File - Effective Language
advertisement

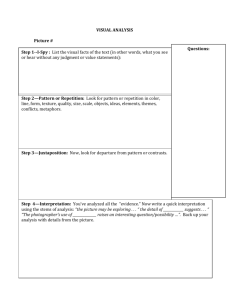
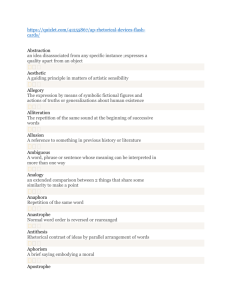
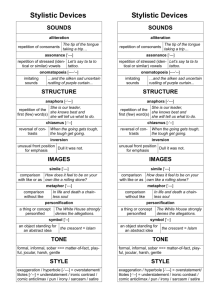
Examining Figures of Speech http://www.seattlemet.com/news-and-profiles/publicola/articles/publicalendar-november-13-2013 • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K7bGilrAQ5 • John Fitzgerald Kennedy was the 35th President of the United States • At age 43, he was the youngest to have been elected to the office, the second-youngest president, and the first person born in the 20th century to serve as president. • The only Roman Catholic president and the only president to have won a Pulitzer Prize. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5C3gqIR8RoI • John F. Kennedy was sworn in as the 35th President at noon on January 20, 1961. • He won the election by one of the smallest popular vote margins in history. • Kennedy’s goals: (1)to inspire the nation (2) alert the world of challenges of the Cold War, and (3) promote hope for peace in the nuclear age. • He also wanted to be brief (power and poetry) • He studied other inaugural speeches and Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address • The finely-crafted final speech had been revised and reworked numerous • 1,355 words in length, comprised of short phrases and words • captivated his audience required a powerful delivery. • Following his inaugural address, nearly seventy-five percent of Americans expressed approval of President Kennedy. A. B. C. D. Figures of Speech Master of rhetoric persuasive Good looking • • • • Graces of language The dressing of thought Embellishment Figures of Speech do decorate prose, but that is not there sole function • According to Aristotle: • They give clearness and liveliness to our expressions • They balance our writing between “the obvious and the obscure” • They help our audience grasp our ideas promptly • According to Longinus: • They “infuse vehemence and passion into our spoken words” • “…when combined with argumentative passages it…persuades the hearer…” • • • • Figures of Speech render out thoughts in a vivid, concrete way. They stir up emotional responses Deliver a message clearly and effectively Allows a writer or speaker’s eloquence exert powerful ethical appeal f • “a form of speech artfully varied from common usage”— Quintilian • Because language has figurative resources • Schemes- deviation from the ordinary pattern or arrangement of words • Tropes- deviation from the ordinary and principal signification of a word • • • • • • Both involve a change in meaning to a degree Both involve transference Trope transfers meaning Example irony Scheme transfers order of meaning Example Hyperbaton • • • • • • • • • • • Alliteration Anaphora Anastrophe Antithesis Assonance Consonance Metaphor Simile Parallelism Paradox Repetition • Alliteration: repetition of the same sound beginning several words in a sequence • Example: • Alie angrily ate apples and acorns. • Anaphora: repetition of a word or phrase at the beginning of successive phrases, clauses or lines. • Example: • Tracy didn’t scream. Tracy didn’t cry. Tracy didn’t say a word—until she saw the blood. • Anastrophe: transposition of normal word order • Example: • “Good, it is,” Yoda squealed while swinging his light saber, “the force to know. Geoge Lucus, your father is. ” http://www.comicvine.com/forums/battles-7/yoda-runs-the-gauntlet-1517214/ • Antithesis: contrast of ideas or words in a parallel structure • Example • He’s easy on the heart, but hard on the eyes. • Assonance: repetition of vowel sounds in non-rhyming words • Example • "I lie down by the side of my bride" • "Fleet feet sweep by sleeping geese" • "Hear the lark and harden to the barking of the dark fox gone to ground" by Pink Floyd http://mosttalentedartists.blogspot.com/2012_ 12_01_archive.html • Consonance: repetition of consonant sounds within words or ending words • Example • I'll swing by my ankles. She'll cling to your knees. As you hang by your nose, From a high-up trapeze. But just one thing, please, As we float through the breeze, Don't sneeze. - The Acrobats by Shel Silverstein • Metaphor: implied comparison through a figurative, not literal, use of words • Example • Life is a highway, and I just got my driver’s license. • Simile- an explicit comparison between two unlike things, yet they have something in common. • Example • I sat still, like jelly in a jar. • Paradox: a statement that seems self-contradictory, yet turns out to have a rational meaning • Example • Mitch is a one-man army. • Repetition: a word or phrase used two or more times in close proximity • Example • “A horse is a horse, of course, of course, And no one can talk to a horse of course That is, of course, unless the horse is the famous Mister Ed.” • theme song of Mr. Ed, a 1960s TV program.