Chapter 3
advertisement

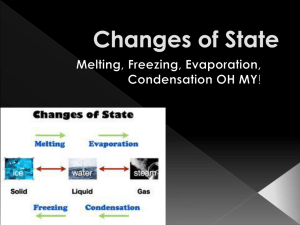
Chapter 3 Solids, Liquids, and Gases 8th Grade Science States of Matter • Solids, liquids, and gases can be _________, elements __________, or ___________. compounds mixtures • _________ - a definite shape and volume Solid – Solids will keep their shape in any position and in any container – Particles of a solid are packed _________together Closely vibrate slightly – they are in – Particles of a solid ______ constant motion. – Particles stay in the same position - ________ in place vibrate Types of Solids • _____________ Crystalline solids - particles in a regular, repeating pattern. Examples: sugar, salt, and snow. – Cyrstalline solids will melt _____ at a specific temperature. Amorphous solids • _______________ - particles are not arranged in a particular pattern. Examples: plastics, rubber, and glass. – Amorphous Solids will _________ not melt at a specific temperature – they may become softer and softer until they change into other substances. Example: butter. Liquids Liquids - a definite volume and takes the • ______ shape of its container. - particles of a liquid are packed almost as closely as a solid. freely than in a -particles move around more _____ solid. - no definite _____ shape but a definite ________. volume Fluid ______ - freely moving particles. Properties of Liquids • ____________ - the result of an inward pull Surface Tension among the particles of a liquid that brings the particles on the surface closer together. – Water particles pull together and bead up on surfaces or form a skin – water striders walk on water due to surface tension viscosity • ___________ - a liquids resistance to flowing. – Depends on the size and shape of the particles and the attractions between the particles. – Liquids with ______ viscosity flow ______ high Slowly (honey) Gases • ______ - can change volume , particles are Gas spread out and free to move, no definite shape. – Particles of gas move in all directions. – As gas particles move, they fill the space around them – Particles of gas can be squeezed into a container. When the container is open, the particles will move freely and spread out. Changes Between Solid and Liquid • Particles of a liquid have more ________ thermal energy than particles of the same substance in solid form. • Particles of the same substance as a gas has even more _________ energy than the liquid thermal or solid form. • A substance changes state when its thermal increases or __________ decreases energy either _______ sufficiently. Melting • A change in state from a solid to a liquid involves the ________ in thermal energy. increase • ___________ is the change in state from a solid Melting to a liquid. Melting point - specific temperature at which the • ___________ melting occurs. • At a substances ____________, the particles that Melting point are bound together begin to vibrate so rapidly that they break free from their fixed positions. Freezing • __________ - the change of state from a liquid Freezing to a solid. • _________ of melting Reverse • ____________ - the particles begin to move Freezing Point so slowly that they begin to form a regular pattern. • Example: water loses energy – water molecules move slowly because they lose energy until freezing is complete Changes between Liquid and Gas • ____________ - the change from a liquid to a Vaporization gas. energy • Particles gain enough _______ to form a gas. evaporation • ___________ - vaporization that takes place only on the surface of a substance. boiling • ________ - vaporization that occurs when a liquid changes to a gas below the surface as well as at the surface of the liquid. Boiling Point / Condensation Boiling point • The __________ of a substance depends on the __________ of the air above. pressure lower less energy • The _______ the pressure, the ___ needed for the particles to escape into the air. Condensation • ___________ - opposite of vaporization. Particles in a ___ Gas lose enough energy to form liquid a _____. Changes between a Solid and a Gas • ____________ - surface particles of a solid Sublimation gain enough energy that they form a gas without passing through the liquid phase. • Example: dry ice (aka