8.11 - Reconstruction and the 1875 Civil Rights Act
advertisement

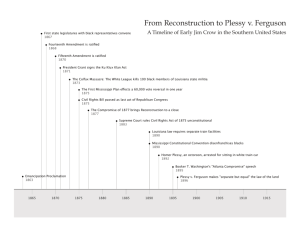
Document-based Lesson Based on documents and lesson planning from the National Archives 1875 Civil Rights Act Passed by Congress in March 1875 "all persons within the jurisdiction of the United States shall be entitled to the full and equal enjoyment of the accommodations, advantages, facilities, and privileges of inns, public conveyances on land or water, theaters, and other places of public amusement," and that such enjoyment should be subject "only to the conditions and limitations established by law, and applicable alike to citizens of every race and color, regardless of any previous condition of servitude." Enforcement If a person is found guilty, they were to be fined $500-$1,000 or jailed for 30 days Enforcement for the law was the responsibility of the federal courts and the U.S. Attorney If the case was not prosecuted, the U.S. Attorney had to pay the claimant $500 and can be fined $1,000$5,000 President Grant did not comment on the bill U.S. Attorney across the U.S. wrote to the Department of Justice obtain copies of the bill Court Cases Between 1875 and 1877 African Americans throughout the U.S. were taking advantage of the law and filing complaints when they were met with discrimination Read the court case Summarize the case and the act of discrimination Discuss the presentation of the case Discuss the verdict if it is given Share out your case Judicial Response Judges stated that the law was constitutional Robert Dick of North Carolina in April 1875 The constitutionality of the Civil Rights bill has been asserted by the deliberate action of Congress, composed of many able lawyers and wise and enlightened statesmen, and it would be very presumptuous in me, collaterally and without argument, to decide differently upon a question which that body carefully considered and acted upon under the solemn sanction of official obligation.” Others found it unconstitutional and relied on the notion of separate but equal Judge Thomas H. Duval of Texas in 1877 " If there are two cars equally fit and appropriate, in a respects, for use of white female passengers and for colored female passengers, there is no offence of denying a colored female passenger entrance to one and requiring her to ride in the other." Supreme Court Not until 1883 did the Supreme Court rule on the constitutionality of the Civil Rights law of 1875 Davis case was one of several decided by this ruling The Supreme Court declared that Congress had no power to pass laws regulating individuals unless it a direct power given to them "But where a subject is not submitted to the general legislative power of Congress, but is only submitted thereto for the purpose of rendering effective some prohibition against particular state legislation or state action in reference to that subject, the power given is limited to its object, and any legislation by Congress in the matter must necessarily be corrective in its character." Citizenship How did definitions of citizenship evolve through the establishment and overturning of the 1875 Civil Rights Act?