ANCIENT CIVILIZATIONS
advertisement

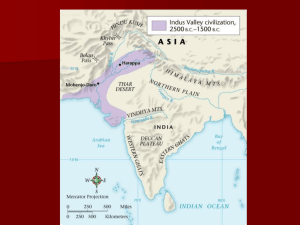
Slide 1 Before we begin…P-E-G-AS Political: Who controls what? What type of government is there? Anything to do with laws or war. Economic: What type of economy? How do people make a living? Geography: Where is it? Is the land mountainous? Desert? Oceanic? Advances/Social: Religious, intellectual, artistic Slide 2 Ancient River Valley Civilizations Slide 3 Early River Valley Civilizations Sumer • Flooding of Tigris and Euphrates unpredictable • No natural barriers • Limited natural resources for making tools or buildings Egypt • Flooding of the Nile predictable • Nile an easy transportation link between Egypt’s villages • Deserts were natural barriers Indus Valley • Indus flooding unpredictable • Monsoon winds • Mountains, deserts were natural barriers China • Huang He flooding unpredictable • Mountains, deserts natural barriers • Geographically isolated from other ancient civilizations Slide 4 ANCIENT MESOPOTAMIA Oldest known civilization Cradle of Human Civilization Old Testament Nebuchadnezzar Ziggurat (right) Hanging gardens Slide 5 Geography This civilization rose in the valleys between the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. Some say this Fertile Crescent was the real Garden of Eden. It has few natural barriers. Slide 6 In what modern day country was the Fertile Crescent? Slide 7 Iraq Slide 8 Ur, the capital city of Mesopotamia Slide 9 Sumerians The Sumerians invented writing called cuneiform. Babylonians wrote using this “wedgeshaped” writing on clay tablets. Number system based on 60. 12 month calendar wheel, plow , sailboat Slide 10 More cuneiform writing Slide 11 Ancient Mesopotamia Social Classes Kings, Priests, Gov’t officials Artisans, merchants, farmers, and fishers Enslaved people Slide 12 More ziggurats Slide 13 Hanging Gardens of Babylonia Slide 14 Babylon under King Nebuchadnezzar II. Herodotus (historian in 450 B.C.) was quoted as saying the following: "In addition to its size, Babylon surpasses in splendor any city in the known world." Outer walls were 56 miles in length, 80 feet thick and 320 feet high. Wide enough to allow a fourhorse chariot to turn. Inside the walls were fortresses and temples containing immense statues of solid gold. Rising above the city was the famous Tower of Babel, a temple to the god Marduk, that seemed to reach to the heavens Slide 15 Another painting of the hanging gardens with Tower of Babel in back Slide 16 Economic: Trade and Farming Traditional Economy Sumerians (Mesopotamians) were known to trade with the Egyptians and the Indus Valley civilizations. In later years, these trade routes became Silk Road. Slide 17 Sumerians Invented The Wheel The wheel was invented by 6000 BC It helped military, farming and trade. At right, this is made of wood. Slide 18 Political: Mesopotamian Law Code of Hammurabi “eye for an eye tooth for a tooth” Slide 20 ANCIENT EGYPT Nile River Mummies Pharaohs Rameses King Tutankhamen Hieroglyphics Slide 21 Egyptian Civilization Egyptian civilization arose after Mesopotamia. Geography: It was centered around the Nile River. The Nile River Slide 21 Nile River Provided fish Supported plants and animals Two rivers, Blue Nile and White Nile, join to make the Nile River. World’s longest river Flows south to north Floods watered the land and provided fertile soils for crops to grow. Slide 22 The Sahara Desert. Largest desert in the world. Egypt is naturally protected from enemies because it was surrounded by deserts, rivers, deltas, and cataracts (rapids). Slide 23 Pyramids Pyramids were tombs for the kings. The most famous are the Giza pyramids (shown to left). These were built in 3500 B.C.E. How old are they? Slide 24 Political: Egyptian Pharaohs Egyptians were led by Pharaohs, who were priest-kings. The most famous pharaoh is King Tut. Using computers, this image was reconstructed using his remains. Eventually, Egypt was divided into 2 kingdoms (Upper and Lower). Tutankhamun Tutankhamen on the throne Abu Simbel was built by Ramseses II Slide 25 Egypt’s Religion They believed in many gods and goddesses and in life after death for the pharaohs. Hapi – main god Isis – main goddess Book of the Dead Slide 26 Mummies Egyptians who could afford to do so would have themselves mummified. They believed in a better afterlife if their body was preserved. Slide 27 Mummification Process Took out all of the internal organs, except the heart because it was believed to be the intelligence and emotion of the person. Organs were put in canopic jars, that were put in the tomb with the mummy. Brain was taken out through the nose because it had no significant value. The body was packed and covered with natron (a salty drying agent). Then the body was left for 40-50 days. Mummies Slide 28 Egyptians wrote in hieroglyphics Made up of sound and picture symbols Only scribes (men) were taught to write Hieroglyphics Slide 29 What did Egyptians write on? Papyrus Also used to make baskets, sandals and river rafts The Great Sphinx is located on the Giza plateau, about six miles west of Cairo. Slide 30 Egyptian Social Classes Slide 31 Egyptian Economy Although Egypt looks really sophisticated, the economy is a traditional economy based on farming and trade. Egyptians traded up and down the Nile, with Mesopotamians and sometimes with the Indus Valley (in Pakistan) Indus Valley Civilization Slide 33 The Land of India Subcontinent Himalaya Mountains Five nations of today: India, Pakistan in the NW, Nepal, Bhutan, and Bangladesh in NE 4/13/2015 48 Slide 34 Fertile River Valleys 2 river valleys: Ganges and Indus South is dry and hilly (Deccan Plateau) Eastern and Western coasts are lush, fertile plains. Monsoons Winter – cold, dry air from mts Summer – warm, wet air from the Arabian Sea 4/13/2015 49 Slide 35 Indus River Valley This civilization is still mysterious. The writing has not been translated. Slide 36 Indus River Civilization We do know the cities were sophisticated enough to have brick walls surrounding them for protection against flooding from the Indus River. Slide 37 India’s greatest advancements were in mathematics. Invented the zero and the symbol for it (another for infinity) They invented the number system we use today (1-9) Algebra Set algorithms Roman XXV -XIII Indian-Arabic XX IIIII - X III XX IIIII - X III X II 25 -13 12 Slide 38 Ancient India’s contributions Farmers raised cattle, made the cow sacred and could not be killed. Grew wheat, millet, barley, and rice Developed iron plow Developed a written language – Sanskitt Slide 39Ancient India’s religions Hinduism-Many gods, reincarnation(Birth-Death-Rebirth), and Dharma is their law Buddhism-Nirvana, 4 Noble Truths, No material possessions Slide 40 Indus Economy Just like the other river valley civilizations, the Indus river valley people were mostly farmers. Traditional economy They traded with the Chinese, with the Sumerians (Mesopotamians) and sometimes with the Egyptians. Slide 41 Ancient India rulers Dynasty – a series of rulers from the same family. 1st dynasty – Mauryan family Gupta dynasty Mahabbarata Slide 42 ANCIENT CHINA Great Wall Began 2000 B.C. Mandate of Heaven Dynasties Silk Astronomy Slide 43 Yellow River Civilization Ancient China was formed around the Yellow River. The color yellow symbolized “centrality”, as in China is the center of the world. Huang He (Yellow River) Slide 44 Chinese Accomplishments During the Zhou and Shang periods achievements in astronomy and bronze work learned to make silk create books developed a complex system of writing. Slide 45 The Chinese Language 3 examples: 1. Pictographs-Pictures that represent things. 2. Ideographs – join together two or more pictographs to form an idea. 3. Chinese Calligraphy Most characters in their language represent whole words and not sounds. Slide 46 Example of Chinese Calligraphy Slide 47 Ancient Chinese Social Classes Landowning aristocrats Peasant farmers Merchants Slide 48 E:Chinese Invented Silk Silk was exotic and expensive, so it was good for trading with the rest of the world. It is made from silk worms. Silk also makes “paper” Slide 49 Silk worm Slide 50 Ancient China Economy •Farming and trade •Traditional economy •First to develop terrace farming-Solution for farming on hillsides. People use Terraces or different levels for farming. •This method is still used today for rice and other crops. Chinese Rice Terrace dyn Slide 51 Dynasty Dynasty-A family or group that maintains power for generations Xia dynasty -1st dynasty Shang dynasty – built first Chinese cities 1750 B.C. – 1045 B.C. Slide 52 Confucius’ ideas Restore family order and social harmony: Fathers should display high moral values to inspire their families. Children should respect and obey their parents. All family members should be loyal to each other. Government: Moral leadership, not laws, brought order to China. A king should lead by example, inspiring good behavior in all of his subjects. The lower classes would learn by following the example of their superiors. Slide 53 Ancient Chinese Religion Believed in gods and spirits Had to keep them happy by offerings of food and other goods Angry gods and spirits may cause a poor harvest or armies to lose a battle Kings received power and wisdom from them Ancient China The Great Wall of China was built to keep the Mongols out. Many died building it, and their bodies were used as filler for it.