Alpine glacier- Alaska
advertisement

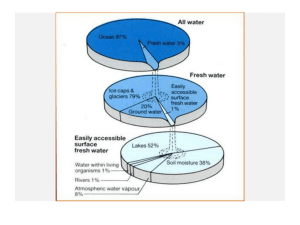
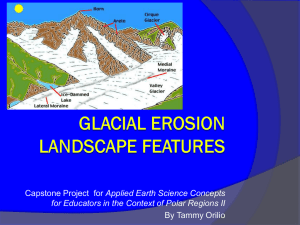
Surface Processes weathering, mass wasting, erosion, deposition GLACIER MOVEMENT SIMILARITIES Alpine and continental glaciers are the same in the way in which the ice moves ----- It is like a slow conveyer belt. Snow enters the glacier at the top or head, becomes compacted and eventually converted to ice. Ice under pressure will flow. Alpine glaciers flow down hill continental glaciers flow from thick areas to thin areas. DIFFERENCES ALPINE VS. CONTINENTAL • Alpine glaciers leave very rugged sharp peaks • Continental glaciated leave rounded and flat areas Alpine glacier- Alaska Alpine/valley glacier Alaska Alpine glacier Mt. Rainier Continental glacier –Mt. Katadin ME rounded mountain top Glacier - Alaska TYPES OF GLACIAL MATERIAL I A. SORTED WATER deposited (glacial-lacustrine) Ex. Kames, eskers (geomorphic features) Outwash plains WIND deposited sediments near the ice margins Ex. Loess deposits DEPOSITIONAL FEATURES OF GLACIERS ( NAMES of FEATURES) • Moraines- end, lateral, recessional, ground, interlobate --- piles of unsorted material • Kames- delta, terrace, moulin---mounds of sorted material • Eskers--- long snake like features of sorted material • Outwash plains---- flat expanses of fine material washed from the base of a glacier Glacial processes and features applied to continental glaciers Depositional features of Continental glaciers Glacial Ice Alaska Alpine Glacier-Mt Rainier Glacial-Fluvial (Kame) deposit Germantown WI Braided stream- at terminus of glacier Moulin Kame-Pike Lake WI Formation of one type of Kame Holy Hill WI - Moulin Kame Myra Esker near West Bend WI Kettle Moraine Area Gilbert lake WI Cobblestone House TYPES OF GLACIAL MATERIAL II • B. UNSORTED GLACIAL MATERIAL Indicates direct contact with ice, moved by the ice Ex. Till ---- which makes up moraines All moraines are basically till But you can find glacial- lacustrine Deposits with the moraines Typical Shoreline Material in S.E. Wisconsin: gray till , red till, and sand EROSIONAL FEATURES OF GLACIERS Striations Rounding of bedrock U shaped valleys (alpine) Potholes Potholes – Taylor Falls MN Produced by glacial meltwater GLACIAL EROSION- ROUNDED SURFACES GLACIAL STRIATIONS DRUMLINS Depositional and Erosional ? • Elongated in the direction of the ice. • Not found everywhere ( Wisconsin and New York state have several drumlin fields) • Can be composed of rock, till, or sorted sediments. • Suggests they could be the result of glacier advancing over former deposits Drumlin Camblesport WI Drumlins in Jefferson Co. Drumlin in Jefferson Co. Inside the Drumlin Shape of Drumlin GLACIAL AGES (ADVANCES AND RETREATS) • • • • TRADITIONAL NAMES Nebraskan 1,000,000 - 2,000,000 yrs ago Kansanan 400,000 yrs. Ago Illinoisan 115,000 yrs. Ago Wisconsinan ( 65,000 years - 10 ,000 years ago CURRENT NAMES • Pre-Illinoisan • Illinoisan • Wisconsinan past 100,000 years. Most complete history starting about 26,000 years B.P. EXTENT OF GLACIATION The Wisconsin glaciation covered a great part of the eastern u.S. It extended to the east coast and formed such places as long island, cape cod And block island. The rocky mts. Were also exposed to the glacial ice, but in the form of alpine glaciation. The great ski resorts are located in the glacial valleys. (Wisconsinites on the other hand ski mostly on glacial deposites) EXTENT OF LAST GLACIATION OTHER FACTS ABOUT CONTINENTAL GLACIERS A . Ice was 1 to 2 miles thick at its central point (in Canada) B. Sea level dropped by 200-300 ft. Because so much water was taken up in ice. C. Glaciers erode material from the middle of its course and deposit it at the end. D.Wisconsin driftless area - no glaciation during Wisconsinan glaciation ? cause? GLACIAL EROSION AND DEPOSITION POINTS OF GREAT INEREST IN WISCONSIN RELATING TO GLACIERS! 1. Glacial lake Wisconsin--- Cranberry bogs 2. Driftless area 3. Wisconsin dells Driftless Area WI MOST IMPORTANT TO US IN SE WISCONSIN 1. Lake Michigan lobe 2. Green Bay lobe 3. Soils / tills left by these glacial advances 4. The problems of lake shore erosion caused by the glacial - lacustrine materials--Grant Park as an example 5. Old beach levels or shorelines – Drs Park, Beach Dr., Audubon Center 6. Mineral resources of sand and gravel POSSIBLE CAUSES OF GLACIATION A. Variation in the rotation of the earth B. Variation in the solar output C. Plate tectonics D. Volcanism