bonaparte - Pittsfield Public Schools
advertisement
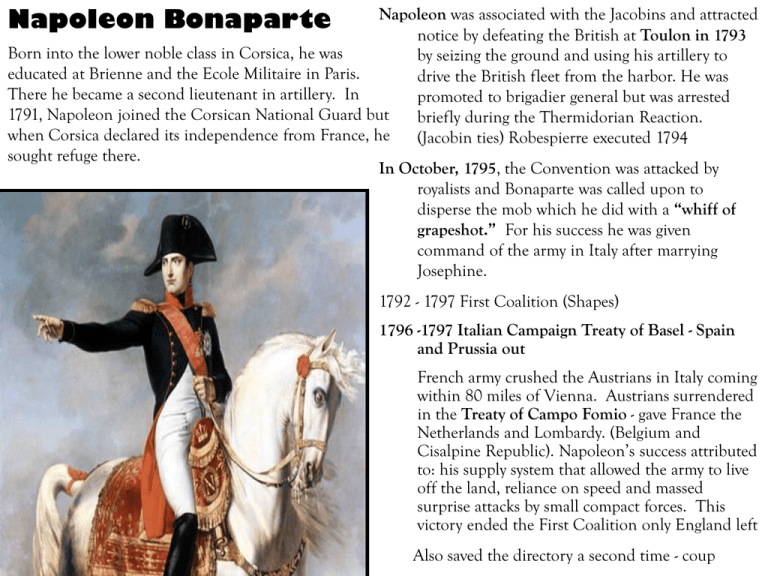
Napoleon Bonaparte Napoleon was associated with the Jacobins and attracted notice by defeating the British at Toulon in 1793 Born into the lower noble class in Corsica, he was by seizing the ground and using his artillery to educated at Brienne and the Ecole Militaire in Paris. drive the British fleet from the harbor. He was There he became a second lieutenant in artillery. In promoted to brigadier general but was arrested 1791, Napoleon joined the Corsican National Guard but briefly during the Thermidorian Reaction. when Corsica declared its independence from France, he (Jacobin ties) Robespierre executed 1794 sought refuge there. In October, 1795, the Convention was attacked by royalists and Bonaparte was called upon to disperse the mob which he did with a “whiff of grapeshot.” For his success he was given command of the army in Italy after marrying Josephine. 1792 - 1797 First Coalition (Shapes) 1796 -1797 Italian Campaign Treaty of Basel - Spain and Prussia out French army crushed the Austrians in Italy coming within 80 miles of Vienna. Austrians surrendered in the Treaty of Campo Fomio - gave France the Netherlands and Lombardy. (Belgium and Cisalpine Republic). Napoleon’s success attributed to: his supply system that allowed the army to live off the land, reliance on speed and massed surprise attacks by small compact forces. This victory ended the First Coalition only England left Also saved the directory a second time - coup 1798 - 1799 Egyptian Campaign Napoleon devised a plan to crush the English empire by attacking Egypt, then India, British assets. He evaded Horatio Nelson and took Malta on his way to Egypt. He won a brilliant victory at the Battle of Pyramids but suffered defeat when the French fleet was destroyed by Admiral Nelson at the battle of the Nile in Aboukir Bay. Since Egypt was a province of the Ottoman Empire, the Turks then declared war on France. English and Turkish forces held against the general so he retreated back to Egypt. Second Coalition 1798 - 1802 (TEAR) In 1799, he defeated the Turks at Aboukir but the previous loss to Nelson stranded the French army and things were not going well back in France. The French army was expelled from Italy by the Second Coalition (EAR) and the Directory faced political ruin. Napoleon left his army and booked it back to France. In October 1799, Napoleon, with the help of two of the five directors, and his brother, Lucien, president of the Council of 500, overthrew the Directory. He was 30 years old. Positive - Rosetta Stone Let’s review the political structure of France 1795 Constitution of the Year III Council of Elders - Men over 40 years of age + Council of 500 - Men over 35 years of age 500 submit list of names for 5 Directors who are chosen by Elders 1797 Coup d’ etat Part 1 by anti monarchial Directory who throw out royalists elected in legislature and replace them with their supporters 1799 Coup d’etat Part 2 Director Abbe Sieyes wants a new constitution with an executive body of 3 Councils who are not at the whim of the masses. Needed military support to make this happen - enter Napoleon back from EGYPT (should he really have left his men? Then there’s that Nelson thing) Write the Constitution of the Year VIII [I wish they would make up their minds] The Consulate in France 1799 - 1804 Napoleon gets his ducks in a row: By 1799 Third Estate - Hereditary privileges ended and careers were opened to talented who could be promoted by merit and receive wealth and status as a result of their jobs. Napoleon guaranteed them protection of their newly acquired property Peasants got land and destroyed feudal privileges that had burdened them so much Makes peace with the Pope •Makes peace with foreign enemies with Treaty of Luneville (1801) with Austria and the Treaty of Amiens (1802) with Britain [Russia is out and the Turks were defeated •Issues a general amnesty to all and accepts RADICALS, those who fled France during the revolution because they favored a CONSTITUTIONAL MONARCHY, and CONSERVATIVES who favored a monarchy. This gives him a supply of politically experienced people and reduces enemies to his plans Political Life The Consulate 1799 - 1804 [closed the French Revolution] Directors needed another coup - Napoleon ----------------------------------Constitution of the Year VIII Established the Consulate - Napoleon ruled as first consul, with a term of ten years. In 1802, the people of France, in an election conducted by universal male suffrage, made Napoleon first consul for life. Middle class and peasants were conservative and wanted someone to protect their rights. 1. Centralized Government •Consul was checked and balanced by representatives •prefects were assigned to 83 departments with sub-prefects to administer districts within the departments (all were answerable to Napoleon) 2. Napoleonic Code Equality before the eyes of the law Commission of legal experts drafted a new civil code that went into effect in 1804 •Serfdom and feudal dues ended as was primogeniture, property acquired during the revolution was reaffirmed and could be divided between male and females heirs •Employment to the state and promotions in the military were based on talent and merit. No one could purchase tax positions. (nobles’ privileges were ended) •Universal State Education put private and public education under the state (University of France) that offered technical and professional training 3. Sound Economy •Government collected taxes and Financial planning was instituted as was a balanced budget •Bank of France was instituted to release currency and process loans •Price of bread was regulated - ending riots •Trade was encouraged with Tariffs, improved roads and canals •Workers could not organize but careers were opened based on merit 4. Men’s rights asserted • Husbands were heads of family, they controlled wife and owned his children •Women could get a divorce based on adultery, conviction of a serious crime, excessive cruelty but it was much easier for a man to do so •If a man surprised his wife in bed with another man, he could legally kill her. A woman who did this would be tried for murder •Women could not vote and unmarried women had fewer rights, could not be legal guardians or witness wills 5. Freedom of Religion Concordat of 1801 Napoleon made peace with the church - Reconciled with Pope Pius VII •Granted Catholic Church special privileges - religion of the majority of the French people but not the established religion of France that was now religiously tolerant •French government nominated bishops who were invested by the Pope. Bishops appointed priests. Elected clergy was ended and the French government took administrative control of the church. (Organic Articles) •Pope regained parts of the Papal state that was under French control •Pope agreed to accept loss of church land during the revolution and government agreed to pay salaries of clergy as well as Protestant pastors and rabbis But Freedom of expression was curtailed as newspapers went out of business and Joseph Fouche headed the secret police. Stamped out royalist rebellions especially in Brittany and Vendee and used a ‘bomb plot” to destroy his Jacobin enemies and royalist foes, duke of Enghien. By 1802 the constitution was ratified and the Second Coalition ended with the peace of Amiens between England and France. Napoleon’s Empire Bonaparte used the bomb plot to make himself emperor and issued a new constitution. He even invited the Pope to his coronation at Notre Dame but placed the crown on his own head. Henceforth, he would be called Napoleon I. The Treaty of Amiens between France and England ended the Second Coalition but this only bought him time to settle affairs in France before he built his empire. Three events that alarmed the British and led to the Third Coalition were: 1. Sent army to Haiti 2. Louisiana Purchase 3. Interfered in Dutch Republic, Italy, Switzerland and reorganization of Germany French Military 700,000 conscripts promoted to officers’ corps by merit. With this large number, one could risk as much as 100,000 in one battle. Defeated First Coalition (SHAPES) 1792 - 1797 Treaty of Campo Formio Austria defeated France received Belgium, Cisalpine Republic and Venice Defeated Second Coalition (TEAR 1798 - 1802) Turks defeated Treaty of Luneville 1801 - Austria defeated at Marengo Treaty of Amiens 1802 - peace with England Napoleon v. Third Coalition 1805 - 1807 [PEAR] ULM October, 1805 72, 000 Austrians under Mack v. 210,000 French French encircled the Austrians and using artillery defeated them before Russians arrived TRAFALGAR Four days after Ulm, Horatio Nelson defeated the French fleet here ending all hopes for a French invasion of England and granting the Brits supremacy of the seas. AUSTERLITZ December 2, 1805 85,000 Austrian and Russian troops v. 66,000 French Napoleon abandoned the high ground but French re-enforcements arrived. Napoleon launched an assault the split his enemies’ forces. Treaty of Pressburg made Napoleon King of Italy (Austria) 1806 - Germany reorganized into the Confederation of the Rhine to serve as a buffer between Austria and Prussia. The Holy Roman Emperor was dissolved and the HRE became the first emperor of Austria. This brought Prussia into the war JENA & AUERSTADT OCTOBER 14, 1806 At Jena, Napoleon could have 90,000 men at his disposal. French pushed Prussians into open ground to see this advantage. French Cavalry fought an exhausted Prussian army. The same day, another French army defeated the Prussians at Auerstadt. Napoleon took the Prussian capital of Berlin. Issued the Berlin Decrees forbidding his “allies” from importing British goods. FRIEDLAND JUNE 4, 1807 40,000 Russians advanced on 16,000 Frenchmen. Suddenly, 80,000 more French troops arrived under Napoleon’s command. Treaty of Tilsit Alex I met with Napoleon on the Niemens River while Frederick William III (what else) watched from shore. Russia and Prussia recognized Joseph, Louis, and Jerome (Napoleon’s brothers) as the rulers of Naples, Holland and Westphalia (Con. Of Rhine) Reduced Prussia by 1/2 giving land to Saxony and duchy of Warsaw Russia got a free hand in fighting the Turks but could not take Constantinople and made Prussia and Russia allies of France. Next up…England Satellite countries were offered Enlightened ideals and Napoleonic reform that will lead to more revolution in the 1830s. This was the height of Napoleon’s Empire. The same nationalism that he unleashed in France and the liberalism promised to satellite nations raised nationalism in the conquered countries. This powerful force would lead to his eventual demise at Waterloo. When the Pope objected to the continental system he imprisoned Pius VII and took the Papal states. And Scandinavia became France’s ally Napoleon’s Demise Unleashed Nationalism in other Nations CONTINENTAL SYSTEM (ENGLAND) Unable to defeat the British military, Napoleon tried to destroy the British economy. The Berlin Decrees stopped France’s allies from trading with England and the new Milan Decrees attempted to stop neutral nations from trading. All European ports were closed to British ships while French privateers attacked British ships. 1. Britain controlled the seas and had access to markets in North and South America 2. Napoleon’s tariff helped only the French but hurt European nations who wanted trade AND he ignored advice to make Europe a free-trade zone. 3. Smuggling increased and that led to Peninsular Wars (SPAIN) To stop Portuguese trade with Britain, Napoleon marched through Spain and to maintain his supply line, he stayed, deposed the Spanish Bourbon King and replaced him with his brother, Joseph. Spain revolted against the threat to its monarchy and church and the only way to stop a more powerful army was guerilla warfare. England sent help, the duke of Wellington, who could observe Napoleonic tactics without him present This long war drained the French economy - reinstitute slavery PRUSSIA Jena made it clear that reform was necessary. Under Baron vom Stein and Count von Hardenberg: Social Serfdom ended breaking Junkers’ monopoly on land ownership. But peasants remaining on the land were forced to perform manorial labor. They could own land if the lord got one third of the land. Some peasants went to the cities but this created problems when they could not find jobs Military Ended inhumane military punishments, opened officers’ corps to commoners and gave promotions based on merit. Organized war colleges to develop military strategies and tactics. To avoid Napoleon’s decree that the army could not exceed 42,000 ment, they trained one group a year as reserves. Army increased to 270,000 Austria Troubles in Spain got Austria to renew war with France in 1809 but the army was quickly defeated at Wagram. Austria lost a great deal of territory and 3.5 million subjects. But Napoleon divorced Josephine and married Marie Louise, daughter of Austrian emperor who bore him a son. But the greatest mistake was…. The Invasion of Russia Due to many factors too numerous to mention, (check book p. 683), the Russians withdrew from the Continental System so Napoleon and his army of 600,000 (400,000 not French) invaded. The Russians had only 160,000 troops so they kept retreating and followed a “scorched-earth” policy so the French army could not live off the land. The Battle of Borodino cost the French 30,000 and the Russians twice as many but it was not destroyed. On September 14, the French entered Moscow but the Russians left it in flames. Napoleon offered Alex I peace but Alex would not respond. Finally, by October 19, defeated by the Russian winter, the Grand Army was forced to retreat. 100,000 of the 600,000 survived. Battle of Nations (Leipzig) After his defeat in Russia, Napoleon still quieted opposition at home and raised an increased army 350,000 men In 1813, Prussia, Russia and Austria joined forces and defeated Napoleon in the Battle of Nations, at Leipzig. Napoleon retreated into France. Then the Dutch revolted and the British, led by the Duke of Wellington invaded southern France. RAP invaded France from Germany and on March 31, the allied armies entered Paris. Napoleon abdicated and was exiled to Elba on the condition that he never leave. The throne of France went to Louis XVIII, younger brother of Louis XVI. Meanwhile the victors met to Vienna to discuss peace terms. The Final Defeat of Napoleon The Hundred Days and Waterloo On March 1, 1815, Napoleon escaped from Elba (who was watching that guy], and returned to France. The King, Louis XVIII, left town and Napoleon promised the French a more liberal constitution. So, eager for glory, the French followed their beloved ruler one more time. [ From March until June (100 days) ] On June 18, 1815, the French forces met their WATERLOO against the combined forces of Wellington and Field Marshall von Blucher. The Prussians had revamped their military and were better prepared. Napoleon split the Anglo Prussian lines but the rains fell and allowed the Prussians to re-enforce troops. Napoleon threw all he had but finally his reserved guard fell and it was over Napoleon was exiled to Saint Helena in the South Atlantic where he remained until his death in 1821. Congress of Vienna Participants Goals: ` 1. Create a lasting peace 2. Prevent another French nightmare 3. Establish a balance of power among European Nations Big Four Prussia Von Hardenberg Russia England Castlereagh Czar Alexander I Austria Metternich Achievements Legitimacy Restore Bourbons: France Spain Naples Two Sicilies Restore Habsburgs: Tuscany Modena Sardinia Holland Restore Pope: Papal States Leniency Encirclement Compensation Restored French borders to 1792 United Belgium and Holland = Netherlands England – Malta, Ceylon, Cape of Good Hope [only lost territories in Italy, Germany and Low Countries] Confederation of Germany [39 states controlled by Austria] Austria – Lombardy, Venetia, Galicia and Illyrian Peninsula France was not forced to pay reparations until the 100 Days Switzerland gained independence Prussia – Rhine Valley, 2/5 Saxony, parts of Poland Sardinia united with Piedmont and Genoa Russia – Poland, Finland, Bessarabia Kept art from European museums Results: France Gladly accepted Terms Rule by Conservatives Peaceful and reasonable settlements between states and not monarchy [peace would survive a ruler] Balance of Power – considered political, economic, resources, technology, education, industry Peace for 50 Years ROUSSEAU KANT BLAKE COLERIDGE WORDSWORTH BYRON SCHLEGEL GOETH METHODIST WESLEY CHATEAUBRIAND SCHLEIERMACHER FICHTE HERDER HEGEL Romantics Enlightenment Rejected Science centered around science Math minimized feelings and imagination Math explained everything Human Nature was irrational Human Nature was very rational Faith and religion were knowledge Physical world and Human Society is explained through Natural laws There was a world beyond empirical senses with dreams and hallucinations Opposed traditional religions Liked Medieval Art, Literature and Architecture Scientific Method and Empirical knowledge proves ALL Folk Lore Looked to ANTIQUITY and ORIGINAL SOURCES Songs Fairy Tales









