Preparation of the Body PowerPoint
advertisement
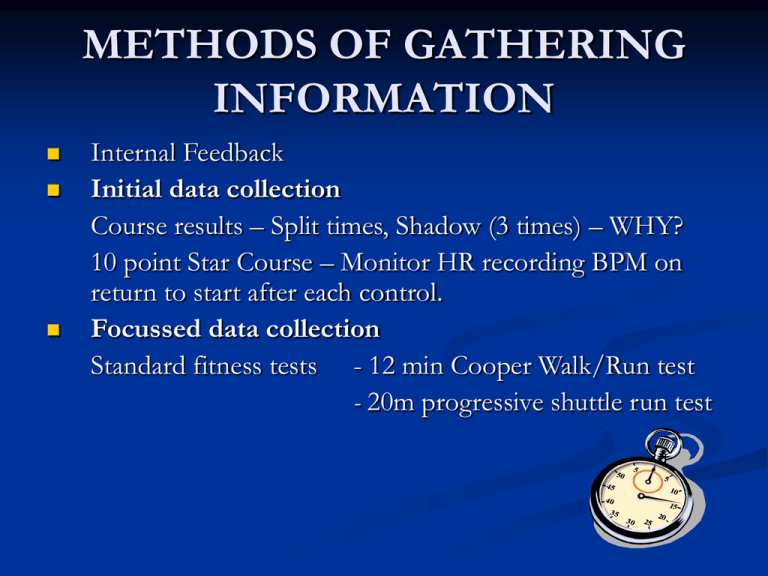
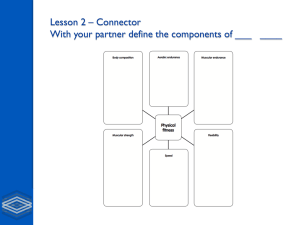
METHODS OF GATHERING INFORMATION Internal Feedback Initial data collection Course results – Split times, Shadow (3 times) – WHY? 10 point Star Course – Monitor HR recording BPM on return to start after each control. Focussed data collection Standard fitness tests - 12 min Cooper Walk/Run test - 20m progressive shuttle run test ASPECTS OF FITNESS Physical Fitness CRE, ME, Speed, Strength, Anaerobic Power, Flexibility Skill-related Fitness Agility, Reaction time, Balance, Co-ordination, Mental Fitness Mental Fitness Mental rehearsal, Managing emotions, Decision making You may be asked to describe or explain the importance of these aspects for Orienteering. You also need to know the components of an orienteer’s fitness/demands of the activity. This can be asked in terms of you or a model. TRAINING WITHIN THE ACTIVITY Example - Clock Relay (Working in Pairs) Each pair is given a flag at the start of the course. The first performer has to place the flag at control point 1 and then return back to base to tag his/her partner who then has to run to control point 1 and move the flag to control point 2. He/She then returns to base and moves the flag from control point 2 to control point 3. In turns this pattern is followed until the flag is back in its original place. There is 10 control points in total. Work to rest ratio for this session is 1:1. Benefits of a conditioning approach? You are also most likely to develop mental aspects of fitness through participation in the activity. TRAINING OUTSIDE THE ACTIVITY Can also be called - Methods of Training Example - Interval Training Tree running in woodland area in 2 groups with similar fitness. Each group had a leader who was responsible for setting the pace whilst the rest of the group followed the leader in and out of the trees 4 sets of 3 X 1 minute reps (4 minute recovery between sets) Recovery time between each rep began at 3 minutes (work rest ratio of 3:1). We then reduced this to 90 seconds to make training more demanding. Benefits of Interval training? PRINCIPLES OF TRAINING Specificity – Training in similar terrain to an actual orienteering event (MAINPALS) Progressive Overload – Increasing Frequency, Intensity, Time or changing the Type of terrain. Adaptability – Adapting to the load after training for a period of time (2 weeks) Reversibility – Use it or Lose it Rest and Recovery – Including rest periods to allow the body time to recover MAKING TRAINING “SPECIFIC” (MAINPALS) Method of training is SPECIFIC to: Aspect of fitness - CRE problem Identified in standard fitness tests physical Nature and demands of activity my Performance by involving an element of skill/fitness Area of body Level of fitness through correct starting load Season through correct load PHASES OF TRAINING PRE Season (Preparation) Loading - General followed by specific training DURING Season (Competition) Maintenance inc. peaking and tapering down CLOSE Season (Transition) Active Rest You must be able to describe your training programme for each phase of training. MONITORING Interim fitness tests Orienteering courses (Whole performance) Heart Rate Monitor Internal Feedback Training Diary Describe and justify monitoring process? HOW TO EVALUATE Same test conditions Compare to previous results Give specific examples of improvements made from standard tests/split times You may also be asked to evaluate whole performance Homework Question Discuss the effectiveness of your training programme on your overall performance. Give examples of your future development needs.