The Era of Thomas Jefferson
advertisement

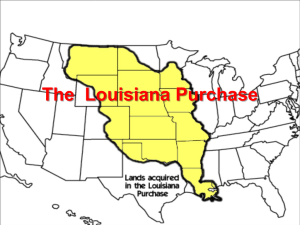
The Era of Thomas Jefferson Chapter 9 Jefferson takes Office Thomas Jefferson was inaugurated in March 1801. He ran against John Adams. Aaron Burr won the same amount of electoral votes as Jefferson The House of Representatives debated for 6 days before Jefferson was chosen In 1804, the electors would vote separately for President and Vice President Jefferson takes Office Jefferson was the first president to get inaugurated in Washington DC The presidents goal was to limit the federal governments power over the states He thought that laissez faire would be the best idea He fired all tax collectors and cut the number of diplomats He reduced the size of the military People who were imprisoned under the Sedition Act were released Jefferson takes Office Adams appointed William Marbury and other judges before he left office Republicans said these were to keep the Federalists in power Jefferson ordered James Madison to cease work on the appointments Jefferson takes Office Marbury sued Madison citing the Judiciary Act of 1789 Chief Justice John Marshall ruled that the Judiciary Act of 1789 was unconstitutional He said the Court’s power came from the Constitution This was important because of the court case Marbury v. Madison, judicial review was established The Louisiana Purchase By 1800, more then a million settlers lived between the Appalachian and the Mississippi Most of these settlers were farmers. The Louisiana Purchase These farmers relied on the Mississippi River to transport their crops to the port at New Orleans Spain had controlled new Orleans and the US negotiated with Spain to guarantee American’s right to ship goods down the Mississippi to New Orleans This was called Pinckney’s Treaty The Louisiana Purchase Jefferson found out in 1801 that Spain had given New Orleans and the Louisiana Territory to France in a secret treaty In 1802, before the official transfer of the land to France, the Spanish governor stopped allowing Americans to ship their goods through New Orleans The Louisiana Purchase The President decided that he would try to buy New Orleans from the French He sent James Monroe and Robert Livingston to try to buy New Orleans and West Florida from France When they arrived they found out that Toussaint L’Ouverture had driven the French from Haiti The Louisiana Purchase They knew the French would have a hard time defending Louisiana They also knew that there were tensions between France and England Napoleon, the leader of France would need money to support the war Napoleon offered to sell not only New Orleans but the entire Louisiana Purchase They purchased the whole territory for $15 Million-4 Cents an acre The Louisiana Purchase No where in the Constitution did it say that the President had power to buy land Jefferson said that the President was allowed to make treaties, the Senate approved and Congress voted to pay for the land In January 1803, Jefferson convinced Congress to pay $2,500 on a western expedition The Louisiana Purchase He chose Meriwether Lewis and William Clark to report back about geography, plants, animals and other natural features He also wanted them to make contact with the Natives and to look for a waterway from the Mississippi to the Pacific Ocean The Louisiana Purchase They took 40 men and traveled up the Missouri River, met up with natives, reached the Great Plains, traveled west, and met up with Native American Sacagawea, who traveled with them and was a translator They climbed the Rockies, reached the continental divide, found the Columbia River and traveled by canoe to the Pacific Ocean It took nearly 6 months to return to Missouri The Louisiana Purchase In 1806-1807, Zebulon Pike also explored the southern part of the Louisiana Territory When he got to the Rocky Mountains, he was stopped by deep snow The mountain he could not climb is now called Pike’s Peak The Louisiana Purchase On his return, he went to Spanish new Mexico Pike and his explorers were arrested by Spanish troops They thought they were spies trying to take over the area They were released and escorted back to the United States Because of Pike’s reports, the Americans grew interested in the Spanish Borderlands. A Time of Conflict Pirate ships began to attack American ships in the Mediterranean Sea These ships came from Morocco, Algiers, Tunisia and Tripoli (the Barbary State) These pirates took property and sailors, holding the sailors for ransom European governments stopped the raids by paying the States tribute A Time of Conflict Jefferson stopped paying tribute and sent warships to the Mediterranean The Philadelphia ran aground near Tripoli and the crew was imprisoned American sailors burned this ship to prevent the pirates from using it. American troops marched across the Sahara desert and captured Tripoli A Time of Conflict By 1803, France and England were at war Americans were Neutral To prevent the other side from getting supplies, the French and English began to seize American ships and stealing the cargo The British again used impressments A Time of Conflict To try to stop this, in 1807, Jefferson passed the Embargo Act Forbid any trade on American ships sailing to any foreign port Jefferson thought this would stop the other countries from seizing ships Instead, the money made by exports fell, prices of crops declined and thousands of Americans lost their jobs Many Americans began to smuggle goods. A Time of Conflict After the Battle of Fallen Timbers, many settlers moved West Diseases such as measles, smallpox and the flu killed thousands of Natives Settlers stole native lands for hunting The Shawnee people were hurt by the settlers In 1805, Tenskwatawa and Tecumseh urged Natives to fight against the settlers This action scared American officials In 1811, William Henry Harrison, marched his soldiers against the Shawnee villages and defeated the Natives at the Battle of Tippecanoe The War of 1812 There was tensions between Britain and the US when James Madison became president in 1809 Arming Natives Impressments of sailors America’s new nationalism Henry Clay and John C. Calhoun became leaders in the House of Representatives They supported war with Britain-They were called War Hawks The War of 1812 Although England was at war in Europe, they would not give into US Demands to avoid war The War of 1812 The US navy only had 16 warships, and the army had only 7,000 men The British set up a blockade of the Coast A major sea battle was in Aug 1812 and the USS Constitution defeated the British ship Guerriere The War of 1812 The British and Americans were also fighting for control of the Great Lakes and the Mississippi American General William Hull tried and failed to invade Canada The Americans did win at Lake Erie, where they defeated the British In the south, Natives attacked American settlements. Andrew Jackson fought back and defeated the natives at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend The War of 1812 The British Attacked Washington D.C. in August 1814 Dolly Madison, the President’s wife gathered important documents and fled the building The British set fire to the White House The War of 1812 They Then moved to For McHenry in Maryland Although the British fought through the night, the Americans had beaten off the attack Francis Scott Key saw this attack and later wrote “The Star Spangled Banner” The War of 1812 Britain had become tired of war and peace talks began in Ghent, Belgium The Treaty of Ghent ended the war Many Federalists did not agree with this war, and met at the Hartford Convention to talk about New England states seceding from the US