The Truman Doctrine
advertisement

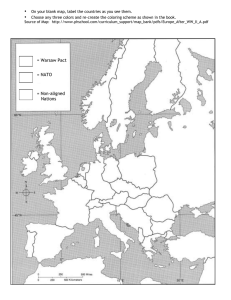
The Truman Doctrine The Truman Doctrine • Truman’s advisors believed that U.S.S.R. was exhausted from WWII, but could easily push western allies out from Germany to establish a communist government • Communist parties in Europe and Japan seized on post-war struggles to make political gains • In response, Truman issued the Truman Doctrine that stated “it must be the policy of the United States to support free peoples who are resisting attempted subjugation by armed minorities or by outside pressures (communists)” The Marshall Plan • Sec. of State George Marshall announces the European Recovery Plan (Marshall Plan) • It was designed to rebuild Europe • Soviets refuse to join and make their own plan called the Mutual Economic Assistance (Comecon) which focused on rebuilding their satellite states The Marshall Plan • Because industrial capabilities of European powers were limited, most of the money spent through the Marshall plan ($13.5 billion) was used to purchase American made goods • This provides an economic boost to the U.S. • Recovery in Japan was based on a similar strategy Berlin Airlift • In response to western Allies attempts to merge their 3 zones of occupation in Germany into a unified state (West Germany), Soviets cut off ground access to western sections of Berlin • Western nations, wary of triggering a war with the U.S.S.R. begin the Berlin Airlift to resupply the Germans living in their zones of Berlin • 11 months later, U.S.S.R. lifts blockade American Responses • In response to Soviet aggressions, Congress reinstates the draft in 1948 and increases defense spending by 30% • The National Security Act of July 1947 creates the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) and the National Security Council (NSC) • CIA is tasked with intelligence gathering and covert operations • NSC joins diplomatic and military advisors in one group • The Department of Defense is created in 1949 to oversee the army, navy and air force NATO and the Warsaw Pact • April 1949, 10 European nations, the U.S. and Canada sign the North Atlantic Treaty as a mutual defense pact (What does this mean?) • Signatories of the treaty make up the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) • U.S. troops are deployed to western Europe as a defense mechanism to any incursion by the U.S.S.R. • ANZUS Pact with Australia and New Zealand was Pacific version of NATO NATO and the Warsaw Pact • • • • • • Original NATO countries Belgium • Luxembourg Canada • Netherlands Denmark • Norway France • Portugal Iceland • United Kingdom Italy • United States Original Warsaw Pact countries • Soviet Union • Hungary • Albania • East Germany • Poland • Czechoslovakia • Romania • Bulgaria Homework Create a comic (hand drawn or on the computer) that tells the story of the origins of the Cold War. Be sure to include: • Communism’s rise in the U.S.S.R. • U.S.S.R.’s relationship with the Western Allies during WWII • The differing views on Europe’s future following the war • How the U.S. and U.S.S.R. solidified alliances through NATO and the Warsaw Pact • The fundamental differences between the U.S.’s capitalist and U.S.S.R.’s communist economic theories and how they wanted to spread their beliefs to other countries (e.g. Korea, Vietnam, China, etc…) • Anything else you find relevant (or amusing, because after all I need to read 90 of these things) Extra Credit 1. Read the introduction on page 342 titled “Famine in Ukraine” in the Sources of the Western Tradition textbook 2. Read the essay that follows on page 343 by Miron Dolot titled “Execution by Hunger” 3. Reflect on the story for a day 4. Write an essay approximately 2 pages long (double spaced, 12 point Times New Roman font) that uses the content of Dolot’s story to illustrate how collectivization and its consequences were an effective tool of punishment aimed at Ukraine’s defiance of the Bolsheviks during their rise to power.