Native Texans PEGS Power Point
advertisement

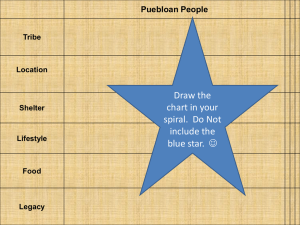
Native Texans “Geography Is Destiny.” Where You Live Effects How You Live Imagine It! • What was it like to live 500 years ago? 2000 years ago? • Can you imagine not having supermarkets or malls to buy food or clothes? • Can you imagine cooking without a stove or building your own house? st 1 Let’s Review 1. What happens as you travel from east to west Texas? Why? 2. How does the vegetation also change going east to west Texas? 3. Remember the types of resources for making shelters in each region. 4. Think of the types of foods and edible animals in each region. Great Plains North Central Plains Northern Coastal Plains Mountains & Basins Southern Coastal Plains Gulf of Mexico North Central Plains Tonkawa & Kiowa Tonkawa • Politically: Had a chief and medicine man. • Caught between the crossfire of regional tribes and Euro-American Settlers • Economic: Used the bow and arrow, spears, and knives for hunting • Traded with the Explorers, especially the French. They traded skins for rifles and other goods. Tonkawa • Geographic: Lived primarily in the Central Texas Area • Were nomadic • Social: Hunted deer, turkey, rabbits, mussels. Occasionally would hunt buffalo if they were in the area. They also fished in the rivers and creeks. • Also ate Prickly Pear Cactus, peaches, acorns, and pecans • Social: Lived in teepees Kiowa- Central Plains • Political: had a chief, a medicine man, & tribal council. • Economic: hunted buffalo • Geographic: roamed the Central Plains - nomadic. • Social: Lived in Teepees. Karankawas Southern Coastal Plains Karankawas • Political: Had a chief and medicine man • Economic: They had long bows for hunting, fishing hooks made of sea shells & fishing nets. • Geographic: Lived along the Coast • Were seasonal wanderers During the winter, Karankawas would fish and hunt and gather shellfish along the gulf coast. During the summer, when fish would migrate out to sea, the Karankawas would break up into smaller groups or bands and go inland to hunt and gather. They ate different varieties of berries and roots and hunted small game such as deer and rabbit. http://www.texasindians.com/karank.htm Karankawas • Social: Built dug-out canoes by hollowing out tree trunks • Social: Ate fish, oysters, and turtles, plant roots, sugar cane, wild berries, other edible plants, and Spanish Explorers (cannibals as part of spiritual ceremony). Karankawas • Social: Camped in shelters that could quickly built with branches, palm leaves and animal hides called a Wickiup • Social: As a custom, men pierced their lower lips and the sides of their chests with sugar cane making them very scary looking. Karankawas • Extra: Were tall and muscular • Extra: They smeared alligator grease all over their bodies to protect against mosquitoes and other insects Wickiups: Sturdy but Temporary Structures Why did the Karankawas sometimes have to relocate? Coahuiltecan • Political: They had a tribal or group leader (chief) • Economy: They used long spears for hunting as well as weapons • Geographic: The lived primarily in the brush country of South Texas along rivers and creeks. • Geographic: Roamed in small bands– nomadic Coahuiltecan • Social: They ate rodents, lizards, snakes, insects, lice, and on occasion killed antelope, deer, and javelina. • Also ate prickly pear cactus, mesquite beans, • Social: used woven baskets to carry food in • Social: They built temporary shelters out of mud, sticks, moss, and brush A modern wickiup reconstruction showing the dome shape and the thatched outer layer covered with animal hide. Coahuiltecan Comanches Great Plains Comanches Comanche • Political: Had chief, medicine man, and tribal council • Economic: Captured wild mustangs or stole horses from other tribes and settlers to demonstrate prowess • expert horsemen • “Lords of the Plains” • Hunted buffalo Economic: They relied on buffalo. The abundance of grass Comanche • Geographic: nomadic, moved according to the hunting seasons • Social: Ate pemmican which was a mixture of dried buffalo meat, nuts, and berries (sort of like trail mix). • Social: • Parted their long hair down the middle with a red stripe and two braids. Comanche • Social: Painted their faces, horses, & teepees • Social: lived in teepees Social: Teepees: Early "Mobile Homes" Used the travois, a sled pulled by a dog or horse, to move their teepees and supplies. Social: Native Americans of the plains were extremely skilled at using the bow and arrow. Lipan Apaches Great Plains Lipan Apaches Lipan Apache • Political: Had chief & tribal council • Economic: Traded with other tribes; hides, robes, honey, pecans, & other Native Americans they had captured The Lipan Apaches hunted buffalo but also gathered plants and farmed. They traded meat, skins, and other animal products for blankets, maize, and other goods. This is a Trade Center. Lipan Apache • Geographic: moved around depending on the season, nomadic • Social: lived in shelters made of animal hides or sticks, depending on available resources • Social: wore footwear that protected their shin from sharp cactus spikes • Social: they were very spiritual & respected all aspects of life as gifts from the Creator Teepees: Early "Mobile Homes" Tigua & Jumanos Mountains & Basins Jumanos Political Government and other facts… Jumanos & Tigua • Political: • Economic: Would hunt for deer, bear, and buffalo using the bow & arrow and spears • Also farming (cotton) • Traded jewelry with other tribes and the Europeans. Jumanos & Tigua • Geographic: both tribes were sedentary: • The Jumanos lived in the Southwest near the Davis Mountains, settling near the Rio Grande River as a water source (used to irrigate their crops) • The Tiguas lived in West Texas near El Paso. Geographic: The Jumanos settled along the Rio Grande River for a water source. The Jumanos used the river to irrigate their farms. Jumanos & Tigua • Social: food- corn, pumpkins, squash, beans, and vegetables. • Built tools to use for gardening. • Social: Made pottery and Wampum necklaces (made from polished ends of shells). Used Turquoise for jewelry. • Social: Built homes out of adobe brick (mixture of ash, dirt, grass, and water that was dried by the sun). Sometimes homes were multi-story, using ladders to get to second level. Pueblos: Community Houses Adobe bricks used to build shelter Economic: Farming allowed Native Texans to be less dependent on hunting wild game.