Model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing
advertisement

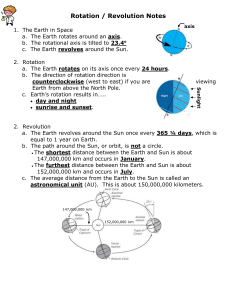
TEKS 8.7A: Model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the Sun causing changes in seasons. What causes day and night? • An imaginary line that passes through Earth’s poles is called its axis. Earth’s axis is tilted about 23.5 degrees. • Earth spins, or rotates, around its axis once every 24 hours, causing day and night. 1. Explain What causes day and night? TEKS 8.7A: Model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the Sun causing changes in seasons. What causes Earth’s seasons? • Earth revolves around the sun once every year. • Earth is tilted at an angle of 23.5 degrees on its axis. • Seasons are caused by the combination of these two factors. 2. Identify Identify the two reasons for seasons on Earth. TEKS 8.7A: Model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the Sun causing changes in seasons. How does sunlight strike Earth? • Near the equator, sunlight hits Earth’s surface from almost overhead. • Near the poles, sunlight hits Earth at a steep angle. • This makes areas near the equator warmer than areas near the poles. 3. Explain Why is it warmer near the equator than near the poles? TEKS 8.7A: Model and illustrate how the tilted Earth rotates on its axis, causing day and night, and revolves around the Sun causing changes in seasons. How does each season occur? • When the Northern Hemisphere faces toward the sun, it is summer there and winter in the Southern Hemisphere. • When the Northern Hemisphere faces away from the sun, it is winter there and summer in the Southern Hemisphere. 4. Explain Explain how Earth’s axis is oriented in relation to the sun for each season in the Northern Hemisphere.