Ch 23, 24 - Darien Public Schools
advertisement
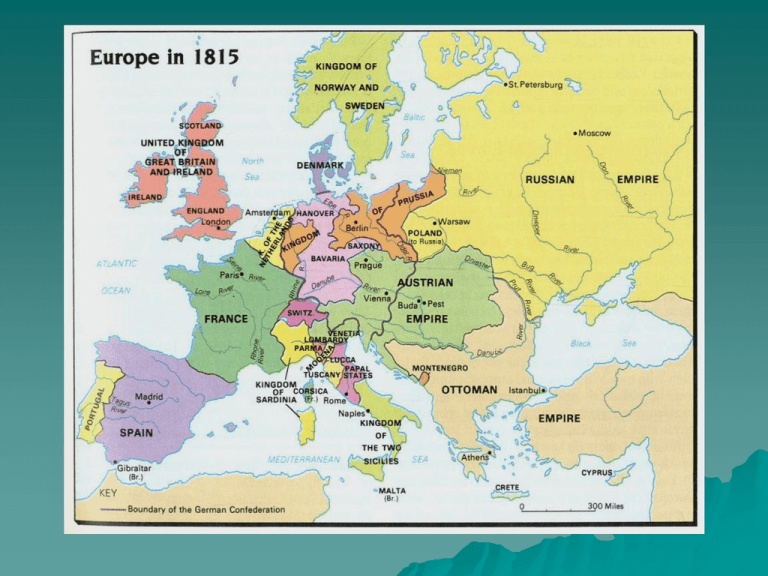
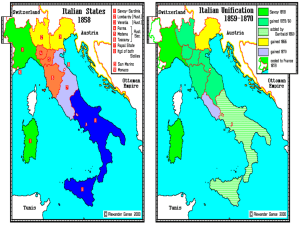
Imagine the excitement and satisfaction of royalist leaders in Vienna in 1815… Who were the 5 Great Powers in 1815? Why is political and social change so often met with resistance? The tension underneath… Question: Were politics from 1815 to 1850 characterized more by change or by continuity? Restoration, Romanticism and Revolution The Difficulty of Keeping Things the Same… European Leaders Sought Stability 1815 Congress of Vienna – – – – St. Helena Five Great Powers Klemens von Metternich What were his 3 Goals? 1. 2. 3. The American and French Revolutions awoke millions to Freedom! ?By 1815, the democracy of ______ at least was still working… Britain and USA had fought War of 1812…Who won? Congress of Vienna: Meeting was run by Conservatives who believed in Monarchy Conservatives However: elsewhere… – Liberals – Radicals Restoring a Balance of Power Encirclement of France Switzerland Kingdom of the Netherlands created German Confederation Chunks of ____________ given to Kingdom of Sardinia See map Nationalistic feelings affected European politics in the 19th Century in a big way Austrian Empire Italy Germany Poland Greece Ireland Nationalism is ready to burst out where it people are restrained… Austrian Empire was a mixture of peoples with different languages Poland was dominated by Russia Greece was ruled by Islamic Ottomans Italian peninsula had many city-states, the Papal State and kingdoms Germany is disunited Ireland wants separation from Britain Group Work on Improved Thesis and Outline – Have your green sheet out – While I check in with each student… Staple a blank piece of paper to the back of your thesis/ outline Circulate theses and outlines and read. On the blank paper, each person must write one question that arises for them about the thesis or content after reading. Discuss each thesis: How could the thesis be improved? Is it clear? 1830 Greece Becomes 1st New Nation 1821- 1830 war: the Ottoman Turks Jacques Louis David, 1791 Lycurgas Lord Byron, British mercenary Latin America Nationalism Breaks Out! What was the French Revolution’s impact on… 1804 Haiti Toussaint L’Ouverture Which of Napoleon’s mistakes had the biggest impact in Latin America? Who are these people?: – – – – – – Peninsulars Creoles Caudillos Mestizos Mullattoes What happened to the Slaves during these years? Simon Bolivar: The Liberator Wealthy Venezuelan Creole Read Voltaire, Rousseau and Locke “Gran Colombia” Equador, Panama 1824 Peru 1825 Bolivia Jose San Martin Argentina, Chile and Peru Mexico – Father Hidalgo mestizos Nationalism, Industrial Change, and People’s Desire for a Voice Great Britain – Reform Bill of 1832 Expanded middle class rights Recreates districts to increase – Manchester Improved male suffrage to 20% from 3% – Factory Act of 1833 – no children < 9 – 8 hours max, day for those 9-13 – Mines Act of 1842 – same for mines French HISTORY REPEATS Revolt of 1830 against French monarchy Louis Philippe, a liberal noble, given throne because he accepts limited monarchy Bourbon King’s Flag of France The Tricolor is revived. Across Europe: 1848 Revolutions 50 separate revolts: WE WANT DEMOCRACY!!! – Radical Parisians – Unhappy Prussians – Nationalistic Hungarians Initially monarchs agree to more democracy…but it ain’t so easy to give up… Then, France tries to get rid of limited monarchy king….AGAIN… Paris radicals force Louis 1848 Philippe out… A Republic! Revolution – And Terror results between two radical factions People demand a new const. And elect a strong leader president named…. – Louis Napoleon Bonaparte, nephew of …you guessed it… (really?) Counterrevolutions (1848-1852) But The Empires Strike Back!!! In France: Louis Napoleon Bonaparte dissolves the Republic and is elected by plebiscite, Emperor Napoleon III (déjà vu!!!) Prussian parliament dissolved Austrians crush uprisings in Hungary and Italy Part of the revolutionary thinking was a Reaction to Reason Romanticism Emphasized : emotions/passion, the individual - and folkheroes - nature, boundlessness rather than lawfulness Ludwig von Beethoven Listen: And respond…. Mary Shelly The Romantics loved symbolism… What is this painting about? Caspar Friedrich Wanderer above the Sea of Fog 1818 Why can the monarchs end the reforms? 1. Liberals and radicals disagree and are easily divided… 2. “The Empire means peace,” - says Louis Napoleon But its temporary Ch 24: Mid 1800s: Industrialism Created a Global, Complicated Economy Transportation of goods and people – RR’s built – Steamships – Suez Canal built by French (1869) Communication – Telegraph (Morse) – Cables laid across oceans and continents Access to capital investment - banks – More corporations develop through stocks Emergence of Communist Theory Karl Marx & Friedrich Engels Working class grows, and grows impatient… Industrial Revolution spreads, creating concentrations of neighborhoods of squalor and discontent Reformers Radical thinkers – Karl Marx – “Workers of the world unite! You have nothing to lose but your chains!” Working People Demanded Influence Socialism – Robert Owen: Utopian socialism Workers should share ownership of large industries through govt control Marxist communism – “Scientific socialism” – Preached revolution by the mass of workers Marxism Rests on 7 Ideas… 1. Historical materialism – History is governed by economic forces – Religion, culture, politics are superficial and have their causes in economics. All other human endeavors Economic Substructure: Desire for material goods Marx 2. Theory of Surplus Value – Workers alone create the products and their value. – Owners “steal” the value of the laborer by selling the products at profit Created by workers Stolen by the capitalists Cost of Production Total Value Profit Or “Surplus Value” Marxism rests in 7 ideas… 3. Class Struggle – “Workers of the world unite! You have nothing to lose but your chains!” – Its bitter and hateful between workers and capitalists Marxism rests in 7 ideas 4. Stages of historical development – History is one of class struggle, but the oppressed are getting close to the final stage of history Proletariat must overthrow the Bourgeoisie They can do so now that the industrial revolution brings them into proximity Goal of History Ideal: Communism Class Struggle Human’s Original Mistake: Personal Ownership of Property Primitive Communal Society Goal of History Ideal: Communism Class Struggle Mistake: Personal Ownership of Property Primitive Communal Society Communism’s Triumph! 5. Force: The workers must use force to overthrow the existing false order. 6. Temporary dictatorship of the worker (proletariat) 7. Peaceful Communism will be established – Dictatorship will wither away – Only public ownership No competition No classes, no rich and poor divisions = no envy Each person will work according to ability, and receive as they need – no more and no less. No starvation or destitute What problems do you see with Marx’s theory? Is there anything to like about it? Finally! Two Major Countries Unite: ITALY AND GERMANY Germany 1815-1860 German Confederation in red Realpolitik Definition: Politics based on toughminded reality. Combine tough diplomacy and military strength Prussia Unites Germany 1st step: 1815 German Confederation Prussia – economic center “Blood and Iron” – STRONGER army – Otto von Bismarck, PM of Prussia – Master of Realpolitik Austria – German speaking cultural and historic center – Vienna!!! Realpolitik in Action Bismarck Provokes 3 Wars to Unify 1. With Denmark Get Schleswig-Holstein 2. With Austria – 7 Weeks War German Confederation expels Austria (This war also helped Italy expel Austria) 3. Franco - Prussian War – Invasion of France: nationalism inspires southern Germany to unite with northern Prussia (1871) Franco-Prussian War Germany wins: – Alsace and Lorraine – 5 billion francs – Lasting French enmity!!! (ooh! another good vocabulary word) 2nd Reich Formed as a Result (1871) 1st Reich was… 2nd Reich (1871-1918) 3rd Reich will be… What are 2 main obstac to Italy’s Unification? Unification of ITALY 4 Men… The Heart… King of Sardinia Victor Emmanuel II The Soul- Mazzini The Brain - Cavour The Sword - Garibaldi The Republican Soul Guiseppe Mazzini Young Italy! Led revolt and Republican govt. in Rome in 1848 Counter-revolution ended it The Brain That United Italy –Camillo Cavour Prime Minister of Piedmont-Sardinia Sends money to help Garibaldi in the South The Sword: Guiseppe Garibaldi: Red Shirts Forces South into One As a young man, Garibaldi had fought for independence in Brazil and Uruguay 1860 Sardinia and Sicily Join Cavour Persuades Napoleon III of France to join them in a fight against Austria The Brain Persuades Garibaldi to steps aside for King Emanuel Italy Unified 1861 - 1871 Constitutional Monarchy under Victor Emmanuel of Sardinia 1871 – Papal States join Italy – Rome – Vatican City established as autonomous under Pope’s rule King Victor Emmanuel: 1871 “After long trials Italy is restored to herself and to Rome. Here, where our people, after centuries of separation, find themselves for the first time solemnly reunited in the person of their representatives: here where we recognize the fatherland of our dreams, everything speaks to us of greatness; but at the same time it all reminds us of our duties. The joy that we experience must not let us forget them. . . . “ After Unification 1870-1910 Italy remained very divided And poor… - Cavour soon died - Sectional rivalries persisted - Governments changed often - economy was weak - 4 million emigrants left for the US, 1 mill for Latin America