Cooling Methods
advertisement

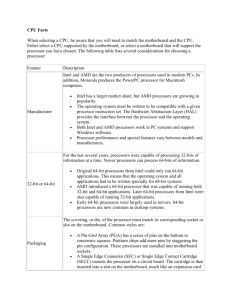
UNDERSTANDING CPU’S By: Matt Walbert, Alex Puleo, Anthony Minnocci, Chris Barrett CPU TYPES • AMD • Intel DIFFERENCES Intel AMD Core Frequency Faster (more cycles per second) Lesser work cycle (more data per cycle) Socket Type 1366 Pins (LGA1366 Socket) 938 Pins (AM3 Socket) Performance has multitasking with its hypertreading technology has graphical processing capability POWER CONSUMPTION • Intel • i3 • i5 • i7 • AMD • Phenom II Series FRONT SIDE BUS (FSB) • carries data to northbridge • connects CPU to rest of chipset • Transfer Rates • 32bit/64bit CPU • FSB operating frequency • number of FSB cycles HYPER THREADING • multiple tasks at once • decreasing dependent instructions • Intel • Improvements • improved reactions • running simultaneous threads • Drawbacks with earlier OS MULTI-CORE PROCESSORS • 2 or more processors working simultaneously on the same integrated circuit to execute instructions • Integrated circuit – another name for computer chip • System can perform more tasks, with better performance DUAL CORE PROCESSORS • 2 execution processor cores side-by-side on the same integrated circuit • Each core has it’s own cache • 2 complete cores to boost a systems multitasking capabilities • Each core executing different instructions http://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/supercharge-javaapplications-on-multi-core-servers/ TRIPLE-CORE PROCESSORS • 3 processing cores on a single chip • All simultaneously co-working for added performance and multi-tasking. • HD entertainment, content creation, & gaming application • Example: AMD Phenom x3 QUAD-CORE PROCESSORS • 2 separate dual-core processors on a chip • Cores 1 & 2 share a cache memory • Cores 3 & 4 share a cache memory • If cores 1 & 2 need to communicate with 3 & 4 it occurs via the front-side bus • Intel and AMD both offer quad-core processors http://www.intel.com/pressroom/kits/quadcore/images/2006.int.qua.txt.EN.13x18.jpg TECHNOLOGY NEEDED? • Operating Systems & applications running to support thread-level parallelism (TLP) • Multi-threading capability • Ability of an OS to execute different parts of a program called threads, simultaneously. • Modern OS • Typically XP or above • Ability to run virus scanner, streaming radio, surfing the web all while not seeing a drop in performance PROCESSOR SPEEDS • Known as Clock-speed, it is the speed at which microprocessors execute instructions. • Every CPU requires a fixed number of ‘clock-cycles’ to execute each instruction • The faster the clock, the more instructions the CPU can execute per second. • Superscalar: • The ability of a processor to execute more than one instruction per clock cycle. All modern processors are superscalar http://singularity.com/images/charts/MicroprocessorClockSpeed.jpg PROCESSOR SPEEDS… • MHz : megahertz • 1 MHz = 1 million clock cycles per second • Ex: 500MHz = 500 million cycles per second to execute • GHz : gigahertz • 1 GHz = 1 billion clock cycles per second • 3.3Ghz = 3.3Billion clock cycles per second to execute OVER-CLOCKING • A technique used by some to squeeze extra performance out of the advertised speed that the CPU was made for. • Can be done by setting a jumper on the motherboard • Typically voids the warranty of the processor • Risks damaging and overheating the CPU CUTTING-EDGE MODERN PROCESSORS • Intel Core i7 extreme edition processor • Hyper-threading technology across 6 cores • Hyper-threading: technology developed by intel that enables multi-threaded software applications to execute threads in parallel on a single multi-core processor • 15 MB of cache • 3.3 GHz processing speed • 1600 MHz front-side bus speed • AMD Operton 6200 series • Worlds first 16 core processor • Features a coreTurbo technology that enables the processor to boost its speed to up to 500MHz - 1GHz depending on what is being asked of it BASICS FOR CACHE • Definition: Specialized form of memory in a computer • It is designed to speed up the computer by prioritizing its contents for quick, easy access MULTILEVEL CACHE • Used for Multicore Processors • Each processor has its own L1 cache • This allows for each core to access its cache without interfering with other core’s caches • Uses the L2 cache as a shared storage for all processors L1 • L1 Level 1 • The smallest, but fastest cache • Generally checked first • It is generally on-chip for optimal speed and bandwidth L2 • L2 Level 2 • Larger, but slower cache • Location • Coupled closely with the CPU • May be on-chip tho TROUBLESHOOTING CACHE • Problem Indications: • Unexplained system crashes • System failed to boot • Slower than usual performance • Reseat the cache module • Check BIOS settings • Check for overheating problems 32 BIT • Maximum amount of memory is 4 Gbytes • Can process 32 bits of information at a time • 32 bit applications can run on 64 bit applications 64 BIT • Can access 64 bits of information at a time • Amount of memory 16.8 TB • Applications can typically run better on a 64-bit systems 32 BIT VS. 64 BIT • 64 bit has an advantage over 32 bit because of the amount of memory it can hold. • As bits increase: • Data can be accessed in larger chunks and more accurately • The system can access larger number of locations in memory COOLING METHODS • Heat Sinks- transfer heat • CPU and Case Fans- move air Over motherboard • Liquid Cooling systems- used on RAM, processor, and chipsets • Thermal Compound- Between processor and heat sink • Staying Cool is key! SOCKET TYPES • Connection between processor and Motherboard • Allow Processor alone to be replaced • Large pin sockets: Zero-insertion (compression used), Land grid array (surface plate) TROUBLESHOOTING PROCESSORS • PC locks up after startup • Beep is heard after startup and boot fails • PC crashes on startup or when running applications PC LOCKS UP • Possibly heating/ cooling problem • Check parts like heatsink, and fan • Is thermal paste there? • If processor is new: - clock jumpers on motherboard - BIOS settings not correct POST BEEP CODE • Is CPU getting power?, replace if so • Motherboard second culprit • Power surge PC CRASHES ON STARTUP • Run diagnostic software • Viruses could be cause • Motherboard or chipset could be cause • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sHJ0EfvDlH8 WORKS CITED • http://heatexchanger-design.com/2011/03/07/heat-sink-2/ • http://www.tweaknews.net/reviews/gigabyte_3d_galaxyII_ liquid_cooling_system/ • http://www.cheap-computers-guide.com/cpu-installationguide.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:CPU_Socket_775_T.jpg • http://www.playtool.com/pages/biosfiddling/fiddle.html • http://www.rumtechit.co.uk/ WORKS CITED • http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Hardware_Software/2005/processor_list.asp • http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/M/multi_core_technology.html • http://www.webopedia.com/DidYouKnow/Hardware_Software/2005/dual_core.asp • http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/Q/quad_core.html • http://www.intel.com/technology/architecture/downloads/quad-core-06.pdf • http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/H/Hyper_Threading.html • http://www.webopedia.com/TERM/G/GHz.html • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multi-core_processor • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sHJ0EfvDlH8 WORKS CITED • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Front-side_bus • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_CPU_power_dissipation • http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hyper-threading • http://maketecheasier.com/differences-between-intel-and-amdcpu/2010/08/04 WORKS CITED • http://www.isi.edu/lsam/about/caches.html • http://www.custom-build-computers.com/L2-Cache-Problems.html • http://www.informit.com/articles/article.aspx?p=102308&seqNum=6 • LabSim