Document 5314657
advertisement

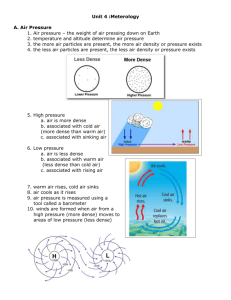
Weather EP.p2X B,C,D,E,G,H WATER IN THE AIR DO NOW What is the difference between Weather and Climate? -Weather is the condition of the atmosphere at a particular time. -Climate is weather over long periods of time Humidity • Humidity- amount of water in the air – Warmer air holds more water vapor • Relative Humidity- amount of moisture in the air compared to (Divided By) how much the air can hold • EXAMPLE: Say the air can hold 24G’s of moisture, but only has 18G’s. What the relative humidity? • Answer- 75%. 18G/24G = .75 – Humidity/ Maximum Possible Humidity • Psychrometer- device that measures relative humidity • Relative Humidity can be affected by: – Rates of evaporation (Water vapor in the air) – Temperature Process of Condensation • Condensation- gas become liquid – Before condensation can occur, relative humidity must be at 100% • Saturated- relative humidity at 100% • Dew Point- temp at which water vapor condenses What’s the Difference? • Dew- when water vapor condenses on a given surface • Fog-cloud with ground surface contact • Clouds- moist air and particles rise quickly, cool, and condense Assignment Day 1 • 1. What is the difference between relative humidity and humidity? • 2. What are the two ways relative humidity can be affected? • 3. What does relative humidity at 75% mean? • Calculate The Relative Humidity: – 4. Possibly Humidity-64G, Current Humidity-16G – 5. Possible Humidty-96G, Current Humidity 24G AIR MASSES AND FRONTS Types of Clouds • Cumulus – Puffy, white, mid-level clouds • Stratus – Thin, long-layered, low-level clouds • Cirrus – Feathery white clouds at high altitudes Prefixes for Clouds • Add these to the front of the cloud types for a new cloud formation – Strato- low level clouds – Alto- mid level clouds – Cirro- high clouds – Nimbo/Nimbus- storm cloud • Air Mass- large body of air with similar temp and moisture – Cold masses bring cold weather, Warm masses bring warm weather • Front- boundary formed between two different air masses – Four types • Cold Front- cold mass meets and pushes warm air masses up • Warm Front- warm air mass meets and moves over top of a cold air mass (brings precip) • Occluded Front- fast moving cold mass over takes a slow warm front and slight warmer cold front, pushing them upward (Lots of Precip) • Stationary Front- cold air mass and a warm air mass meet. Neither move up or down Assignment Day 2 • 1. What is the relationship between air masses and front? • 2. What are the four types of fronts? • 3.What kind of front occurs when two masses meet and neither overtakes the other? • 4. What kind of front occurs when warm air meets cold air and overtakes it? • 5. What kind of front occurs when cold air over takes two masses at once? FORECASTING WEATHER Technology • Thermometer- measures temp • Barometer- measures air pressure • Wind Vane/Sock- measures wind direction • Anemometer- measures wind speed Eyes in the Sky • Weather balloons carry forecasting equipment as high as 30km – Temp, pressure, humidity • Radar is used to find location, movement, intensity of precip Weather symbols used on Weather Maps • Isobars- lines on weather map that connect areas of equal pressure Assignment Day 3 • 1. What are at least three tools for collecting weather data? • 2. How high can weather balloons travel? • 3. For what reasons would you use radar? • 4. How to isobars help when reading a weather map? • 5. Why would meteorologists compare new maps with ones 24hrs old? – (what could they be monitoring?) REASON FOR THE SEASONS What are the reasons for the seasons? DO NOW: • Give a guess as what you think are the reasons for the seasons here on Earth? The seasons are caused as the Earth, tilted on its axis, travels in a loop around the Sun each year. Summers happens in the hemisphere tilted towards the sun, and Winter happens in the hemisphere tilted away. • Bill Nye-Seasons SEVERE WEATHER