Unit 4 Vocabulary #2
advertisement

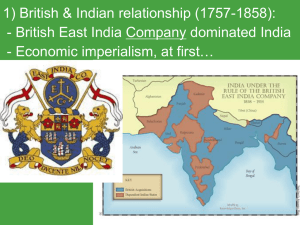
Unit 4 Vocabulary #2 AP World History Unit 4 Vocabulary #2 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Declaration of the Rights of Woman and of the Female Estates Feminism Gran Colombia Jacobins Liberalism Natural rights Proletariat Queue Radicalism Reign of Terror Revolutions of 1848 Self-strengthening movement Separation of Powers Seven Years War Social contract Socialism System of Checks and Balances *A complete definition is needed 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. Taiping Rebellion Universal male suffrage Berlin Conference Boers Boer War Duma Economic imperialism Great Trek Imperialism Indian National Congress Manifest Destiny Raj Revolution of 1905 Sepoy Rebellion Sepoys Social Darwinism Spanish American War **Number each word Declaration of the Rights of Woman and of the Female ►A statement of the rights of women written by Olympe de Gouge in response to the Declaration of the Rights of Man Estates ► The divisions of society in pre-revolutionary France Feminism ► The movement to achieve women’s rights Gran Colombia ► The temporary union of the northern portion of South America after independence movements led by Simón Bólivar; ended in 1830 Jacobins ► Extreme radicals during the French Revolution Liberalism ► An Enlightenment philosophy that favored civil rights, the protection of private property, and representative government Natural Rights ► Rights that belong to every person and that no government may take away Proletariat ► In Marxist theory, the class of workers in an industrial society Queue ► Hair braid worn by Chinese men that was required by the Qing leaders to be cut off or be executed Radicalism ► Western European political philosophy during the nineteenth century; advocated democracy and reforms favoring lower classes Reign of Terror (1793-1794) ► The period of most extreme violence during the French Revolution Revolutions of 1848 ► Democratic and nationalistic revolutions, most of them unsuccessful, that swept through Europe Self-Strengthening Movement ►A late nineteenth century movement in which the Chinese modernized their army and encouraged Western investment in factories and railways Separation of Powers ► The division of powers among the legislative, executive, and judicial branches of the government Seven Years’ War (1756-1763) ► Conflict fought in Europe and its overseas colonies; in North America, known as the French and Indian War Social Contract ► Enlightenment concept of the agreement made by the people living in a state of nature to give up some of their rights in order for governments to be established Socialism ► Economic and political philosophy based on the idea that the benefits of economic activity should be equitably distributed throughout a society System of Check and Balances ► Constitutional system in which each branch of government places limits on the power of other branches Taiping Rebellion (1853-1864) ► Revolt in southern China against the Qing Empire Universal Male Suffrage ► The right of all males within a given society to vote Berlin Conference (1884-1885) ► Meeting of European imperialist powers to divide Africa among them Boers ► South Africans of Dutch descent Boer War (1889-1902) ► War between the British and Dutch over Dutch independence in South Africa; resulted in a British victory Duma ► The Russian parliament Economic Imperialism ► Control of a country’s economy by the businesses of another nation Great Trek ► The emigration of some 12,000 to 14,000 Boers from Cape Colony in South Africa between 1835 and the early 1840s, in rebellion against the policies of the British government and in search of fresh pasturelands. The Great Trek is regarded by Afrikaners as a central event of their 19th-century history and the origin of their nationhood. Imperialism ► The establishment of colonial empires Indian National Congress ► Political party that became the leader of the Indian nationalist movement Manifest Destiny ► Concept of U.S. territorial expansion westward to the Pacific Ocean that saw the occupation of the rest of the continent as a divine right of the American people. The term was used to justify the U.S. annexation of Oregon, New Mexico, and California and later U.S. involvement in Alaska, Hawaii, and the Philippines. Raj ► In many Indian languages, it literally means Prince or Royalty though is often used to mean something more like the English term of empire and as such is often used in reference to the Mughal Raj and the British Raj: the period of direct colonial rule of India by the British Empire. Revolution of 1905 ► Strikes by urban workers and peasants in Russia; prompted by shortages of food and by Russia’s loss to Japan in 1905 Sepoy Rebellion (1857) ► Revolt of Indian soldiers against the British; caused by a military practice in violation of the Muslim and Hindu faiths Sepoys ► South Asian soldiers who served in the British army in India Social Darwinism ► The application of Darwin’s philosophy of natural selection to human society Spanish-American War (1898) ► Conflict between the U.S. and Spain that began the rise of the U.S. as a world power. The U.S. gained possession of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines as a result.