File
advertisement

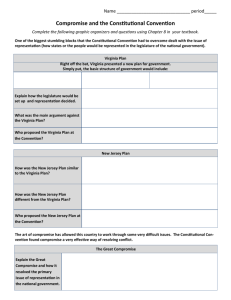
Creating A Constitution Constitution = a document stating the rules under which a government will operate Creating a Constitution Targets • I can determine the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation. • I can evaluate and debate why the Constitutional Convention decided to create an entirely new framework of government. • I can describe what shaped the outcome of the Constitutional Convention in 1787 • I can explain how compromises solved crises in the Constitutional Convention. Constitutional Convention of 1787 Virginia Plan • strong central government • Three branches of government: – Executive – Legislative – Judicial • Legislature divided into two houses • Representation based on population • Small states objected to the plan because the more people a state had, the more seats it would have. (which means more VOTES) Population of the 13 original states from the official census of 1790 • • • • • • • • • • • • • Connecticut Delaware Georgia Maryland Massachusetts New Hampshire New Jersey New York North Carolina Pennsylvania Rhode Island South Carolina Virginia 237,946 59,096 82,548 319,728 378,787 141,885 184,139 340,120 393,751 434,373 68,825 249,073 691,737 Constitutional Convention of 1787 New Jersey Plan • Single house (s) in Congress • Equal representation for each state • Expanded powers of Congress to raise money and regulate commerce Constitutional Convention of 1787 The Great Compromise Two houses of Congress • Lower house: House of Representatives – Representation based on population • Upper house: Senate – Each state had two seats Slave population-1790 census • • • • • • • • • • • • • Connecticut Delaware Georgia Maryland Massachusetts New Hampshire New Jersey New York North Carolina Pennsylvania Rhode Island South Carolina Virginia 237,946 59,096 82,548 319,728 378,787 141,885 184,139 340,120 393,751 434,373 68,825 249,073 691,737 2,764 8,887 29,264 103,036 0 158 11,423 21,324 100,572 3,737 948 107,094 292,627 1% 15% 35% 32% 0% <1% 6% 6% 25% <1% 1% 43% 42% 1790 Census Free African Americans = 1.5% Slave= 17.9% White population= 80% Constitutional Convention of 1787 The Three-Fifths Compromise • Southerners said that enslaved people should be counted in calculating how many representatives a state should have in Congress. Northerners objected because enslaved people were not allowed to vote • As a compromise each enslaved person was counted as three fifths of a person (for taxes and representation) Chart • Who proposed the plan? • What was included in the plan? • Who supported the plan? • Virginia Plan page 213-214 (read through The Great Compromise) • New Jersey Plan page 214 • Great Compromise page 214-215 (Terms of Compromise) Virginia Plan • • • • Proposed by Edmund Randolph Wanted a new, stronger central government James Madison was the main author Called for 3 separate branches – Legislative-congress – Executive – enforce laws – Judicial – interpret laws • Congress would have 2 parts – Lower house – Upper house • Representation based on population (more people a state had, the more seats it would get) • Supported by big states (like Virginia, Pennsylvania, Massachusetts) New Jersey Plan Introduced by William Paterson Single house of congress Equal representation for each state Expanded power of Congress to raise money and regulate trade Supported by smaller states Great Compromise Roger Sherman worked out the compromise Created 2 house Congress Lower house called House of Representatives-based on populationsupported by large states Upper house called Senate – each state has two seats (equal for all states)– supported by smaller states US Debt • • • • • • • 1791 $75,463,476.52 Lowest= 1834 $33,733.05 1850-1861 Stead decline Then Civil War-HUGE increase US Debt • • • • • • Thousand (3 zeros) Million (6 zeros) Billion (9 zeros) Trillion (12 zeros) Quadrillion (15 zeros) Quintillion (18 zeros) US Debt • • • • 1st time over billion 1862 1st time over trillion 1982 US Debt • National Debt Clock Who do we owe the $$$$ to?