Steam Water 1870 Wind 1907 Energy Intensity and Energy Prices World GDP and Energy Consumption in the 20th Century 400 35 30 300 25 250 20 200 15 150 10 100 5 50 0 0 1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 Primary Energy Consumption EJ 1950 1960 1970 1980 World GDP trillions of 1990 Dollars 1990 2000 World GDP Trillions of 1990 Dollars Primary Energy Consumption EJ 350 US Energy Consumption, 1949-2009 Energy Consumption per-capita, US, 1949-2009 Energy Consumption per unit of Real GDP, 1949-2009 Energy Expenditures/GDP, 1970-2007 Productivity, Energy and Output in the United States Energy Intensity in the 20th Century, major economies Energy use and Income per person Twentieth Century Gains in Energy Efficiency: Fossil Fuel Plants Twentieth Century Gains in Energy Efficiency: Aircraft Engines Twentieth Century Gains in Energy Efficiency: Iron Smelting Twentieth Century Gains in Energy Efficiency: Ammonia Synthesis Average Price of US Electricity Crude Oil Prices History of US Energy Consumption History of US Energy Consumption Primary Energy Use by Fuel US Primary Energy Flow by Source and Sector US Energy Consumption Non-OPEC Production and the Oil Price GDP, Oil Prices and Oil Capacity OECD Inventories and the Futures Spread OECD liquid fuels consumption and WTI crude oil price Non-OECD liquid fuels consumption and GDP World liquid fuels consumption, GDP, and WTI crude oil prices Changes in OPEC production targets and WTI crude oil prices OPEC spare production capacity and WTI crude oil prices World Crude Oil Prices by Source Crude oil prices and key geopolitical and economic events 1: US spare capacity exhausted 2: Arab Oil Embargo 3: Iranian Revolution 4: Iran-Iraq War 5: Saudis abandon swing producer role 6: Iraq invades Kuwait 7: Asian financial crisis 8: OPEC cuts production targets 1.7 mmbpd 9: 9-11 attacks 10: Low spare capacity 11: Global financial collapse 12: OPEC cuts production targets 4.2 mmbpd Rising oil prices held down global oil consumption growth from 2005-2008, despite high economic growth Average daily open interest in crude oil futures on U.S. exchanges U.S. exchange-traded short positions by physical participants consistently exceed longs Money managers tend to be net long Simon-Ehrlich Commodities Wager Simon-Ehrlich Wager for the Century China’s Energy Production and Consumption Coal in UK GDP, Coal and Oil in UK Uses of a Barrel of Petroleum World Primary Energy Source R R Q1 Q0 K Log of the Real Oil Price (1970:1=100) Nord Stream Pipeline Route Major Pipeline Routes Average Total Cost per ton of Pig Iron TFP in Pig Iron Production Proportion of Iron Smelted from Coke Cost Components of Pig Iron Production in 1755 prices Price of Labor Relative to Energy, early 1700’s Wages relative to the Price of Capital Real prices in London and cumulative output from the north east coalfields, 1700s-1860s Laborer’s Wages Across the World World Oil Reserves, years and totals Natural Gas Reserves, years and totals Exponential Reserve Index EIA Forecast: World Marketed Energy to 2035











