File
advertisement

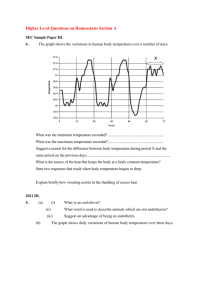
12.1 Learning Objectives Define homeostasis Explain the importance of homeostasis Describe how control mechanisms work Explain how control mechanisms are co-ordinated Success Criteria You can define homeostasis and suggest what things need to be maintained in the body You can create a mind map of ideas for why homeostasis is important You can take notes on control mechanisms You can answer an exam question on homeostasis Starter What is homeostasis? The maintenance of a constant internal environment What things need to be maintained? Temperature Oxygen levels Water levels Tissue Fluid Composition of blood Independence: Stops organisms being reliant on the external environment (wider choices of where to live etc.) Enzymes: sensitive to pH and temperature changes. Big changes could cause denaturation and stop reactions occurring. Why is homeostasis important? Blood glucose: essential to maintain this to maintain water potential and also give cells a constant supply of glucose for respiration. Water Potential: changing this in blood/tissue fluid could make cells shrink or even burst. Would prevent cells operating normally. Control Mechanisms Stages of Homeostatic Control The Set Point (the norm) Receptor (detects variations) Controller (co-ordinates info and sends instructions) Effector (brings about changes) Feedback Loop (tells receptor about the changes) Control Mechanisms Input Fall in some parameter Receptors Detect the change Control Centre Coordination Effector Have an effect on the system Output Rise in some parameter Analysing Info from Receptors Changes can be detected by a number of different receptors This gives the brain a better picture of what is being altered Allows a more informed response to be made Plenary – Exam Q How does maintaining a constant body temperature allow metabolic reactions in cells to proceed with maximum efficiency? (5) Plenary – Exam Q ANSWERS 1. Body temp./37°C is optimum temp for enzymes; 2. excess heat denatures enzymes/alters tertiary structure/alters shape of active site/enzyme; 3. substrate cannot bind/eq,; 4. reactions cease/slowed; 5. too little reduces kinetic energy of molecules / molecules move more slowly; 6. fewer collisions/fewer ES complexes formed’ max 5 Learning Objectives Define homeostasis Explain the importance of homeostasis Describe how control mechanisms work Explain how control mechanisms are co-ordinated Success Criteria You can define homeostasis and suggest what things need to be maintained in the body You can create a mind map of ideas for why homeostasis is important You can take notes on control mechanisms You can answer an exam question on homeostasis