Think of a place on Earth visit someday.
advertisement

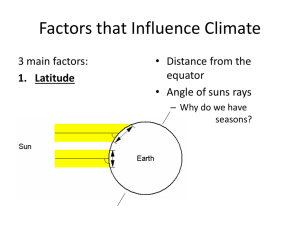
Think of a place on Earth where you would like to live or visit someday. Write a description of the climate at this location and list the various factors that might influence the climate there. Climatogram New York, NY San Francisco, CA Las Vegas, NV Denver, CO Richmond, VA Anchorage, AK Seattle, WA Miami, FL St. Louis, MO Honolulu, HI Hazleton, PA (Scranton/Wilkes-Barre) www.worldclimate.com www.climate-zone.com The state of the atmosphere at a particular place at a particular moment The long-term prevailing weather conditions at a particular place based upon records taken What Factors Determine Climate? Latitude Atmospheric Circulation Oceanic Circulation Topography Other Influences Seasonal Changes in Climate What Factors Determine Climate? #1-4 TABLE 1: Latitude #5-9 TABLE 2: Atmospheric Circulation #10-13 TABLE 3: Oceanic Circulation #14-18 TABLE 4: Topography #19-23 TABLE 5: Other Influences #24-27 TABLE 6: Seasonal Changes in Climate What Factors Determine Climate? #1-5 TABLE 1: Latitude #6-10 TABLE 2: Atmospheric Circulation #11-15 TABLE 3: Oceanic Circulation #16-20 TABLE 4: Topography #21-24 TABLE 5: Other Influences #25-29 TABLE 6: Seasonal Changes in Climate Latitude Distance from the equator measured in degrees north or south of the equator most important factor in determining climate influences climate because the amount of solar energy an area receives depends on its latitude more solar energy falls on areas near the equator than those near the poles Latitude Atmospheric Circulation 3 important properties: Cold air sinks because it is denser than warm air. As it sinks, it compresses & warms. Warm air rises. It expands & cools as it rises. Warm air can hold more water vapor than cold air can. As it cools, the water vapor may condense to form rain, snow or fog. Atmospheric Circulation The movement of air within the atmosphere wind Because the Earth rotates, and because different latitudes receive different amounts of solar energy, a patter of global atmospheric circulation results. This circulation pattern determines Earth’s precipitation patterns. Atmospheric Circulation Oceanic Circulation Patterns Ocean currents have a great effect on climate because water holds large amounts of heat. Movement caused by winds & the rotation of the Earth Redistribute warm & cool masses of water around the world & affect the climate Topography Temperatures fall by about 6oC (about 11oF) for every 1,000m increase in elevation Mountains and mountain ranges also influence the distribution of precipitation Rain shadow: warm air hits mountains, rises, cools, and causes rain on the western side of the mountain By the time the air reaches the eastern side of the mountain, it is dry Topography Other Influences on Earth’s Climate Sun Ultraviolet (UV) radiation warms the stratosphere, then the lower atmosphere & even the surface of the Earth Volcanoes Sulfur dioxide gas can reach the upper atmosphere Reacts with water vapor & dust. Forms a bright layer of haze that reflects enough sunlight to cause the global temperature to decrease Seasonal Changes in Climate Seasons result from the tilt of the Earth’s axis