CHORDATES:
FISHES
(JAWLESS, BONY AND CARTILAGINOUS CREATURES)
Barbara Leary and Amy Vallis
AP Biology
Ms. Bergman
April 8, 2011
BODY STRUCTURE AND COVERING
BONY FISH (Teleosts)
-Scales are flatter covered by
thins layers of skin and
mucus making them slippery
-Body cavity with air filled
bladder (used to float)
beneath spinal column
JAWLESS FISH
-covered in skin, not
epidermal or dermal cells
CARTILAGINOUS FISH (Elasmobranchs)
-No ossified bone
-No swim bladder (must be in constant motion)
-Scales project through the skin and
are rough
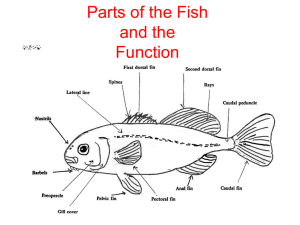
Fins maintain the stability and maintain the direction of the fish.
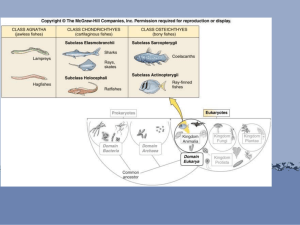
JAWLESS FISH: Lampetra fluviatilis
CARTILAGINOUS FISH
BONY FISH
GAS EXCHANGE
• Gills found in other creatures
besides fish such as:
•Mollusks
•, annelids,
•crustaceans,
•echinoderms,
•vertebrates.
•Gills must be very efficient to
meet the respiratory demands of
aquatic animals.
•Fish gills, for example, can
extract more than 80% of the
oxygen dissolved in water.
GAS EXCHANGE CON’T
Fish gills are made of
numerous suspended
curtains of tissue,
called filaments, that
increase their respiratory
surface area. Gill tissue is
permeated with many
small water-bearing
channels surrounded by
capillaries. Because the
water channels and
capillaries are so close to
one another, O2 and
CO2 readily diffuse
between the blood and
water.
FISH HEARTS
-Simplest vertebrate hearts (single-circuit circulation):
-Two main chamber:s
-Thin walled atrium
-Muscular ventricle
Process: Atrium pumps blood into the ventricle
which pumps blood into the copus which pumps the
blood to the gills to oxygenize it and return it to the
atrium.
MODE OF FERTILIZATION
Fish can use both internal and external fertilization, but external is more common.
97% of fish a oviparous (developing outside the mother’s body with no
nourishment), while the rest are the opposite—viviarous.
EXTERNAL
Spawning occurs-release of egg and sperm in aquatic animals
-Female fish grow thousands of unfertilized eggs inside their body for several
weeks to increase chance of fertilization.
-Once produced, they are then laid in a safe place for male fish to fertilize them
with their semen.
-This allows conception to take place, and immediately the fish eggs start to
become fish.
INTERNAL
-Modified fin- gonopodium- used to insert itself in the sex opening of the female
and sperm is preserved in the oviduct to be used when they please
INTERNAL TEMP. REGULATION
Cold-blooded
Warm-blooded
•Most fish are ectotherms
(cold blooded), as all of
their heat comes from the
surrounding water.
However, some are
homeotherms (warmblooded) because their
temperature is very stable.
•This can be due to their
location, type of water,
how they breed, etc..
INTERNAL
Male gonopodium compared to
regular female fins
EXTERNAL
Fish during spawning season
(Salmon especially)
MODE OF DEVELOPMENT
•The most common reproductive
strategy for fish is known
as oviparity, in which the female
lays undeveloped eggs that are
externally fertilized by a male. and
the eggs are then left to develop
without parental care.
•A few fish, notably the rays and
most sharks use ovoviviparity in
which the eggs are fertilized and
develop internally. However the
larvae still grow inside the egg
consuming the egg's yolk and
without any direct nourishment
from the mother.
•In certain rare scenarios, some fish such as certain sharks, with the egg
being fertilized and developed internally, but with the mother also
providing direct nourishment.
SUBGROUPS
JAWLESS
-Hagfish (slime eels)
-Lamprey Eels
CARTILAGINOUS
-Sharks
-Rays and Skates
BONY
-Lobe-finned
-Ray-finned
Works Cited
http://www.texaseducator.com/family/jbouyer/lessons/Science/askew/mycourses/fisheart.gif
http://users.rcn.com/jkimball.ma.ultranet/BiologyPages/F/fish_heart.gif
http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRpF3gq4eNZv-nIKcafkKHy7wytdqXSVCiHp0zAqlfZE7Ljr_O2w&t=1
http://www.arthursclipart.org/biologya/biology/fish%20spawning.gif
http://blogs.kcls.org/librarytalk/sockeye-salmon.jpg
http://aqualandpetsplus.com/Livebe6.jpg
http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/food-kitchen/food/cartilaginous-fishes.jpg
http://images.quickblogcast.com/55522-48672/bony_fish.jpg
http://faculty.fmcc.suny.edu/mcdarby/animals&plantsbook/Animals/10-Vertebrates.htm
http://www.instablogsimages.com/images/2007/09/05/sea-lamprey-makes-return-to-river-tamar_9.jpg
http://www.animalport.com/img/Shortfin-Mako-Shark.jpg
http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/resources/Grzimek_fish/Rajiformes/v04_id149_con_ventral.
jpg/medium.jpg
http://t1.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcTowxa0CbkD1sTpVaid7nuwW69y4Hair_AL1URJDojXUd41zLj
fYA
http://animaldiversity.ummz.umich.edu/site/resources/Grzimek_fish/structure_function/fin_function_d
iversity.jpg/medium.jpg