Storage Systems
advertisement
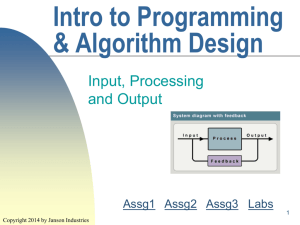
Intro to Info Tech Storage Devices This presentation can be viewed on line at: http://web.fscj.edu/Janson/cgs1060/wk08.Storage.ppt Copyright 2003 by Janson Industries 1 Objectives Explain the various devices Explain and compare the relative advantages and disadvantages 2 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Storage Devices Hold data and instructions, can also hold output Comprised of a device and media Device writes to and reads from a particular medium Been around since beginning of computers Early medium – punch cards 3 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Storage Devices Measured two ways Speed (access/write/rewrite) Capacity Also, compared according to – can medium be moved to another device Portability – once written to can medium be it be changed "Rewritability" 4 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Storage Devices Secondary storage vs. Internal storage (Main Memory/MM) Slower access SS measured in microseconds, PC MM nanoseconds Holds PC much more MM measured in GB, SS TB 5 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Storage Device Types Magnetic Disks Optical Disks Other 6 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Magnetic Disks Surface can be magnetized and demagnetized Magnetic state represents a 0 or 1 Surface broken up into Tracks Pie shaped sections Sectors Tracks and sections numbered This provides identifier for sectors Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries 7 Magnetic Disks 2 types Floppy disk/floppy drive Portable Hard media disk/hard drive Some are/some are not portable Most desktop PCs have a single unit where medium can't be separated and moved to another device 8 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Floppy Disks Historically, different sizes 3.5, 3.5 5.25, 8 holds about 1.44 megs Single vs. double sided Zip disks hold a lot more 9 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Hard Disk Made up of multiple inflexible platters Read/write heads One for each platter surface How heads and platter work: Heads 2 millionths of an inch over surface Sense the magnetic state of platter surface Head crash – Bad! 10 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Hard Disk How the whole thing works Arm extended to correct track Platter spun so correct sector is under read/write head Surface read and value sent via circuitry through the arm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9 eMWG3fwiEU 11 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Hard Disk With hard disks, different units of storage Cluster: group of adjacent sectors, smallest unit of allocatable storage Cylinder: all same tracks on different platter surfaces To make access faster try to store info In one track If data larger than a track, store in same cylinder Why? Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries 12 Other Hard Disks External hard disks One unit separate from system unit Plugs into USB port Capacity in TBs Some more portable than others Removable HD Very portable Machines must have a removable HD bay 13 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Other Hard Disks Miniature HDs Often built into a mobile device like camera, headphones Pocket HD has more capacity than a thumb Large systems have many hard drives Will have disk controller(s) Specialized chip that manages communication with disk drives Decreases work for the CPU 14 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Optical Disks Surface of the disk is altered to affect it's reflectivity To read, a beam of light is shot onto the surface The amount of light reflected will represent a 0 or 1 15 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Optical Disks Compared by their Sidedness Capacity Speed Read/Write capability Reading is called ripping Writing is called burning 2 major types CDs DVDs 16 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Compact Discs Usually One sided Capacity 650MB – 1GB Different types determined by the read/write capability CD-ROM CD-R CD-RW 17 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Compact Discs CD-ROM (Read Only Memory) Single Can read many times Used session – can write to disc once to be called a WORM disc What good is this type of CD? S/W mfgs write to these type of disks and then distribute Users can't inadvertently erase the application 18 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Compact Discs CD-R (Read) – can write to one portion of disk and then later to another Multi-session Can read many times Can't erase what is written CD-RW (Rewritable) Can write, read, erase, and rewrite to disc 19 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries CD Drives Compared by The type of discs they support Can Read, they read and/or write write, rewrite speed Measured like this: Read 128X Write 64X Rewrite 24X 20 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries DVDs Digital Versatile Disc Holds more than CDs 4.7GB to 100GB Capacity depends on whether Single or double sided Regular or high capacity DVD Single or multiple layers Battle for high capacity DVD format between Blu-ray and HD Blu-ray won! (BD) 21 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Reading and Writing to DVDs For Blu-ray, two types of discs BD-R is read only BD-RE can read and write Regular discs are more complicated DVD+R and DVD-R are read only DVD+RW, DVD-RW, and DVD+RAM can read and write The DVD drive must support the particular DVD format Most DVD drives support CDs 22 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Reading and Writing to DVDs DVD-R approved by DVD Forum Mitsubishi, DVD+R supported by the DVD+RW Alliance. Sony, Sony, Hitachi, and Time Warner Yamaha, Philips, Dell, and HP Differences Defects management How DVDs are formatted and rewritten What TV DVD players will play them For computer backups, either one will do 23 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Other Storage Tape A magnetic ribbon Two formats: Cartridge Reel Only to reel provides sequential access Discs Tapes provide direct access often used for back up 24 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Other Storage Flash memory cards Flash memory (i.e. chip based) Used in notebooks, cameras, PDAs Need a special drive/slot in device USB Flash drives (aka Thumb drives) Comprised of both media and device Don't need special drive/slot, just need a USB port 25 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Other Storage Smart cards Chip based memory Can also process information Holds a defined amount of money You buy something, that amount is decreased Online Can access files from anywhere Give others access Many Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries are free 26 Online Storage Three big players (as of 5/2012) Google 5 Drive GB free, 100GB more $59.88 OneDrive 15 GB free (7/14), 100GB more $50.00 Dropbox 2 -formerly Skydrive (MS) (Dropbox Inc.) GB free, 100GB more $199.00 27 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Online Storage Also compared based on Search – can file content be basis Dropbox only scans file names OneDrive supports content scan for MS formats (Word, Excel, PP, etc.) Google supports many formats, even uses OCR for scanned content Others With access Google Drive, file is either view or edit OneDrive Dropbox Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries lets you specify for each file/user 28 must set up a shared folder for edit Other Storage Microfilm and Microfiche Film is reel to reel, fiche is small rectangle of plastic film Hold microscopic images Need separate devices to read and write Readers considered auxiliary devices not peripheral devices Don't need the CPU to access the storage medium Extremely long lasting 100-500 years Magnetic disk 5-30 yrs Optical 10-100 yrs Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries 29 Other Storage Enterprise storage - vast amount of capacity Storage array Separate device comprised of hundreds of disks Have multiple processors Act as "storage servers" Capacities up to .5 PB (half a quadrillion bytes) 30 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Other Storage Solid state hard drive (SSD) Uses non-volatile memory chips No moving parts Much faster than magnetic disk (up to 100X) More expensive (up to 20X) Limited number of writes (1-5 mill) Often used in combination with magnetic disk SSD acts as cache for frequently used files 31 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries Points to Remember Secondary storage: non-volatile storage managed by a dedicated storage device Secondary storage serves as a source of input and target for output Wide variety of media measured by Speed Capacity Durability Read/write capability 32 Copyright 2012 by Janson Industries