here
advertisement

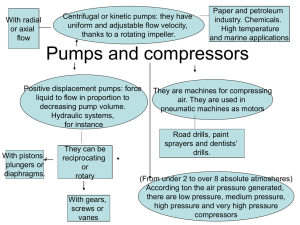
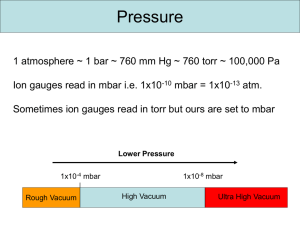
Overview of Vacuum Systems Tejas Deshpande 24 July, 2014 Outline • Introduction • Pumps • Positive displacement pumps • Momentum transfer pumps • Entrapment pumps • Pressure gauges • Vacuum seals • Manipulation and motion under vacuum Introduction Introduction: definitions Kinetic Theory of Gases • Ideal gas equation • Velocity of molecules hitting chamber walls Introduction: definitions Pumping • Rate of mass flow • Mass “conductance” http://fisica.ufpr.br/sharipov/tubefm.html Introduction: definitions Pumping • Pump capacity & effective pumping speed • Rate of evacuation • Example: Pfeiffer Hena-25 pump + cylindrical chamber • Finite C with a hose Introduction: definitions Pumping • Conductance of KF 40 hose (L = 10", D = 2.165") [1] [1] http://www.vacuumlab.com/Articles/Knowing%20Eff%20Pump%20Speed.pdf Positive displacement pumps Rotary vane pumps • Principle of operation Positive displacement pumps Scroll pumps • Principle of operation Positive displacement pumps Diaphragm pumps • Principle of operation Positive displacement pumps Roots “blower” • Principle of operation Momentum transfer pumps Diffusion pumps • Air diffuses to vapor stream • Baffles condense vapor • Oil backstreaming problem Momentum transfer pumps Turbomolecular pumps • Principle of a molecular “drag” pump • Mechanically similar to rotary pump • Good compression ratio • Poor pumping speed • Turbo pump Momentum transfer pumps Turbomolecular pumps • Principle of operation Entrapment pumps Ion pumps • Penning cell • Magnetic field acts as electron trap cyclotron orbits • Ions deposit on Cathode Entrapment pumps Titanium sublimation pumps • Titanium as evaporatable “getter” material • Chemical sorption • 40-50 Ampere current evaporates Ti Pressure gauges Liquid Manometers • Simplest U-tube manometer • Atmospheric pressure = 1 bar The Diaphragm Manometer • Capacitive sensor • AC vs. DC • DC capacitance bridge • AC resonant circuit tuned to diaphragm vibration Pressure gauges Thermal Conductivity Gauges • Convection of heat through the gas • Other heat losses • Radiation ~ T4 • Solid conduction • Operating conditions • Free molecular flow • > 10-3 torr Pressure gauges Ion Gauge • Measurement of ion current • Gauge sensitivity • Bayard-Alpert gauge • • • • Collector potential: -10 V Grid potential: 180 V Cathode filament: 30 V Screen: 0 (ground) Vacuum Seals O-ring seal • Elastomers, Viton-A, Polyimide • Quick and reusable • Limited baking range (< 250 °C) ConFlat flange seal • “Leak-tight” (< 10-12 Pa m3s-1) • Metal gaskets (typically copper) • Bakable to 450 °C • Not reusable Manipulation and motion under vacuum Metal bellows • Mechanical feedthroughs • Bakable to 450 °C • Limited linear/angular stroke Continuous rotation • Speeds up to 2000 RPM • High torque bellows • Low torque magnets Manipulation and motion under vacuum Gate Valve • Large bore • Sample transfer Right-angled valve • Small bore • Air evacuation Manipulation and motion under vacuum Transfer arm • Significantly greater stroke than bellow-sealed manipulator • Magnetic power transmission Summary • Introduction • Pumps • Positive displacement pumps • Momentum transfer pumps • Entrapment pumps • Pressure gauges • Vacuum seals • Manipulation and motion under vacuum