Ancient Greece
advertisement

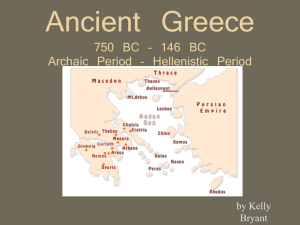
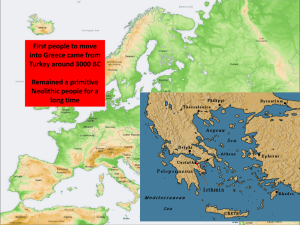
The Rise of Ancient Greece Lesson 1 •The rise of Greek Civilization •Lesson 2 •Religion, Philosophy, and the Arts Name________________ MOD______ Bell Ringer : What do you know about the land that makes up the country of Greece Objective • Understand the relationship between setting and development of civilizations • Examine early Greek history • Examine the development of democracy in Greece • Epic – A long poem that tells a story • Acropolis – A high rocky hill where early people used to build cities • City-State – A city with its own traditions, government and laws. Both city and independent state • Aristocrat – A member of a rich and powerful family • Tyrant – A ruler who takes power with the support of the middle and working class • Democracy – A form of government in which citizens govern themselves Alliteration a repetition of a beginning sound Write an alliteration describing the Minoan civilization “Minoan Men of the Mainland Mastered the Mediterranean” Captured in clay, the culture of Knossos and Crete create a constant account to cover. Greece’s Geographic Setting 169 1. What do we mean when we say the Ancient Greeks were all Islanders? We say that Ancient Greeks were islanders because even if they were living on the mainland they lived in places that were surrounded by mountains cutting them off to the rest of the land mass 2. Contrast how the Minoans and Mycenaean's spread their power? Minoans used their location to control the seas by trade. Mycenaean people controlled the sea by conquest. 3. List what happened during Greece’s Dark Ages? 172 The people were poor and no longer traded outside their country. They forgot how to write and kept traditions alive by word of mouth. Some people moved to more fertile areas to grow more crops. Bell Ringer • The fly buzzed past…… This is an example of a Simile, metaphor, personification, or onomatopoeia? Democracy in Greece 175 4. Why did some Athenians benefit more from democracy than others? Some Athenians benefited more from democracy than others because only a man over the age of 18 could participate fully in government. Bell Ringer • I nearly died laughing. This is an example of a Simile, metaphor, hyperbole, personification, or onomatopoeia? Religion, Philosophy and the Arts Objectives • Identify religious beliefs of ancient Greeks • Explore how the Greeks searched for knowledge about the world • Describe the relationship between the rise of democracy and the spread of new ideas in Greek city- states • Immortal – Someone or something that lives forever • Oracle – In Ancient Greece, a sacred site used to consult a god or goddess: Any priest that spoke to the gods • Philosopher – Someone who uses reason to understand the world • Tragedy – A type of drama that ends in disaster for the main character 1. How did Pericles strengthen democracy? Pericles made reforms that strengthened democracy such as paying salaries to officials, which meant that even poor citizens could hold office. Ancient Greek’s Religious Beliefs183 2. How did Greeks honor their gods? The Greeks honored their gods with the Olympian festival and games 3. How did Socrates challenge the values of the people of Athens? Socrates made people think about their important values and beliefs by questioning 4. What role did education and growing wealth play in the development of philosophy and the arts in Ancient Greece? Education was at the heart of philosophy and Arts in early Greece Chapter 7 • Lesson 1 • Daily life in Athens • Lesson 2 • Athens and Sparta • Lesson 3 • The spread of Greek Culture Objectives • Learn about public life in Athens • Find out how Athenians spent their time when they were at home • Understand how slavery operated in ancient Greece • AthensA city state in ancient Greece; the capitol of modern-day Greece • Agora – A public market and meeting place in an ancient Greek city • Vendor – A seller of goods • Slavery – A condition of being owned and forced to work for someone else 1. What kinds of food did Athenians eat ? Athenians ate simple meals. Bread fish olives, cheese and vegetables were common. Meat was eaten during religious festivals. 2. Describe the home life of the Athenians. Home life of Athenians was simple. Men and women living quarters were often separate. Their rooms were set up around an open courtyard hidden from the street. 3. What were the responsibilities of men in comparison to women in ancient Athens? Greek men spent their time in the agora discussing politics philosophy and current events. Women worked in the home and managed the slaves. 4. Describe the various roles slaves in Athens and those in the rest of ancient Greece? Slaves constructed buildings, forged weapons, cooked, and served food, tended to children, cleaned and wove cloth. Athens and Sparta • Objectives : • Learn how people lived in ancient Sparta • Discover some results of the Persian invasion of Greece Understand the conflicts that the Athenian empire faced • SpartaA city-state in ancient Greece • Helots – In ancient Sparta, the term for slaves who were owned by the state • Peloponnesian WarWar fought between Athens and Sparta in ancient Greece almost every other Greek city-state was involved in the war. • Plague – A wide spread disease • Blockade – An action taken to isolate the enemy and cut off its supply 1. What type of people were the Spartans? The Spartans were war like people who were in constant fear of a helot uprising 2. What was the Spartan’s attitude about trade? Spartans were against trade. They believed that mixing with outsiders was a threat to their way of life 3. Why did Greeks believe they had won their wars with Persia? The years following the Persian wars led to a golden era for Athens. 4. What did Greek city-states do to overcome oppression by Athens? Greek city-states joined together in the fight against Athenian oppression The Spread of Greek Culture Objectives • Learn how King Philip of Macedonia came to power and how Alexander the Great built his empire • Understand what role the conquests of Alexander the great played in Greek culture • AssassinateTo murder for political Reasons • Hellenistic – Describing Greek history and culture after the death of Alexander the Great • Alexander the Great – King of Macedonia conquered Persia and Egypt and invaded India Bell Ringer • Why didn’t Alexander the Great wipe out his enemies? • What did he do instead? 1. Why did King Philip think Greece would be easy to conquer? King Philip thought it would be easy to conquer Greece because he would use diplomacy and military strength. He had a strong army. 2. Why was Alexander so successful as a military leader? He watched his father. He learned from Aristotle and he was driven 3. Why was Alexandria in Egypt such an important city? Alexander was important because it was a center for trade, business and education. It had two ports and it lasts until this day.