Overview of Tsarism - heathenhistory.co.uk
advertisement

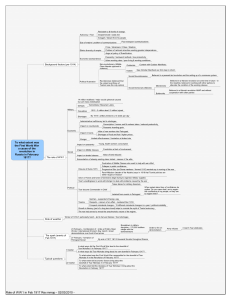
Russian and its rulers 1855 - 1917 Russia c.1855 Ruled autocratically by Romanov Tsars since 1613 Ruled since 1825 by Tsar Nicholas I (‘Thirty wasted years’) Supported by Russian Orthodox Church; the ‘divine right’ to rule (the ‘little father’ of the Russian people’) Landowning nobility were the elite (though not necessarily very rich) Opposition exiled / imprisoned; secret police - The Third Section Economically backwards; little industry and few railways whilst Western Europe was industrialising rapidly Primitive agricultural methods and low outputs / yields 90% of the people were peasants and most were serfs (slaves) Working and living conditions were harsh Between 1853 and 1856 defeat in the Crimean War exposed just how backward the Russian Empire had become See OXLEY Chapter 1 pages 8 - 21 for detail Russia 1855 - 1881 The reign of Tsar Alexander II Introduced ‘reform from above’, to modernise Russia Key Reform - The Emancipation of the Serfs 1861 Several other reforms including the introduction of some local government (zemstva) and trial by jury Most of these reforms had significant flaws and were met by mounting opposition - the intelligentsia (‘westernisers’ and ‘slavophiles’) Key Opponents include – The Narodniks in the early 1870s – Land and Liberty – The People’s Will Alexander was unwilling to give up his own autocratic power; reconsidering this when assassinated in March 1881 An ‘ineffective liberal’ and an ‘inefficient autocrat’ See OXLEY Chapter 2 pages 22 - 41 for detail Russia 1894 - 1917 The reign of Tsar Nicholas II Attempted to rule like his father - stern autocracy and repression -but his character and changing circumstances made this impossible Condemned liberal demands for a constitution as ‘senseless dreams’ Faced rising opposition from groups like the Social Democrats (Bolsheviks & Mensheviks) and the Social Revolutionaries Defeat in the Russo-Japanese War (04/05) and events on Bloody Sunday (Jan 05) sparked off the 1905 Revolution Nicholas survived 1905 by reform (The October Manifesto - granted a Duma or parliament) From 1906 Nicholas ignored demands from Duma for reform and rigged elections in 1907 to ensure the election of supporters Stolypin 1906 - 1911 repressed severely but introduced reform in countryside By 1906 Nicholas II was increasingly under influence of Rasputin See OXLEY Chapter 3 pages 50 - 63 & Chapter 4 64 - 89 for detail Nicholas II - Page 1 Russia 1894 - 1917 The reign of Tsar Nicholas II Stolypin assassinated in 1911 Massacre of striking miners in Lena goldfields in 1912 suggests regime in trouble Entry into the First World War in 1914 probably doomed Nicholas II Disastrous defeats on Eastern Front as troops lacked modern weapons Nicholas II appointed himself supreme army commander in 1915 (which left no-one else to blame) Government increasingly in hands of his unpopular German wife, Alexandra, and Rasputin (until his murder in December 1916) War led to rapid inflation, food shortages and starvation Bread riots in February 1917 spiralled into revolution and led to the abdication of Nicholas II and the end of the Romanov dynasty See OXLEY Chapter 3 pages 50 - 63 & Chapter 4 64 - 89 for detail Nicholas II - Page 2 1917 The Russian Revolutions Two revolutions – February (March) – October (November) – October (November) The February Revolution – Tsar Nicholas II abdicated – Two groups claimed power: • The Provisional Government (former members of the Duma) • The Petrograd Soviet (Workers’ Council) The Provisional Government failed to reform and lost popularity – Continued fighting (and losing) in the First World War – Failed to re-distribute the nobles’ land to the peasants Lenin and the Bolsheviks (Communists) gained support with their demand for ‘Peace, Bread and Land’. In October 1917 the Provisional Government was overthrown and the Bolsheviks, who by then dominated the Petrograd Soviet, seized power. See OXLEY Chapter 5, pages 90 - 109, for details