Thicknet 5-4
advertisement
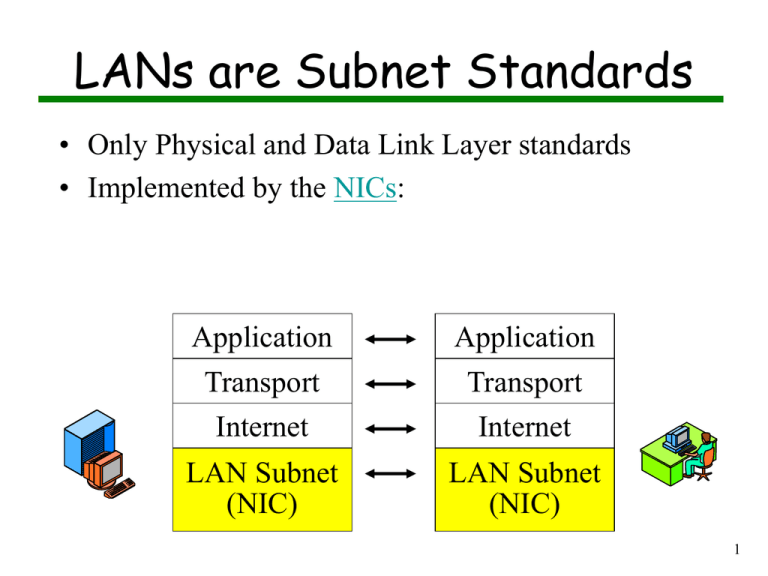
LANs are Subnet Standards • Only Physical and Data Link Layer standards • Implemented by the NICs: Application Application Transport Transport Internet Internet LAN Subnet (NIC) LAN Subnet (NIC) 1 Subnets 8 pin RJ-45 jack f or 10Base-T Jumpers to enable/disable media interfaces BNC connector for 10Base-2 (thin coax ethernet) DB-15 AUI AUI or transceiver cable DB-15 AUI connector for 10Base-5 (thick coax ethernet) DB-15 AUI Transceiver thick coax ethernet GOLDMAN: DATACOMM FIG. 06-07 2 Ethernet (802.3) Transmits signal Detects signal Carrier Sense Multiple Access Characteristics Collision detected Collision Detection Description Access Method CSMA/CD Transfer Speed Standard Ethernet – 10 Mbps Fast Ethernet – 100 Mbps Gigabit Ethernet – 1 Gbps (1000 Mbps) 3 Ethernet: CSMA/CD CSMA/CD process 4 Sample Ethernet Frame 5 Ethernet Ethernet frame 6 Logical Topology • Bus logical topology: signals travel from one network device to all other devices on network – Broadcast – Required by bus, star, star-wired physical topologies 7 Bus • Single cable connects all network nodes without intervening connectivity devices • Devices share responsibility for getting data from one point to another • Terminators stop signals after reaching end of wire – Prevent signal bounce • Inexpensive, not very scalable • Difficult to troubleshoot, not fault-tolerant 8 Bus 9 Star A typical star topology network 10 Star • Any single cable connects only two devices – Cabling problems affect two nodes at most • Requires more cabling than ring or bus networks – More fault-tolerant • Easily moved, isolated, or interconnected with other networks – Scalable • Supports max of 1024 addressable nodes on logical network 11 Hybrid: Star-Wired Ring A star-wired ring topology network 12 Star-Wired Bus A star-wired bus topology network 13 Network Cables Twisted-Pair 10BaseT Unshielded (UTP) Shielded (STP) Coaxial 10Base2, 10Base5 ThinNet ThickNet Fiber-Optic 14 10Base2 /Thinnet 15 The 5-4-3 Rule • A thinnet network can combine as many as five cable segments connected by four repeaters; but only three segments can have stations attache – " This is known as the 5-4-3 rule. • repeaters can be used to join Ethernet segments and extend the network 16 ThinNet 5-4-3 Rule 17 10Base2 Standard • Coaxial cable, or thinnet, which has a maximum segment length of 185 meters. • Thinnet cabling components include: • BNC barrel connectors. • BNC T connectors. • BNC terminators 18 10Base-5 / Thicknet 19 Thicknet 5-4-3 rule 20 10BaseT Standard • In 1990, the IEEE committee published the 802.3 specification for running Ethernet over twisted-pair wiring. – UTP • Most networks of this type are configured in a star pattern, but internally they use a bus signalling system like other Ethernet configurations 21 10BaseT Specifications Summary 22 10BaseFL Standard • is an Ethernet network that typically uses fiber-optic cable to connect computers and repeaters. • The maximum distance 2000 meters (about 6500 feet). 23





