Bill of Rights & Incorporation: 14th Amendment Explained
advertisement
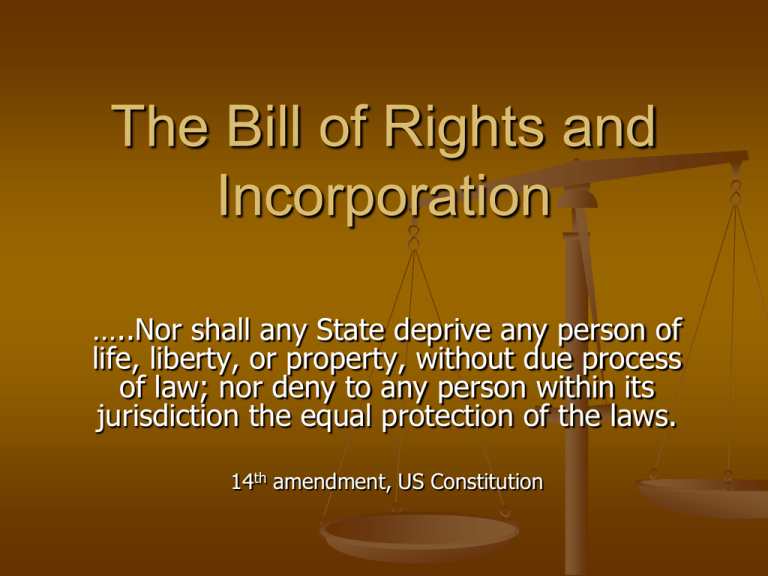
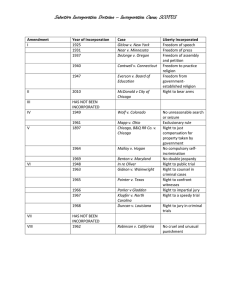
The Bill of Rights and Incorporation …..Nor shall any State deprive any person of life, liberty, or property, without due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws. 14th amendment, US Constitution Incorporation Definition: Applying all or some of the Bill of Rights to the states; means the federal government can make sure states do not violate the rights of their citizens Evolution of Incorporation Barron v. Baltimore (1833)–the Supreme Court determined that the Bill of Rights restricted the national government but NOT the state government Gitlow v. New York (1925)–Court overturned Barron decision, citing 14th amendment restrictions on states (“no state shall…deprive any person of life, liberty, or property w/o due process of law; nor deny to any person within its jurisdiction the equal protection of the laws.”) Selective Incorporation Since Gitlow court applies Bill of Rights to state law on a case-by-case-basis; Process is called Selective Incorporation Following Rights have NOT been incorporated Second Amendment bear arms) Third (quartering troops in private homes) Fifth (provision: right to indictment by grand jury) Seventh (right to a trial by jury for disputes >$20.) Eighth (provision against “excessive bail and fines” Selective Incorporation All other provisions of Bill of Rights apply equally to the state and national government. (Thus states may place restrictions on gun ownership–2nd amendment is not incorporated, they may NOT deprive accused felons of their right to legal counsel–a right incorporated in Gideon v Wainwright, 1963) Selective Incorporation In defining individual rights, the Supreme Court has consistently weighed the rights of individuals against the needs of society at large (Therefore no right is absolute).