The Arab Empire and Its Successors
advertisement

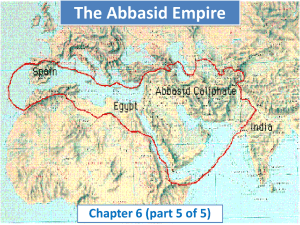
The Arab Empire and Its Successors Creation of an Arab Empire Muhammad’s death posed a problem because he had not named a successor and didn’t have a male heir. His closest followers selected Abu Bakr as his successor. In 632 Bakr was named Caliph. Arab Conquest Abu Bakr was able to suppress political and religious uprisings, uniting the Muslim world. The Quran permitted fair, defensive warfare as Jihad, “struggle in the way of God”. At Yarmuk, in 636, the Arab army defeated the Byzantine army, and four years later took control of Syria. By 650, the Arab Empire had grown to include Egypt and other parts of northern Africa, and the entire Persian Empire. Arab Rule After the death of Abu Bakr, there was no clear successor, and a number of caliphs were assassinated. In the conquered territories, the Arab administrators were tolerant. Christians and Jews were allowed to practice their religions. Those who didn’t convert to Islam only had to be loyal to Muslim rule and pay taxes. The Umayyad Empire In 661, the general Mu’awiyah became caliph. He moved to make the office of caliph, called the caliphate, hereditary. This established the Umayyad dynasty. Mu’awiyah moved the capital of the Arab Empire from Madinah to Damascus in Syria. The Arab Empire expanded into southern Europe in the West and western Asia to the border of the Byzantine Empire. Continued… As a result, the Arab Empire would be influenced by Byzantine and Persian culture. Because the empire was so vast it was difficult to rule from a capital so far away. A revolt led by Hussein in present day Iraq led to a split of Islam into two groups. Shia – descendants of Ali as the true rulers. Sunni – didn’t agree with Umayyad rule, but accepted them as caliphs. Abbasid Dynasty Overthrew the Abbasid dynasty and lasted from 750 to 1258. Abbasid Empire moved the capital to Baghdad. Abbasid caliphs encouraged charity and supported artists and writers. A shortage of qualified Arabs for key positions in the army and civil service led to non-Arab people coming to power. Eventually the Muslim Empire split politically. Seljuk Turks Seljuk Turks were nomads from central Asia who were hired as nonnative soldiers. In 1055 a Turkish leader captured Baghdad and took control of the empire under the title of Sultan, “holder of power”. The Crusades Byzantine emperor Alexius I asked the Christian states of Europe for help. Europeans agreed and a series of crusades began in 1096. Saladin made himself sultan of Egypt in 1169 and took the offensive against the Christians. Saladin and his forces invaded and conquered Jerusalem in 1187.