Improving Team Collaboration with
Rapid Visualization and Analysis of
Key Data
Project Team:
© Chevron 2005
Steve Rees, Chevron
Bruce Grant, Chevron
John Holmes, Chevron
Pam Howlett, Chevron
Alicia Seward, Chevron
Troy Ruths, Chevron Contract
John Pederson & Jeff Mathews, Chevron
Agenda
General Field Overview
Current State, Target Workflows, Future State
Project Development
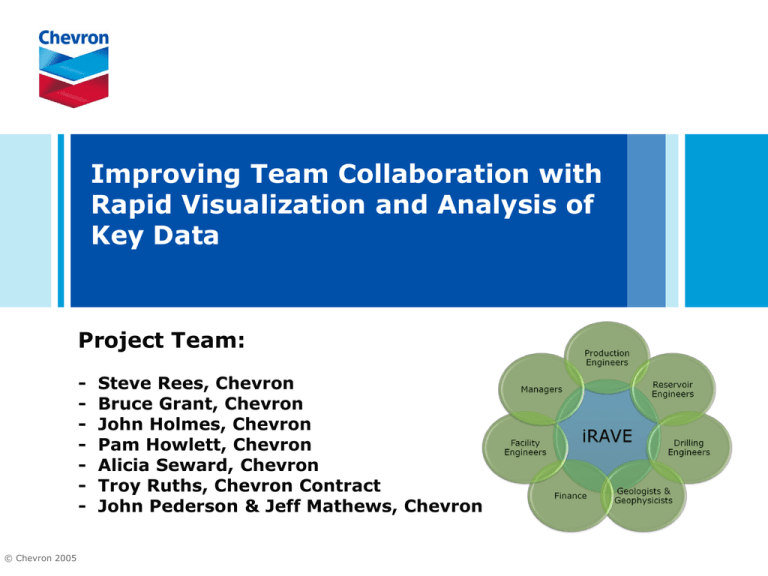
What is iRAVE?
iRAVE Demo
Challenges, Lessons Learned, Best Practices
Go Forward Plan
Conclusion
Q&A
© Chevron 2005
2
General Field Overview
Large offshore oil field -> expected recovery >1B bbls
Multi-layer reservoirs; multiple blocks; water & gas injection
operations; artificial lift
Mature field; balancing multiple field constraints
Production, water & gas injection, overboard water
Voidage replacement/minimum pressure requirements
Limited well slot capability; dry tree & subsea
Ongoing base development activities and new growth
opportunities; additional 20-40 year field life
Non-operated partner; limited staff working multiple projects
Significant non-discretionary activities; data management
challenges
© Chevron 2005
3
Current State
Inefficient Data Management and Analysis
Data sent via email, eQuest, CD and ftp site in form of daily production and
drilling reports, presentations & reports, OFM data, log data, etc.
Information/documents then saved to our shared drive, while OFM and daily
production report data is loaded into ppdm database
Individuals access and manipulate data as they see fit and save back to shared
drive
© Chevron 2005
OFM and some daily production report data pulled into DSS for
visualization and analysis; cumbersome and has limited user group
Majority of data extracted into individual user spreadsheets for further
manipulation, visualization and analysis
Often leads to duplication of work
Significant time spent managing and manipulating, rather than analyzing
data
4
Target Workflows
Immediate Impact to Team
Daily &
historical
production
monitoring &
analysis
Standard &
automatic
visualization
of routine
data
Nondiscretionary
reporting &
forecasting
Well, block,
production
area and field
analysis
User friendly
collaborative
environment
Spotfire -iRAVE
Planned vs
actual
forecast
© Chevron 2005
Field
Reliability
Field
production
constraints
5
Future State
Utilizing Spotfire and iRAVE*
Creation of a high quality, integrated and collaborative
environment that will: enhance the NOJV Team’s ability to
perform both routine and advanced well, block, reservoir and
field level reservoir management; improve decision quality;
reduce time spent managing data; and enhance ability to
interface with key internal and external stakeholders.
*iRAVE – integrated Reservoir Analysis and Visualization Environment utilizing Spotfire
© Chevron 2005
6
Project Development
Timeline and Team Structure
4Q2010
May 2011
First Look at
iRAVE
3Q2011
Early Look
Corporate
“iRAVE”
Oct-Nov
2011
Where our
Asset fits into
Corp Rollout
Dec 2011
Project
Framing &
Execution
Timeline
1Q2012
Commence
Project
Release 1
Complete
Identify Value to Team
Prototype Panels
Data Types & Sources
Database
New data & tables
Data-> SF interface
iRAVE & Spotfire Expertise
Learnings/best practice sharing
Data-> SF interface
Transform data -> visualizations
Development of iRAVE
© Chevron 2005
7
What is iRAVE
Under-the-Hood Look at iRAVE Tool
Data Sources
Information from a large, heterogeneous set of data sources is brought
together in iRAVE (Oracle tables, map files and network flat files)
Both structured and unstructured repositories were designed to store the
data; significant data clean-up resulted ( a hidden benefit of iRAVE!)
Panels
iRAVE Release 1 consists of 9 panels with more than 100 visualizations
20% of the visualizations were customized using Spotfire extensions
designed by Troy Ruths (HMTL reports, Map Zoom Sync, Maps on
Demand)
Deployment
© Chevron 2005
iRAVE was initially developed for another Chevron NOJV Field and
deployed in 2009
5 person team was formed to adapt the original iRAVE application for redeployment to our Asset; result was delivered in 4 months (able to re-use
much of underlying code)
8
What is iRAVE
Panel Development
Mocked up
Panels
Pulled from database,
various spreadsheets &
fixed files
Actual
Spotfire
iRAVE Panels
One Stop Shopping
© Chevron 2005
What is iRAVE
Workflow Optimization Example: Variance Analysis for Monthly Forecasting
Old Workflow
Manually transfer
‘Month A & B’ well rates
into a spreadsheet
and QC data
Identify reason for rate
change by opening
daily reports to check
(uptime, choke size,
GOR and water cuts)
Either extract monthly
welltests to
spreadsheet of
compare on daily
production reports
Calculate ‘Month A’ and
‘Month B’ variance
Highlight significant
rate changes
View monthly change in
Oil, GOR , WCUT, and
uptime by well in
iRAVE. Future portal
Investigate rate
changes: First, check
uptime by opening
another spreadsheet
On ‘Well Analysis’ tab,
check water or gas
injection rate, choke
size, bottomhole
pressure trends
Repeat investigation for
each well
Total Time = 2 hours
© Chevron 2005
New Workflow
On ‘Well Test’ tab,
compare month to
month well tests.
Total Time = 20 mins
10
Live Demo of iRAVE Tool
IT Components
Importing data and fixed files
Connection between multiple panels
Consistent color coding tied to production areas
Incorporation of user friendly page options
Critical Workflows
Production Reporting, Analysis and Forecasting
Facility Reliability and Field Operating Constraints
Well and Block Analysis
© Chevron 2005
11
Challenges and Lessons Learned
Challenges
Entire core team, except developer, unfamiliar with Spotfire
Team spread across 3 different offices and time zones
Timing of project (October to February)
Some pushback from Asset Team members
Lessons Learned
Unclear roles & responsibilities led to initial inefficiencies in project
Asset Team required more routine access to tool to ensure it was meeting
teams needs
Poorly defined review process resulted in rework by developer and IT.
Required more routine check point meetings to view tool as it was being
built to ensure it was meeting Asset Team needs
© Chevron 2005
12
Best Practices
Best Practices
Multi-disciplinary project team approach (Asset, IT, Developer)
Develop robust and clearly defined communication plan, especially for non
co-located teams
Identify Asset Team champion with broader knowledge of critical
workflows; targeted higher value opportunities and managed scope of
initial build
Engaged end users on project team positively impacts the design process
and greatly increases the effectiveness of the deployment
© Chevron 2005
13
iRAVE Go Forward Plan
User Feedback and Additional Workflows
Release 1 - Complete
Release 2.0?
Release 1.1
Field Summary
Release 1 fixes
Benchmarking
Facility & Reliability
D&C Workovers
Minor enhancements
to existing panels
Drilling Curves
Business Plan
Historical vs
Forecasts/Outlooks
(CVX and Operator)
Production
Outlook/Lookback
Reserves
Additional Panels
Voidage
Replacement Ratio
Heat & Tree
Mapping
Well Portal
Well Analysis
Block Analysis
Petrophysics
Well Test
Reservoir Properties
Simple Map Portal
Daily Report
Comment Summary
Expansion of
Mapping Capability
Operational Changes
Other G&G
Additional enhancements on the way
Transition “developer” responsibilities to IT Team
© Chevron 2005
14
Conclusion
Successful deployment of iRAVE Release 1
Immediate and positive impact to individuals workflows
Improving availability of cross functional information
Expanding overall understanding of field
Exposing team to Spotfire’s capabilities
Additional teams in business unit interested in iRAVE
Evaluating opportunities to utilize tool to engage partners
with iRAVE tool
Sharing iRAVE with other Chevron teams
Significant upside still to be captured
© Chevron 2005
15