4.3 Persia Attacks the Greeks
advertisement

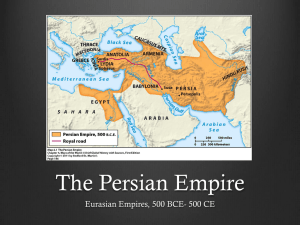
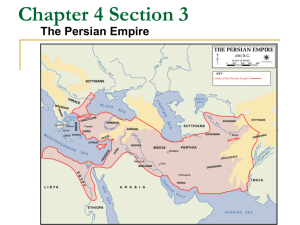
4.3 Persia Attacks the Greeks The Persian Empire PERSIA BACKGROUND • Persians were warriors and nomads who lived in Persia, the southwestern area of what is today Iran. • Cyrus the Great united the Persians. • The Persians built a large empire, conquering Mesopotamia, Asia Minor, Syria, Canaan, and Phoenician cities. PERSIA BACKGROUND • Darius came to power in 521 B.C. and reorganized the government. • The empire under Darius was divided into satrapies-states, each with a ruler known as a satrap-a protector of the kingdom. • The military of Persia consisted of full-time, paid soldiers known as Immortals. The Persian Wars • As the Greeks set up colonies in the Mediterranean area, they often clashed with the Persians. • By the mid-500s B.C., Persia already controlled the Greek cities in Asia Minor. • In 499 B.C. Athenians helped the Greeks in Asia Minor rebel against their Persian rulers….The Greek Rebellion Failed • After this, King Darius decided to stop the Greeks from interfering in his empire ever again. BATTLE OF MARATHON • The Battle of Marathon occurred in 490 B.C. on the plain of Marathon, a short distance from Athens. • There were 20,000 Persian troops and 10,000 Greek troops. • The Persians waited there several days for the Athenians. • When they did not come, the Persian commander ordered the troops back on the boat. • When the horsemen were on the boat, the Greeks charged the Persian foot soldiers and defeated them. • Legend has it, that the Athenians sent a messenger home with the news. He ran for about 25 miles and with his last breath yelled, “Victory.” Then he died • Thus the reason why we called a 26 mile race a Marathon The Persian Wars (Continued) • After Darius’s death, his son Xerxes became king. • He vowed a new invasion of Greece. • The Persians had 180,000 troops. • Athens and Sparta joined forces to defend against Xerxes’s attack. – Greek Army led by Leonidas and were mostly Spartan – Greek Navy led by Themistocles and were mostly Athenian Battle of Thermopylae • Greeks knew Persians were marching south for shipments of food. • Greek Game Plan: Army of 7000 would meet Persians at Thermopylae while the Navy attacks troops transport and supply ships. – Thermopylae • Delay Tactic • Greek Traitor, gives Persians alternate route through mountains • Leonidas, Spartan warrior, sends all but a few hundred troops to safety • 300-800 men wait in a mountain pass for Persians • Hold off Persians long enough for ALL GREEKS to get out of Athens – Salamis • Greek Navy attacks supply lines and destroys Persians naval force at the Strait of Salamis • Able to do this because they had fast ships that could maneuver quickly through the narrow pass. Battle of Plataea • Greeks in Crete – Have a Persian army in Greece with no supplies and no reinforcements. – Greek navy and people congregated in Crete. – While in Crete in 479 they form the largest Greek Army and head back to Mainland Greece. – They attack the Persians at Plataea and the Greek defeat the Persians. The Persian Wars • Marathon (490 BCE) – 26 miles from Athens, Greek victory • Thermopylae (480 BCE) – 300+ Spartans at the Mountain pass, Persian victory • Salamis (480 BCE) – Athenian navy victorious • Plateau (479 BCE) – Greek victory Fall of the Persian Empire • The Persian Empire fell for several reasons. – The Persians were weakened by war, and their rulers taxed the people and spent the money lavishly. – Persian royal families fought over who was to be king. Many kings were killed by family members who wanted the throne – Persian kings had many wives and children and all of the sons were constantly trying to take over the throne – 6 of 9 rulers after Darius were murdered Assignment