Radiative Transfer, Clouds and Climate
advertisement

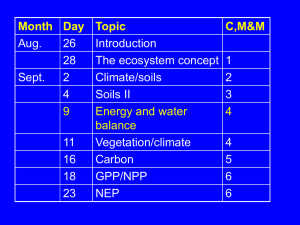
Chapter 3 Atmospheric Radiative Transfer and Climate To date, we have learned 1) The greenhouse effects, through understanding the simplest greenhouse model, 2) The aerosols effects on radiation, clouds, and temperature, 3) The global energy balance, that shows how global energy components are budgeted at the TOA, in the atmosphere, and at the surface. Now, we will further learn here 1) How greenhouse gases affect radiation, 2) How clouds influence radiation, 3) How they together impact temperature profiles, and 4) What is cloud radiative forcing? Recap of the greenhouse effect Solar radiation Long-wave radiation 236 Wm-2 236 Wm-2 Equivalent T = 255 K (-18ºC) 390 Wm-2 T = 288 K (+15ºC) Do you know where is this 236 coming from? How greenhouse gases affect radiation? How does the atmosphere affect radiation? Nitrous Oxide Atmospheric Absorption Earth's re-emitted longwave energy either fits through a narrow window or is absorbed by greenhouse gases and re-radiated toward earth. Methane Absorption (100%) Solar radiation passes rather freely through earth's atmosphere. Ozone Water Vapor Carbon Dioxide UV IR Total Atmo Wavelength Through this atmospheric “window”, satellite sensors are designed to “see”, observe, measure or monitor the Earth’s surface. Spectra of outgoing radiation from Earth observed by IRIS on Nimbus 3 What are the dominant gases in the atmosphere? N2 and O2 Are they greenhouse gases? Why not? Diatomic molecules like N2 and O2 have no permanent dipole moment and no bending moment and so have no capacity to absorb or emit low energy thermal radiation. What are greenhouse gases? CO2, N2O,H2O, O3 Nuclear Configuration and Permanent Dipole Movement Symmetric, linear molecules (Both ends look the same) Nonlinear or bent Have pure rotation bands Vibrational Modes of Diatomic and Triatomic Molecules How do greenhouse gases affect the temperature profile? (1/2) How do greenhouse gases affect the temperature profile? (2/2) Thermal equilibrium profiles How do clouds affect radiation? 1. Liquid water path and solar zenith angle How do clouds affect radiation? 2. Cloud particle size How do clouds affect radiation? 3. Cloud phase (water versus ice) How do clouds affect the temperature profile? How do clouds affect net radiation at TOA? How do clouds affect shortwave radiation? Cloud forcing = average ( or cloudy) – cloud-free How do clouds affect longwave radiation? Cloud forcing = cloudy – cloud-free How do clouds affect net radiation? Cloud forcing = cloudy – cloud-free NET = SW + LW How do clouds distribute globally? How are clouds measured from space? High clouds measured from space? Low clouds measured from space? Summary Now, we have learned: 1) How greenhouse gases affect radiation, 2) How clouds influence radiation, 3) How they together impact temperature profiles, and 4) What cloud radiative forcing is. Seasonal patterns of shortwave cloud radiation Seasonal patterns of longwave cloud radiation Seasonal patterns of net radiation cloud forcing