Template southern-alps

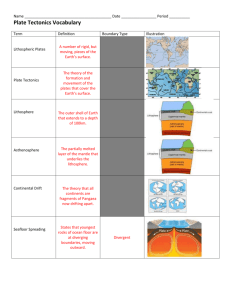
Southern Alps
Key surface features:
• High mountain ranges (1 st )
• V-shaped valleys and jagged ridges
(2 nd )
Internal processes:
• Convection currents move the plates
• Both plates colliding (destructive plate boundary) leading to uplift
External processes:
• Weathering by ice, water, wind, bio
• Erosion of sediment and deposition on the plains
• Three processes must be linked to the surface features for E. At least one internal and one external process is needed (last one can be either).
• One of each must be linked for M.
• All info must be in the context
Step one
Find/draw a diagram (cross section) to show the three ideas:
• Surface features
• Internal processes
• External processes
Annotate this diagram (around the diagram or refer to in the report).
Step two
• A description of the surface features:
• Mountain ranges
• V-shaped valleys and ridges
• Canterbury plains
Step three
Explain the first internal process that has caused the mountain ranges to form.
• Convection currents (explain how they occur)
• Name the two plates that the sounds are found on
• Link the direction of the current to how the plates are moving
• What type of plate boundaries has this caused?
• When was this happening? (most recently)
Step four
Explain the second internal process that has caused the mountain ranges to form.
• What type of plate boundary has this caused?
• When was this happening? (most recently)
• Where has uplift occurred (why did subduction not occur?)
• What type of rocks were being exposed (age type?)
• CONTEXT, CONTEXT – LINK TO THE SURFACE
FEATURES
Step 5
Explain the first external process that reduced the height of the southern alps
• Weathering and erosion
• The cold winters and frost cracking
• Weathering due to melting snow/water
• Erosion of rock due to wind and water
• Change in the appearance of the mountains over time, due to the above.
Step 6
Explain the second external process that has impacted the appearance of the South Island.
• Erosion of weathered rock
• Transportation by rivers that flow down the valleys
• Deposition of sediment forming the
Canterbury plains