Chapter 11 An Emerging World Power
advertisement

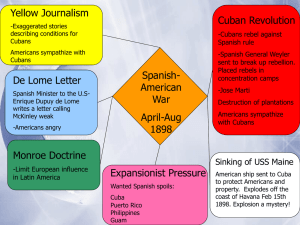
An Emerging World Power 1890-1917 Chapter 11 The Roots of Imperialism Chapter 11 section 1 Imperialism • The policy by which strong nations extend their political, military, and economic control over weaker countries – Extractive Economies: • Imperial country extracted, or removed, raw materials from weaker country Imperialist Stirrings • Americans started to think about expanding overseas as a way to expand US markets • Other nations were expanding their empires – America felt they needed to keep up • Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan – The Influence of Sea Power Upon History 1660-1783 was written in 1890 – Argued control of sea’s was essential to world domination – Also needed naval bases around the world • USA began making a modern, steel/steam powered Navy National Superiority • Social Darwinism helped justify imperialism – Religion as well • Manifest Destiny • Frederick Jackson Turner – The Significance of the Frontier in American History • Said frontier was closed • America needed frontier as a “safety valve” • Colonies would provide this new safety valve Spreading Over the Pacific • Japan had been closed off to the world for a couple hundred years • 1853 USA sent Matthew C. Perry to Japan with a fleet of warships – 1854 Perry got Japan to sign a treaty to open commercial ties with USA Alaska • By 1867 Russia was looking to sell Alaska • 1867 Secretary of State William Seward bought Alaska for US for $7.2 million • People thought he was crazy – Called it “Seward’s Folly” • Government hoped it would pay off in the future – It did! – Rich in resources – Oil, lumber… Spurning the Hawaiian Pear • Hawaii was used as a re-supply station in the early 1800’s • Most land owned by White sugar plantation owners • 1887 treaty signed allowing US naval base at Pearl Harbor • 1890 McKinley Tariff hurt the American sugar planters – Thought best way to avoid tariff was to have Hawaii annexed • Queen Liliuokalani didn’t want Hawaii annexed • 1893 whites in Hawaii revolted and overthrew the Queen • Treaty for annexation submitted to Senate during Harrison’s presidency • Cleveland removed treaty when he took back over – Investigated situation – Found most Hawaiians didn’t want to be annexed • Hawaii wouldn’t be annexed until 1898 The Spanish-American War Chapter 11 section 2 Cubans Rise in Revolt • 1895 Cubans began a scorched-earth campaign to try to get the Spanish to leave • Spanish started putting Cubans into concentration camps – Horrible conditions • American public outraged – On Cubans side • President Cleveland refused to help Cuba The Maine • Joseph Pulitzer and William R. Hurst – Yellow Journalism • Reported atrocities and made them up if they didn't exist • “You furnish the pictures and I’ll furnish the war” • • • 1898 US sent the battleship Maine to Havana harbor Feb 15, 1898 Maine blew up killing 260 men Americans blamed a Spanish mine – Most likely an accidental internal explosion • Yellow press went nuts – Remember the Maine! To hell with Spain! • Americans very upset “Cry Havoc, and Let Slip the Dogs of War” • Americans wanted war, President McKinley didn’t • McKinley came to realize war would come sooner or later, so he might as well give the people what they wanted – Good for his party (Republicans) • April 11, 1898 McKinley asked Congress to declare war – They do • Begins the Spanish-American War – They also passed the Teller Amendment • Said after Spanish were defeated they would give Cuba independence Philippines and War in Cuba • Americans excited to go off to war – An adventure • Europeans thought we were over confident – US Army ~30,000 men • Spanish had 200,000 in Cuba – US Navy appeared weaker than Spain’s • Actually Spain’s navy was in bad condition • Commodore George Dewey was instructed to attack the Spanish Philippines in the event of war • May 1, 1898 Dewey steamed into Manila harbor and destroyed the entire Spanish fleet – 400 Spanish casualties – 0 US casualties • Dewey became a war hero and was promoted to Admiral • Dewey had no troops to land in Manila – Was forced to wait for troops to arrive from US • August 13, 1898 US troops took Manila, working with Filipino insurgents led by Emilio Aguinaldo • July 7, 1898 Hawaii annexed by US Invasion of Cuba • America not prepared to fight a war in the tropics – Soldiers provided thick woolen uniforms – Rotten food • The Rough Riders – A volunteer cavalry regiment – One of its commanders was Theodore Roosevelt • Resigned from Naval Department to get into action • • 17,000 men left Tampa, Florida in June of 1898 Battle of San Juan Hill – Rough Riders and two Black regiments charged up the hill – Took heavy casualties, but they took the hill End of the War • July 3, 1898 Spanish fleet around Cuba destroyed – – • America quickly moved to invade Puerto Rico before the war ended – • • 500 Spanish killed 1 US killed Greeted as liberators August 12, 1898 US and Spain signed an armistice US Army devastated by disease – – – Malaria, typhoid, dysentery, yellow fever 400 US killed in combat 5,000 killed by disease After the War • Delegates met in Paris to discuss the peace treaty • Americans given Guam, Puerto Rico, Cuba, and Philippines (for $20 million) • The real question was what to do with the Philippines? – McKinley decided to keep them for the US American Imperialism? • Not everyone in America liked the idea of imperialism – 1899 the American Anti-Imperialist League formed • Said imperialism was “open disloyalty to the distinctive principles of our government” The United States and East Asia Chapter 11 section 3 War in the Philippines • Filipinos were hoping for independence like the Cubans – They didn’t get it • Feb 4, 1899 Emilio Aguinaldo started an insurrection (rebellion) against the Americans – Turned into guerrilla warfare • Fighting was brutal – Jungle warfare – Torture used – Concentration camps • Aguinaldo captured in 1901 – Fighting slowed down after 1901, but didn’t stop – US sent 100,000 men • 5,000 Americans died • 200,000 Filipinos died • USA poured millions of dollars into the Philippines – Built roads, sanitation, hospitals – American teachers set up schools making English a second language • 1916 Jones Act passed – Filipinos would get independence eventually • Filipinos wouldn’t get independence until July 4, 1946 Open Door in China • 1894-1895 Japan defeated China in the First Sino-Japanese War • European powers began to move into China and set up economic spheres of influence • 1899 US Sec of State John Hay sent a note around to all the major powers – Open Door note • Asked everyone to respect Chinese rights and fair competition – The major powers accepted and Open Door was in effect • Patriotic Chinese didn’t like this, felt it was too much foreign influence – 1900 Boxer Rebellion (Righteous and Harmonious Fists) • 200 missionaries and other whites killed • Foreign diplomats besieged in capital – A multinational force of 18,000 arrived to put rebellion down • 2,500 US soldiers – The victorious invaders charged China $333 million in reparations • $24.5 million for USA – We gave back $18 million (Scholarships) • After rebellion John Hay sent around a new letter stating that the Open Door would not just recognize the economic integrity of China, but also the territorial integrity of China – Kept China from being conquered and partitioned into colonies American Relations Worsen • 1904 Russo-Japanese War broke out • Russia occupied parts of Manchuria, China • Close to Japan – Japan was winning but running out of money – Secretly asked TR to arbitrate peace • Delegates met in Portsmouth, New Hampshire in 1905 – Peace agreed upon • TR given the Nobel Peace Prize in 1906 • Both Russia and Japan felt robbed by peace treaty – Hurt American relations with both countries American Relations Worsen Cont… • 1884 Japanese immigrants started going to Hawaii and then Cali • 1906 San Francisco school board segregated Chinese, Japanese, and Korean students – Japan outraged • 1907-1908 US diplomats worked out a “Gentlemen’s Agreement” with Japan – Japan would stop the flow of laborers to US – Cali would not segregate schools • TR wanted to make sure Japan didn’t think the US was weak • 1907 16 white battleships left Virginia and sailed around the world – Known as the “Great White Fleet” • Japan was impressed with the US’ “big stick” • Root-Takahira agreement signed in 1908 – US and Japan would respect each other’s territorial possessions in the Pacific and uphold the Open Door in China The United States and Latin America Chapter 11 section 4 Cuba • US withdrew from Cuba in 1902, honoring the Teller Amendment • Cuban’s had to write the Platt Amendment into their constitution in 1901 – Could not go into debt beyond their resources – US could use troops to keep order – Cuban’s would sell or lease 2 (then 1) military bases • Guantanamo Bay “Big Stick” Diplomacy • Teddy Roosevelt – “Big Stick” Diplomacy • America’s foreign policy with regard to Latin America • Had to have a strong military • America had a special responsibility to “civilize” weaker nations Trying to Build a Canal • TR wanted a canal built through the Central American Isthmus – Would make US fleets more powerful – Would increase trade • Torn between a Nicaraguan route and a Panamanian route • France had begun a canal in Panama and had given up – Offered to sell the New Panama Canal Company to US for $40 million • US agreed • Panama was under the control of Colombia • US and Colombians agent worked out a treaty – US would lease a six mile wide zone for $10 million and $250,000 annually • Colombian government said they wanted more money – TR outraged How About a Revolution? • Panamanians feared US would now go to Nicaragua • France feared losing their $40 million • A small Panamanian army revolted on November 3, 1903 • TR sent US Navy down to Panama • Colombia raised their army to crush the rebellion – US Navy would not allow them to cross the Isthmus into Panama • 3 days after uprising TR recognized the new Panamanian country • 15 days later Panama signed a treaty for canal – Same price, but a 10 mile wide canal zone • US looked down upon by other countries for this “Cowboy Diplomacy” Completing the Canal • Canal hurt US Latin American relations – Look what happens when you defy the US • Construction was very difficult – Disease, landslides, labor problems – Col George Washington Goethals put in charge • Construction completed in 1914 and cost $400 million TR and the Monroe Doctrine • Latin American countries were having problems paying their debts to Europeans • 1903 Germany bombarded a Venezuelan town for not paying • TR feared Europeans trying to collect debt would bring them into Latin America • Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine – In the future, if a L.A. Country could not pay debt, US would take over that countries customs houses and pay the debt – No one could interfere in L.A. except the US • L.A. didn’t like this “bad neighbor” policy Dollar Diplomacy • Taft tried a different tactic to deal with Latin America after he became President • Taft’s “Dollar Diplomacy” – Bankers would invest their surplus money in foreign areas of strategic concern to the US – US would try to prevent economic and political instability by pumping dollars into a troublesome country • Especially used in China and Caribbean New Directions in Foreign Policy • Wilson hated the “big stick” and Dollar Diplomacy – He ended Dollar Diplomacy during the first week of his administration – Replaced it with “Moral Diplomacy” – Would be friends to Latin America and help them, but never force them to do what we wanted • Wilson did not like imperialism • Wilson was forced to enforce the Roosevelt Corollary – Sent Marines to Haiti in 1916 – Sent Marines to Dominican-Republic in 1916 Moralistic Diplomacy in Mexico • Mexicans revolted in early 1900’s – Killed their president and installed General Victoriano Huerta as President • US had invested ~$1 billion in Mexico – Investors wanted Wilson to send troops into Mexico • Wilson refused to send troops – Also refused to recognize Huerta’s government – Started sending supplies to Huerta’s rivals; Carranza and Pancho Villa • 1914 Wilson sent US Navy to capture the port at Vera Cruz to help bring down Huerta – Mexicans did not like that • Huerta lost power and Carranza became President – Pancho Villa then began fighting Carranza • Villa wanted to start a war between US and Carranza’s government • 1916 Villa killed 16 US mining engineers in Mexico • 1916 Villa crossed the border into New Mexico and killed 19 Americans • Wilson sent General John J. Pershing into Mexico to capture Villa – Never did • January 1917 Pershing withdrawn to prepare for war in Europe Thunder Across the Sea • WWI begins…