Global Interactions: Japan, Mongols, Trade, Renaissance
advertisement
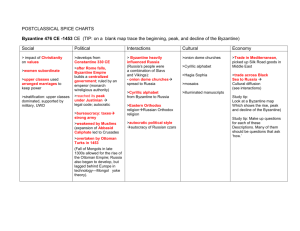
Unit 3 Global Interactions Section 1 Early Japan and Feudalism Geography Archipelago Impact on Japanese life: Mountainous – terrace farming Fishing industry Lived in river valleys Isolated and protected Religion Shintoism – respect and honor nature Also Zen Buddhism and Confucianism Influenced by China and Korea Japanese Feudalism Emperor Shogun Daimyo Samurai Peasants and Artisans Merchants Tokugawa Shogunate Centralized gov’t Economic prosperity – ^food production, trade Culture traits – Zen gardens and tea ceremonies and haiku Sec. 2 Mongols and Their Impact Mongols – nomads of Central Asia Location – grasslands of Central Asia Date:1200 Genghis Khan – 1,100’s ruled empire; great conquerors b/c skilled horsemen, bowmen and advanced weapon technology Grandsons Batu and the Golden Horde – conquered pts of Russia Kubla Khan – conquered parts of China – Yuan Dynasty Pax Mongolia – time of peace in empire Impact on Russia – absolutism and isolation prevented Russia from progressing Sec. 3 Global Trade/Interactions Expansion of Chinese Trade Han Dynasty – Silk Road – China to Russia and Asia Minor Zeng He of Ming Dynasty Goals: promote Chinese trade and collect tribute from less powerful lands Traveled: SE Asia, around coast of India and Arabian Peninsula to port cities of East Africa Canton – an important center for global trade Major Trade Routes Across Indian Ocean and Arabian Sea – Asia and East Africa Land routes linked Asia, Middle East, North Africa, and Europe; China and the Silk Road through Russia and Constantinople Mediterranean Sea – Middle East to Europe Resurgence of European Trade - impact of Crusades: cultural diffusion between Europe and East Rise of Italian city states – Venice, Genoa, Florence Trade fairs and growth of cities Hanseatic League – union of traders and merchants in Germany: Portugal established posts in Africa, India, Japan and China – spice trade The Plague – Black Death (mid 1300’s) Began in China and spread through mid East, Africa and Europe Results: 1.↓ in population 2. economic decline 3. break down of social classes and feudalism Resurgence of Europe 1,000-1300 Commercial Revolution – business revolution in Europe after the Middle Ages Rise of middle class ↑in trade, ↑ in towns/cities, Development of guilds led to 1.↑ quality of goods 2. provided social services for members (hospitals and aid to widows) 3. regulated hours and wages 4. masters and apprentices Commercial Revolution 1300-1700 ↑ capitalism New business practices 1.partnership and joint stock companies 2.rise in banking 3.insurance Renaissance 1300-1500 rebirth in learning Humanism – focus on the individual Important People of Renaissance DaVinci - Painter, sculptor, inventor, Mona Lisa Michelangelo – Sculptor, Sistine Chapel, Statue of David Dante Author – Divine Comedy Shakespeare Comedies and tragedies Machiavelli -Author of The Prince (how to gain and maintain power) Invention of printing press – 1400 1.↑books 2. ↑literacy 3. →cultural diffusion Reformation and Counter Reformation Protestant Reformation 1500’s Causes: 1.Renaissance 2.strong monarchs 3.problems w/ church (corruption in church, taxes, selling indulgences) Leaders: Martin Luther and 95 Theses John Calvin – Calvinism Henry VIII- Anglican Church Effects of Reformation 1. division in church – Protestant churches 2. rise of anti-semitism 3. witch-hunt Counter Reformation Reforms in the Catholic Church Pope Paul III - reform Catholic Church Council of Trent 1545 reaffirmed beliefs end abuses set up schools for clergy Rise of Nation States End of feudal era and beginning of European boundaries. England and France Common Law – law that is the same for all people Magna Carta – 1215 – limited powers of king Parliament becomes representative assembly Anglican Church becomes official church of England under Henry the VIII (1588) African Civilizations Ghana Gold/salt trade West African states Strong Military – expanded empire Muslim influence in gov’t, and culture Mali - Mansa Musa - Gold Trade - Muslim influence –laws based on Quran - University at Timbuktu Songhai West Africa Expanded trade route to Europe and Asia Muslim Influence Axum Linked Africa to India and Mediterranean world Jewish and Christian influence Contributions: Art – ivory, wood, bronze, jewelry Literature – histories and folk tales in oral tradition and written form Education – university of Timbuktu becomes great center for learning Contributions: Art – ivory, wood, bronze, jewelry Literature – histories and folk tales in oral tradition and written form Education – university of Timbuktu becomes great center for learning