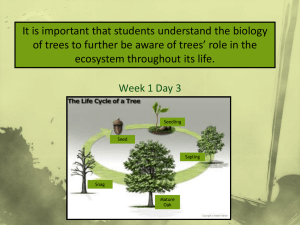
a TREE IS GROWING
advertisement

Lesson 13 Day 1 Question of the Day • What does your body need in order to stay healthy and keep growing? • In order to stay healthy and keep growing, I need _______. Read Aloud • Listen to the poem to find out how the poet feels about fall. Autumn Why might we I lie on my back and look up to see reread a A towering giant way above me. poem? Drifting down from branches tall, Bright colored leaves begin to fall. Very soon the tree is bare, Cold but swaying in autumn air. And though this tree seems dead today, It will bloom again, one fine spring day. • What does the poet mean by “And though this tree seems dead today”? • How do you think the poet feels about autumn? T221 Phonics • ice ace edge age • Notice that the letters c and g are followed by the letter e. • What sound does the c stand for in these words? • /s/ • What sound does the g stand for in these words? • /j/ Phonics ice ace edge age dice face hedge cage mice lace ledge page nice pace wedge rage rice race dredge sage vice place pledge wage price space slice brace spice trace twice Notice that the letters c and g are followed by the letter e. stage Phonics • • • • • • • • • • • police office refrigerator imagine celery ceiling margin difference Notice what letter follows the letters c &g. Find the words in the following sentences with the soft c & g sound. The prince ate a bowl of rice. prince rice Do not write in the margin of the page. margin page Take my advice and do not glance away from the road. advice glance Please slice a wedge of cheese for me. slice wedge Fluency: Intonation • When good readers read nonfiction aloud, their voice expresses the feeling of the passage. They change the pitch or intonation of their voice, making it go high and low when reading words and phrases that need emphasis. They also use end marks as clues for reading particular words and sentences. • When you read nonfiction try to make your voice go up and down, depending on: • how important words are • end marks and other punctuation • Open your book to page 388 and listen as I read. I notice that the first sentence is about fifty thousand acorns. That’s a lot from one tree, so I will emphasize the words fifty thousand by raising my voice slightly. • Turn to your partner and practice reading using intonation on page 388. Author’s Purpose • Authors write something to entertain, inform, or to persuade. Sometimes, a writer might want to entertain readers while also informing them. • In “A Tree is Growing” the main message is what trees are like and how they grow and change during the year. The author wants to inform readers about trees. Author’s Purpose • Turn to pg. 379 and look at the first paragraph. • Look for facts and details and jot them down on a sticky note. These should help you find the author’s purpose. • Roots hold the tree in place, roots are like pipelines, roots absorb water and carry it to the tree. • The author’s purpose is to tell what roots are and what they do. • Now look ate page 380. • Bark is the skin of a tree and the outer layer of bark protects the tree • The author’s purpose is to tell what bark is and what is does. • Try on page 383. • Cambium is a layer of growing bark. • The author’s purpose is to tell what bark is made of. Non-fiction Text Features: Graphic Aids • There are many kinds of graphic aids that help readers understand the text. • Photographs, captions, bolded print, highlighted text, maps, drawings, titles, sub-titles, charts, graphs and diagrams • Look at page 382 and look at this graphic aid or N-F text feature. • What can you see if you slice through the tree trunk? • growth rings • Where does cambium appear in the tree trunk? • between phloem and xylem Non-Fiction Text Features: Graphic Aids turn to pg. 384-385 • Read and study over pg. 384-385. • What is spread across these pages? • A tree at different stages, beginning at 10 years of age and going up to 200 years • What animal is shown in front of the 30-year-old tree? • A wild turkey • At what ages is the tree on page 385? • 50 and 200 • How are the changes shown as the tree gets older? • The tree gets taller and thicker. • What doesn’t change as the trees get older? • The marked point that is about as high as the turkey’s head doesn’t change. • What does the graphic aid help you understand? • That the top, not the rest of a tree, grows taller • • • • • This is a news feature. A news feature in nonfiction, tells about current events or interesting topics, and is found in a newspaper. A news feature may include: a headline with the title of the article a first paragraph that tells what the article is about. One purpose for reading a news feature is to gain information. What can you see if you slice through the tree trunk? growth ring Where does cambium appear I the tree trunk? between phloem and xylem These are graphic aids. Why do you think the author calls the bristlecone trees “survivors”? because they are able to live where most other trees could not How do you think the author feels about bristlecone pine trees? How can you tell? She admires them; she says that the ancient trees have stories to tell. How can you tell that “Ancient Trees Survive” is a news feature? It has a headline. The first paragraph tells what the article will be about. Paired Selection pg. 396-399 • What do you think the author calls the bristlecone trees “survivors”? • Because they live where most other trees could not • How do you think the author feels about bristlecone pine trees? How can you tell? • She admires them; she says that the ancient trees have stories to tell. • How can you tell that ”Ancient Trees Survive” is a news feature? • It has a headline. The first paragraph tells what the article will be about. • • • • • • • • • 1. Text to text Like: Needs sunlight, has bark, lives long 2. text to self 3. text to world Other plants and animals use parts of the tree as food or as a source of water. 1. Text to text Different: Has needles instead of leaves, can grow with little water, soil, or warmth, much older than the oak. Robust Vocabulary • • • • • • • • • • tugged If you tugged at the branch of a tree, what might happen? paused Why might a teacher pause in the middle of speaking to a class? scavenger What kind of animal do you know of that is a scavenger? self-sufficient In what ways are you self-sufficient? absorb What can a towel absorb? • • • • • • • • • • columns If you built a tree house, would you want columns on the front? particles Imagine that you find particles of crackers on the kitchen floor. What might have happened? dissolve Do you think sugar will dissolve in water? protects How can you protect yourself from sunburn? rustling When would it be pleasant to hear a rustling noise? Grammar: Subject and Object Pronouns • • • • • • • • • • • Think of pronouns we have learned so far. I, me, you, he, him, she, her, it, we, us, they, them Mrs. West wrote a sentence on the board. I -subject The class read the sentence back to Mrs. West. Me- object When you refer to yourself as part of a group always name yourself last. My friends and _____ walked home. I - subject The teacher called on Jack and ________. Me - object DOL 6. Were you planning on spending the weekend us ? with we ^ we T 7. to get to the mall, us have to pass the stadium. Writing: explanation • Open your book to page 379 and look at the third paragraph. Listen as I read. • This paragraph gives a definition of what minerals are, how they dissolve in water, and why. • Explanation • Gives facts and details about a topic • Explains what or how • Starts with a topic sentence • Answers “what?” “how?” and “why?”