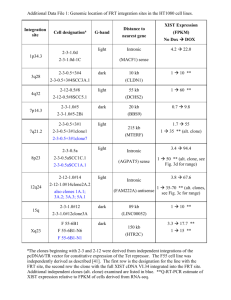
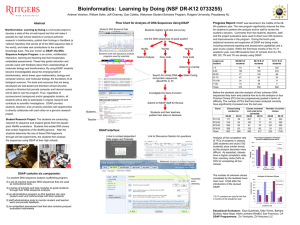
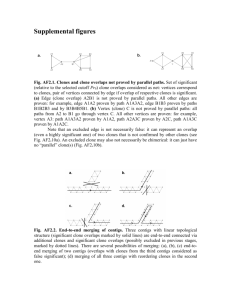
Mining Logical Clones in Software: Revealing High
advertisement

Mining Logical Clones in Software: Revealing High-Level Business & Programming Rules Wenyi Qian1, Xin Peng1, Zhenchang Xing2, Stan Jarzabek3, Wenyun Zhao1 1Fudan University, China 2Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 3National University of Singapore, Singapore Logical Clones • may not well documented • revealing high-level rules Logical Clones • Logical clones consisting of: – Similar methods – Similar code fragments – Similar entity classes – Persistent data projects Logical Clones • Today’s techniques on clone/similarity detection: – Simple clone (text, token, AST…) – Structural clone (simple clone) – Similar design structures (similarity metrics, machine learning) • They are not enough to detect high-level clones: – lack of high-level information – need of pre-defined templates, such as certain design pattern Approach Overview output input abstraction Program Model • • • • Methods & functional clusters Entity classes Code clones Persistent data objects Program Model • Methods & functional clusters – Semantic clustering Program Model • Entity classes – Encapsulating information with getter/setter Program Model • Code clones – Simple clones in different methods Program Model • Persistent data objects – Data tables in DB or data entries in files Mining Process <Method> PosClearPayment PosPayCheck <Entity class> PosScreen <Method> <Method> processPay <Entity class> PosScreen PosPayGiftCard <Method> <Entity class> PosScreen processPay<Method> Mining Process <Method> PosClearPayment PosPayCheck <Entity class> PosScreen <Method> <Method> processPay <Entity class> PosScreen PosPayGiftCard <Method> <Entity class> PosScreen processPay<Method> Mining Process Mining Process <Method> PosClearPayment PosPayCheck <Entity class> PosScreen <Method> <Method> processPay <Entity class> PosScreen PosPayGiftCard <Method> <Entity class> PosScreen processPay<Method> Mining Process Mining Process <Method> PosClearPayment PosPayCheck <Entity class> PosScreen <Method> <Method> processPay <Entity class> PosScreen PosPayGiftCard <Method> <Entity class> PosScreen processPay<Method> Mining Process Tool: MiLico Case Study • Project: Opentaps 1.4.0 – 14,351 classes & interfaces – 253,743 methods • 1690 logical clones mined – at least 3 nodes & 2 instances Case Study Categories of Logical Clones • Categories of Mined Logical Clones (manual work) – – – – Programming Convention (37%) Design Structure (24%) Business Task (23%) Business Process (16%) Categories of Logical Clones • Programming Convention – Similar ways to implement similar functions Categories of Logical Clones • Design Structure – Similar interaction structures Categories of Logical Clones • Business Task – Similar ways to implement similar business task Categories of Logical Clones • Business Process – Similar business process or sub-process Human Study • 5 senior graduate students, 2 questions: • Helpful for Programming understanding? • Helpful for Reuse/Evolution? Human Study Human Study • 5 senior graduate students, 2 questions: • Helpful for Programming understanding? YES • Helpful for Reuse/Evolution? YES Discussion • Helpful for reuse, without knowledge of code details • Developers with good domain knowledge will use logical clones better • Making MiLiCo integrated with IDEs will make logical clones more useful Conclusion • • • • The concept of logical clones The approach for mining logical clones The tool: MiLoCo A case study, showing that logical clones are helpful in software understanding, reuse and maintainance Thanks for your attention!