Leaning Tower of Pisa
advertisement
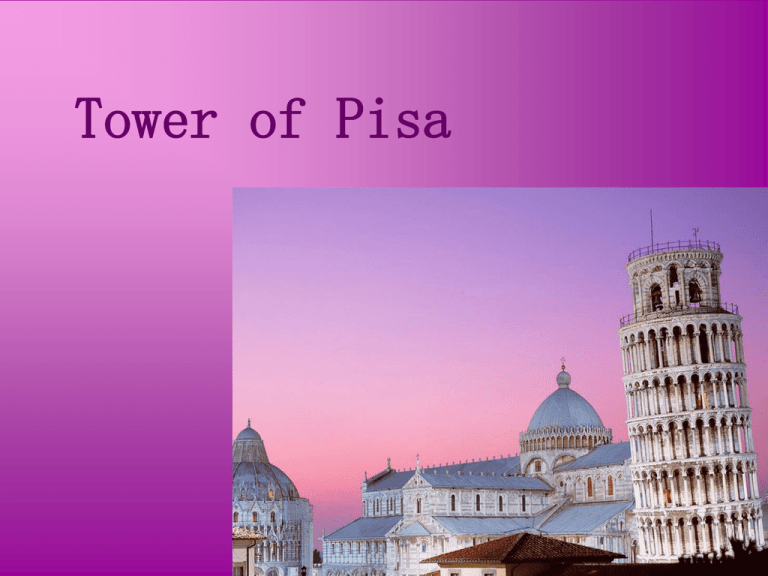
Tower of Pisa The main information • The Leaning Tower of Pisa or simply the Tower of Pisa (La Torre di Pisa) is the campanile, or freestanding bell tower, of the cathedral of the Italian city of Pisa. It is situated behind the Cathedral and is the third oldest structure in Pisa's Cathedral Square (Piazza del Duomo) after the Cathedral and the Baptistry. • The height of the tower is 55.86 m (183.27 ft) from the ground on the lowest side and 56.70 m (186.02 ft) on the highest side. The width of the walls at the base is 4.09 m (13.42 ft) and at the top 2.48 m (8.14 ft). The tower has 296 or 294 steps; the seventh floor has two fewer steps on the north-facing staircase. Construction • • • • The Tower of Pisa was a work of art, performed in three stages over a period of about 177 years. Construction of the first floor of the white marble campanile began on August 9, 1173, a period of military success and prosperity. This first floor is a blind arcade articulated by engaged columns with classical Corinthian capitals. In 1272, construction resumed under Giovanni di Simone, architect of the Camposanto. In an effort to compensate for the tilt, the engineers built upper floors with one side taller than the other. This made the tower begin to lean in the other direction. Because of this, the tower is actually curved. Construction was halted again in 1284, when the Pisans were defeated by the Genoans in the Battle of Meloria. The seventh floor was completed in 1319. The bell-chamber was not finally added until 1372. It was built by Tommaso di Andrea Pisano, who succeeded in harmonizing the Gothic elements of the bell-chamber with the Romanesque style of the tower. There are seven bells, one for each note of the musical major scale. The largest one was installed in 1655. After a phase (1990-2001) of structural strengthening, the tower is currently undergoing gradual surface restoration, in order to repair visual damage, mostly corrosion and blackening. These are particularly strong due to the tower's age and to its particular exposure to wind and rain. The architect • There has been controversy about the real identity of the architect of the Leaning Tower of Pisa. For many years, the design was attributed to Guglielmo and Bonanno Pisano, a well-known 12th-century resident artist of Pisa, famous for his bronze casting, particularly in the Pisa Duomo. Bonanno Pisano left Pisa in 1185 for Monreale, Sicily, only to come back and die in his home town. A piece of cast with his name was discovered at the foot of the tower in 1820, but this may be related to the bronze door in the façade of the cathedral that was destroyed in 1595. However recent studies seem to indicate Diotisalvi as the original architect due to the time of construction and affinity with other Diotisalvi works, notably the bell tower of San Nicola (Pisa) and the Baptistery in Pisa. History following construction • • • • Galileo Galilei is said to have dropped two cannon balls of different masses from the tower to demonstrate that their speed of descent was independent of their mass. This is considered an apocryphal tale, its only source being however Galileo's secretary. During World War II, the Allies discovered that the Nazis were using it as an observation post. A U.S. Army sergeant was briefly entrusted with the fate of the tower and his decision not to call in an artillery strike saved the tower from destruction. On February 27, 1964, the government of Italy requested aid in preventing the tower from toppling. It was, however, considered important to retain the current tilt, due to the vital role that this element played in promoting the tourism industry of Pisa. A multinational task force of engineers, mathematicians and historians was assigned and met on the Azores islands to discuss stabilization methods. It was found that the tilt was increasing in combination with the softer foundations on the lower side. Many methods were proposed to stabilize the tower, including the addition of 800 metric tonnes of lead counterweights to the raised end of the base. In 1987, the tower was declared as part of the Piazza del Duomo UNESCO World Heritage Site along with the neighbouring cathedral, baptistery and cemetery. • On January 7, 1990, after over two decades of work on the subject, the tower was closed to the public. While the tower was closed, the bells were removed to relieve some weight, and cables were cinched around the third level and anchored several hundred meters away. Apartments and houses in the path of the tower were vacated for safety. The final solution to prevent the collapse of the tower was to slightly straighten the tower to a safer angle, by removing 38 cubic metres (50 cu yd) of soil from underneath the raised end. The tower was straightened by 18 inches (45 centimetres), returning to the exact position that it occupied in 1838. After a decade of corrective reconstruction and stabilization efforts, the tower was reopened to the public on December 15, 2001, and has been declared stable for at least another 300 years.