RUSSIA: Physical geography
advertisement

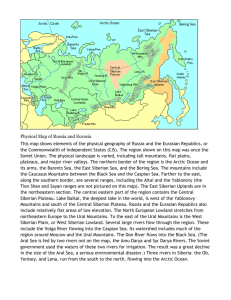
RUSSIA AND EURASIAN REPUBLICS: PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY The Land, Climate and Vegetation The Land Classwork: Geography Book--- Page 295: 1-4 Answers: 1. chernozern—rich, black topsoil; kums—deserts 2. North European Plain, West Siberian Plain, Turan Lowland 3. Long and navigable 4. Minerals and energy, soils, forests, wildlife and fish The Land Standards: H.S. 14 – Create and use maps, technology, imagery, and other geographical representations to extrapolate and interpret geographic data. H.S. 63 – Engage in informed and respectful deliberation and discussion of issues, events and ideas. Objectives—At the end of this section students will be able to: 1. Define terms related to the physical geography of Russia. 2. Use maps of Russia to identify, locate and compare regions, locations, places, movements, and physical features 3. Compare and contrast the physical features of Russia and the Eurasian republics with the U.S. 4. Research and discuss current issues/events related to physical features of Russia The Land: Introduction The Ural Mountains—Describe where they are located in relation to Europe and Siberia Siberia Urals iberi Europe Plains Areas The North European Plain Center of economic life Rich, black topsoil called chernuzem Ukraine, once a former Soviet Republic and now an independent country, is one of Europe’s best farming areas Label the following places on your map: North European Plain, Ukraine, Kiev, Moscow, Volga River, St. Petersburg, Dniester River, Dnieper River, and the Don River (Use the map on page 293) Plains Areas The West Siberian Plain East of the Ural Mountains World’s largest area of flat land Mostly swamps, marshes, evergreen forests and tundra Label the following places on your map: West Siberian Plain, Ural Mountains Turn to the neighbor on your right and complete “Focus on Geographic Themes” questions under the map on page 293 Plains Areas Answers to map questions: 1. Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan 2. Kiev 3. The Black Sea 4. Kara-Kum The Turan Lowland Some areas irrigated for agriculture Consists mostly of the Kara-Kum, or black sand desert (Turkmenistan) and the Kyzylkum, or red sand desert (Uzbekistan) Locate the following places on your map: KaraKum, Kyzylkum, Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Turan Lowland, Caspian Sea, Tian Shan Mountains Mountains and Plateaus Mountains The Carpathian Mountains are extensions of the Alps The Caucasus Mountains are covered with pine and deciduous forests and form the Russian frontier with Azerbaijan and Georgia Communism Peak in the Pamir Range is the regions highest peak at 24,590 feet Mountains The Tian Shan Mountains, or heavenly mountains, have some of the world’s largest glaciers The Ural mountains are mineral rich; they divide European Russia from Asian Russia Mountains East Siberian uplands—largest area of Siberia made up of forests, mountains and plateaus it runs to the Pacific The Central Siberian Plateau rises in elevation as you go north, creating fast moving rivers that cut large canyons Label your map: Carpathians, Caucasus, Communism Peak, East Siberian uplands, Central Siberian Plateau, Kyrgyz steppe Other Land Forms Kyrgyz Steppe The largest steppe, or savannah, in the world Flat, dry grasslands that connect the end of the Urals and the Kara Kum Sparsely populated Similar to Great Plains in the US The Land The Ural Mountains: Stuff They Don’t Want You to Know Fill in the blanks as you watch the film. Seas and Lakes On Your Map (Use page 293): Locate and label these seas, which are in the north of Russia and are ice locked in winter: White, Barents, Kara, Laptev, Ease Siberian, Chukchi In the northeast, the sea of Okhotsk, the Bering Sea Seas and Lakes The Black Sea is a warm-water sea that connects Russia to the Mediterranean Many wars have been fought to control the straits and keep Russia land-locked Locate and label the Black Sea on your map Seas and Lakes Seas and Lakes The Caspian Sea Largest inland body of water in the world Shrinking due to reduced flow of rivers The Aral Sea Shrinking due to so much water being used for irrigation Answer the three questions in your notes. Answer: both are shrinking; Aral is fresh water Locate the Caspian and Aral Seas on your map Seas and Lakes Lake Baikal Oldest and deepest lake in the world Holds 1/5 of the world’s fresh water Locate and label Lake Baikal on your map Rivers Long Navigable Connected to seas and each other by canals Important for trade Volga is called the “Mother Volga” Longest in European Russia Frozen 4-6 months of year Provides hydroelectric power and water for cities, industry and irrigation Rivers Locate and label these rivers: Volga, Amur, Ural, Lena, Ob, Yenisey, Dnieper, Don Indicate with a N, S, W, or E the direction of flow Tver, Russia, in winter Catherine’s Palace Natural Resources of the Eurasian Area Leads the world in production of manganese, chromium, coal, copper, silver, and natural gas Second in the world in gold, lead, salt, tin, tungsten, and zinc Produces 20% of the world’s coal and lignite Siberian diamond Natural Resources of the Eurasian Area Abounds in iron ore, nickel, asbestos, bauxite, antimony, and precious stones Third in the world in oil production Leader in hydroelectric power Natural Resources of the Eurasian Area Ukraine is the breadbasket of Eurasia with rich, black chernozem soil Produces rye, wheat, barley and sugar beets About 1/3 of Eurasia is forest, mostly pine Siberian taiga forest Natural Resources of the Eurasian Area Wildlife includes the Siberian tiger, bear, reindeer, elk, deer, wolf and boar Fish are an important regional resource including salmon from the Pacific coast Russian Life Russian Fun And You Thought American Drivers Were Bad Section 1: The Land Assignment Complete the table and article assignment located on the Library Web Site, Teacher Pages. Select the assignment, open it and save it to your H drive. Use the World Book and your notes to complete the table. Click on the link to the article on the online document to open it. Type the answers in on the Word document you saved. Bibliography Images courtesy of Wikipedia Commons