Coniferous Forest - Rachel V Salyer`s Blog
advertisement

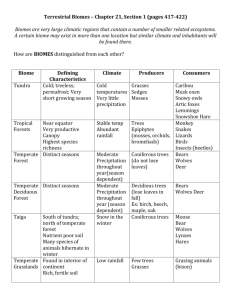
Coniferous Forest By: Jordan Heatherly Salyer Period 3 APES Locations • Coniferous forests are found mostly in Canada, and Asia. However, they are also commonly found in the US, and Europe. • Northern boreal forests, a type of coniferous forest, are typically found between 50 and 60 degrees North latitudes • Temperate coniferous forests, another type, are typically found in lower latitudes of North America, Europe, Asia, or even in higher elevations of mountains. • Coniferous forestsconsidered the largest terrestrial biome in the world Precipitation • The average coniferous forest receives 300 to 900 millimeters of precipitation per year. • However, there have been times that up to 2,000 millimeters were recorded in only one year. • The precipitation in these areas, due to the long, extremely cold winters, is usually snow. • During the moderately warm, moist summers, it has a better chance of being a very cold rain. • Precipitation depends on the location of the forest; In lower latitudes, precipitation is more evenly distributed than in higher latitudes. Temperature • The average temperature of a coniferous forest ranges from -40 degrees Celsius to 20 degrees Celsius, which is converted to -40 degrees Fahrenheit to 68 degrees Fahrenheit. • The average temperature during summer time is around 10 degrees Celsius, or 50 degrees Fahrenheit. • Coniferous forests usually consist of a more subarctic climate Amount of Light • Winter: 6-8 hours a day • Summer: up to 19 hours a day • However, the sun does not bring much warmth. • Also, due to the excess amount of trees, most of the light stops at the tops of the trees and does not protrude through the canopies. • Because of this, little plant life exists below the trees, besides small lichens, and mosses. Air Quality • Air pollution majorly effects the air quality in coniferous forests • It kills off the conifer trees, which provides shelter for animals, homes for animals, oxygen for humans and animals, etc. • It greatly affects environments and their inhabitants in multiple ways Nutrient level • The nutrient level is very poor. • The soil beneath the tall canopies does not get much sunlight, and has an excess amount of pine needles from the conifer trees. • The soil there is also very acidic, causing the soil to not have nearly enough nutrients to successfully sustain other plant life, not counting the small lichens, mosses, and obviously, the trees. Common species Vegetation • • • • • Mostly conifers, trees that grow needles instead of leaves and cones instead of flowers. Conifers tend to be evergreen- bare needles all year long Needles help trees survive in cold or dry areas. Most commonly found conifers in the coniferous forest- spruces, pines, furs Other species- lichens and mosses (cover ground) Plant diversity= low, due to cold temperature and soil moisture is frozen Animals • • • • • • • • • • • • • Woodpeckers Hawks Moose Bears Weasels Lynxes Foxes Wolves Deer Hares Chipmunks Shrews Bats Endangered species Vegetation • • • • • Santa Cruz Cyprus Florida Torreya Wawae’iole (moss) Diellia Falcata (fern) Aleutian Shield Fern Animals • • • • • Grizzly Bear Spotted Owl Woodland Caribou Siberian Tiger Siberian Crane Man’s influence Cause-Effect • Extensive logging-loss of many trees and life, and may eventually cause complete disappearance (endangered) • Burning of fossil fuelspollution some coniferous forests (slowly kills all life, and ruins environments and habitats) Sources • http://www.appsychology.com/Book/Biological/nervous_sy stem.htm • http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Experiments/Biome/bioc oniferous.php • http://www.temperatureworld.com/ctable1.htm • http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/glossary/gloss5/biome/for ests.html • http://www.ehow.com/about_5299579_endangeredanimals-coniferous-forests.html • http://www.ehow.com/facts_5860827_endangered-plantsconiferous-forests.html • http://www.fs.fed.us/psw/publications/documents/psw_ gtr195/psw_gtr195_2_10_Temple.pdf