Convention and Compromise
advertisement

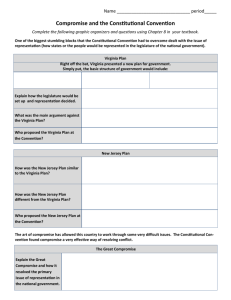
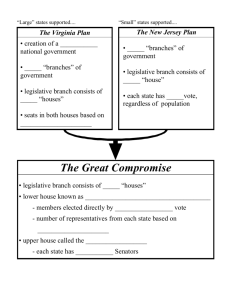
Convention and Compromise 7-2 Objectives • Learn how the Constitutional Convention broke the deadlock over the form the new government would take. • Learn how the delegates answered the question of representation. Economic Depression After the war the nation suffered an economic depression. Trade had slowed, money was in short supply, debts could not be paid. Shay’s Rebellion Times were extremely difficult for farmers. Led by Daniel Shays, in 1786 farmers closed courts stopping them from seizing farms. In January 1787, they attacked the federal arsenal at Springfield MA. The revolt was stopped by Massachusetts State Militia. Issue of Slavery Since one of the cornerstones of the Revolution was independence, the question of slavery began to rise. Soon the idea of manumission, freeing slaves, became widely discussed. A Call for Change James Madison Alexander Hamilton The Constitutional Convention Beginning May 5, 1787, 55 delegates met through the summer at Independence Hall in Philadelphia. James Madison’s notes give historians the most accurate account of the events of the convention. Organization of the Convention George Washington was chosen to lead the convention. A simple majority would decide issues. And more than half the states needed to be present (quorum) to conduct business. Proceedings were held without the public. The Virginia Plan James Madison Representation • In the Virginia Plan, representation in the Congress would be proportional to a state’s population. Greater the population, the more representatives. The New Jersey Plan William Paterson Equal Representation • The New Jersey Plan called for representation to be on an equal basis for all. The Great Compromise The Great or Connecticut Compromise was introduced by Roger Sherman of Connecticut. It called for a bicameral (two house) legislature. One based on the Virginia Plan, and one based on the New Jersey Plan. Three-Fifths Compromise Disagreements arose of how enslaved people should be counter. Southerners believed slaves should be counted as a whole for representation purposes. Northerners thought slaves should only be counted for taxation. A compromise counted slaves as three fifths of a person. Slave Trade Congress agreed not to interfere with the issue of slavery until 1808. Bill of Rights George Mason proposed that a Bill of Rights be adopted since no individual freedoms were spelled out in the Constitution. The measure failed. Approving the Constitution The Convention concluded its work on September 17, 1787. Nine states would have to ratify (approve) the Constitution for it to become the law of the land. Self Check Questions • Why was George Washington chosen as president of the convention? • Why is compromise so important in politics? • Compare and contrast the Virginia and New Jersey Plans. • What did the Great Compromise create?