6th Grade Science SOL Review: Key Concepts & Questions
advertisement

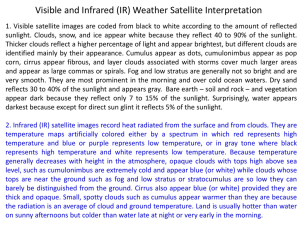
6th Grade SOL Review Unit 1 – Scientific Method Unit 2 - Matter Unit 3 – Properties of Water • Adhesion vs. Cohesion • Adhesion – water sticking to other things • Cohesion – water sticking to other water molecules Surface Tension Capillary Action Changing States Review Questions • What causes water to change states of matter? • Temperature • Water is often called the universal solvent. Why • A large number of substances will dissolve in water. • What is it called when water goes from a liquid to a gas? • Evaporation Unit 4 Weather and Atmosphere Instruments • Barometer • Measures air pressure • Drop in pressure means precipitation is coming Anemometer • Measures wind speed Thermometer • Measures temperature Weather Vane • Measures wind direction Sling Psychrometer • Measure humidity Hygrometer • Measure humidity Review Questions • What instrument measures temperature? • Thermometer • What instrument s measure humidity? • Hygrometer and Sling Psychrometer • What instrument measures wind speed? • Anemometer • What instrument measures wind direction? • Weather Vane • What instrument measures air pressure? • Barometer Types of Clouds Review Questions • • • • • What are the normal fluffy clouds? Cumulus What are the wispy high-level clouds? Cirrus What are the layered clouds that are associated with precipitation? • Stratus • What are the fluffy clouds associated with precipitation? • Cumulonimbus Review Questions • Which layer of the atmosphere has the most mass? • Thermosphere • Which layer of the atmosphere has weather and clouds? • Thermosphere • What layer of the atmosphere has the ozone layer? • Stratosphere The Water Cycle and the Sun • The Sun powers the water cycle. • Solar power causes water in the ocean to evaporate (3) , condense (2) into clouds and fall back to Earth. Earth’s shape and tilt • Earth is round. • Different parts get different amounts of sunlight. • The equator gets the most direct sunlight. • The poles get indirect sunlight. Air pressure and Wind • Wind is moving air. • Differences in air pressure cause wind. • Warmer areas have low pressure. • Cooler areas have high pressure. • Air moves from high pressure areas into low pressure areas. Sea Breezes • During the day the land heats more quickly than the water does. • Warmer air rises over the land. • Cooler air sinks over the water. • A breeze moves from the water to land. Land Breezes • At night the land cools more quickly than the water does. • Warmer air rises over the water. • Cooler air sinks over the land. • A breeze moves from the land to water. Review Question • • • • • How do land breezes happen? Air cools faster over land and moves H to L How does the Earth cause weather? Tilt High pressure areas are associated with what kind of air? • Cool air Air Masses (1) • Air masses are large bodies of air that have the same properties as the area of the Earth’s surface over which it forms and moves. • For example, deserts produce hot dry air masses. Fronts • The place where air masses meet is called a front. • Weather is caused by the way these air masses interact. Cold Fronts • Incoming dense cold air pushes up warm air • This forms a narrow band of violent storms Warm Fronts • Warm air slides over departing cool air. • This forms feathery clouds. Stationary Front • A cool air mass and a warm air masses meet and stop moving (neither one advances). • This causes a few days of rainy and windy weather. Review Questions • • • • • What cloud type can become tornadoes? Cumulonimbus (same as thunderstorms) Where do hurricanes form? Over water Describe how a cold front is represented on a weather map? • Blue line with triangles Unit 5 Space Rotation Revolution Tides Review Questions • What is the difference between rotation and revolution? • Rotation is spinning and revolution is going around or orbiting • What causes tides? • Pull of the moon • What side of the moon is lit during a waxing crescent? • Right Review Questions • • • • • What happened to Pluto? Pluto was declassified to a dwarf planet Which planets are the gas giants? Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune Which planets are the terrestrial planets? • Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars Unit 6 Watersheds Review Question • What states belong to the Chesapeake Bay watershed? • PA, VA, WV, DE, NY, MD and DC • What are the 3 places water in VA will eventually go? • Chesapeake Bay, Gulf of Mexico and North Carolina Sound • What is the name of or local watershed? • Potomac Review Questions • What is the difference between point and non-point pollution? • Point source pollution is identifiable • What are some causes of chemical weathering? • Acid rain • What is an example of abiotic factor in the environment? • Temperature and water (nonliving) Unit 7 Resources Unit 8 Energy