CHAPTER 13 Reconstruction and the New South
advertisement

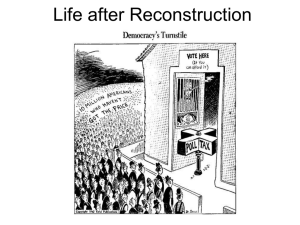
CHAPTER 13 Reconstruction and the New South SECTION 1 PRESIDENTIAL RECONSTRUCTION A. Old South Destroyed Mass destruction on the South, many buildings in ruins 2. Southern economy – 1. Tens of thousands of Confederate veterans looking for jobs and 4 million freed slaves were jobless and homeless a) b) “40 acres and a mule” B. Lincoln and Reconstruction What was Reconstruction? 1. Plan to rebuild the former Confederate states and reunite the nation 2. Beginning of Reconstruction Amnesty – Full pardon for a crime a) Lincoln would give amnesty to almost all southerners who would swear allegiance to U.S. 10-Percent Plan (Lincoln’s Plan) – Would allow states to rejoin the Union when 10 percent of its residents swore loyalty to U.S. b) Said nothing about African American rights except for outlawing slavery B. Lincoln and Reconstruction c) Wade-Davis Bill (July 1864) – Congress’ response to 10-Percent Plan States readmitted when a majority of white males in each state took loyalty oath Called for Confederate states to abolish slavery States to form new governments after readmitted Vetoed by Lincoln – Why? “With malice toward none, with charity for all… let us strive on… to bind up the nation’s wounds… to do all which may achieve… a just and lasting peace.” – Abraham Lincoln, Second Inaugural Address – March 4, 1865 B. Lincoln and Reconstruction 3. Lincoln’s assassination a) b) c) d) e) f) g) h) John Wilkes Booth April 14, 1865 Watching British play “Our American Cousin” at Ford’s Theatre Died the next morning Conspiracy – Johnson, Seward and Stanton also targeted Booth killed two weeks later Country mourns Lincoln’s death Why did Booth do it? Reaction? C. Johnson and Reconstruction 1. The New President – Andrew Johnson – a) b) Democrat, former slaveholder and senator from Tennessee Thought he would appeal to North and South 2. Immediately proved unpopular – racist, wouldn’t compromise 3. May 1865 – Johnson gives complete pardon to almost all former Confederates Would leave out more ex-Rebels than Lincoln C. Johnson and Reconstruction 4. Johnson’s readmission plan – much more lenient than people were expecting a) b) c) Each state had to nullify its acts of secession Refuse to pay Confederate government debts States had to abolish slavery No punishment, few restrictions 5. Confederate leaders take charge in the South 6. New state constitutions continued to discriminate against blacks 7. 13th Amendment (Jan. 1865) – CHAPTER 13 Reconstruction and the New South SECTION 2 CONGRESSIONAL RECONSTRUCTION A. Moderates vs. Radicals Moderates (most Republicans) 1. a) b) c) Wanted to reunite the Union Keep former Confederates out of government Favored giving African Americans some rights but not the right to vote 2. Radical Republicans a) Wanted to punish the South for the Civil War b) Give African Americans equal rights, including the right to vote c) Also wanted to give land to former slaves d) Frederick Douglass – B. Congress vs. Johnson Race Riots –Memphis and New Orleans 1. a) b) Furthered highlighted the divide between whites and blacks Moderates and Radical Republicans to join forces after 2. Freedmen’s Bureau a) b) Created to aid the millions of former slaves left homeless and hungry by the war Gave out food and clothing, served as an employment agency, set up hospitals and ran schools Originally approved for one year, Johnson vetoed the extension saying “it was never intended that the Freedmen should be fed, clothed, educated and sheltered by the United States” Veto was overridden by Congress C. Congress vs. Johnson 1. Civil Rights Act of 1866 (1st Civil Rights law) a) b) c) Said everyone born in the U.S. was a citizen with full civil rights Did not guarantee voting rights Vetoed by Johnson, but overridden by Congress C. Congress vs. Johnson 2. 14th Amendment (June 1866) a) Required states to give equal citizenship to African Americans and all people “born or naturalized in the United States” b) Denied states the right to deprive anyone of “life, liberty or property without due process of the law” c) Promised all citizens “equal protection of the laws” D. Radicals Come to Power 1. Election of 1866 and Reconstruction Acts a) b) c) d) Johnson called Radicals traitors People voted overwhelmingly Republican Radicals took control of Reconstruction Reconstruction Acts of 1867 – Ex-Confederate officials and army officers couldn’t vote States couldn’t be readmitted until the 14th Amendment was ratified and showed that African Americans had the right to vote Blacks right to vote, 14th and 15th Amendments Divided the former Confederate states into five military districts, new state Constitutions approved by Congress E. Presidential Impeachment Relationship btw Johnson and Congress bad 2. Tenure of Office Act (1867) – 1. Required Senate OK before President could fire a Cabinet member 3. February 1868 – Johnson fires Secretary of War Edwin Stanton without Senate approval 4. House impeaches Johnson Charged with violating the Tenure of Office Act, making “scandalous” speeches and bringing Congress into “disgrace” 5. Result – Johnson acquitted by only one vote despite weak case (35-19 in favor of conviction) Key: Red = both senators voting to acquit; Orange = senators split 1-1; Yellow = both senators voting to convict; Gray = unrepresented in the Senate in 1868; White = states were not yet admitted. F. More Issues 1. Radical Republicans too radical 2. Election of 1868 a) b) Gen. Ulysses S. Grant (R) vs. N.Y. Gov. Horatio Seymour (D) Result – Grant beats Seymour in popular vote, 214-80 in electoral vote 3. 15th Amendment What did it say? Citizens could not be denied right to vote “The right of citizens of the United States to vote shall not be denied or abridged by the United States or any state on account of race, color or previous condition of servitude” What groups were not included? CHAPTER 13 Reconstruction and the New South SECTION 3 RECONSTRUCTION IN THE SOUTH A. African American Activism After the passage of Congressional Reconstruction, African Americans hoped for further equality 2. Politics 1. a) b) African American delegates made up the largest percentage of Republicans in the South Hiram Revels – elected to U.S. Senate in Mississippi to fill Jefferson Davis’ seat, first African American More than 600 African Americans elected to state legislatures, 16 to Congress B. Reconstruction Govt. 1. 2. 3. 4. Carpetbaggers – insult given to northern Republicans who moved to the South Scalawags – insult given to southern whites who supported the Union during the Civil War and now supported Reconstruction Republican alliance – supporters of Reconstruction who wanted to take control from rich planters and rebuild the South What do you think was the bigger insult? Carpetbagger or scalawag? C. Ku Klux Klan 1. Greek for “Circle” and Scots- Gaelic “Brothers” 2. Secret group formed to prevent African Americans from voting 3. Nathan Bedford Forrest – “Grand Wizard” a) b) Klan tactics – murder, assault, harassment, burning houses, churches, schools, stealing cattle Forrest resigns in 1869 after KKK gets too violent C. Ku Klux Klan 4. Steps against the Klan a) b) c) d) African Americans started standing up to Klansmen and even burned their barns Enforcement Acts (1870-71) – empowered the federal government to combat terrorism with military force and to prosecute guilty individuals Democrats called them the Force Acts and said they threatened individual freedom Overall result D. Violence - lynching 1. Illegal seizure and execution of a suspected troublemaker or criminal 2. Often the victims were just someone who was in the wrong place at the wrong time D. Lynchings •Public and sadistic murders •1882-1968 – 4,730 •3,440 Black men and women •Intimidation – keep freedmen “in their place” E. Reconstruction Changes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Government involvement led to a decline in KKK violence Panic of 1873 – severe depression Panic means the end of the Republican Alliance Thousands of immigrants joined the Democratic party Civil Rights Act of 1875 – made it illegal for businesses that served the public such as hotel and trains to discriminate against African Americans Redeemers – Democratic supporters of whitecontrolled government, used violent tactics E. Reconstruction Changes 7. Election of 1876 a) Samuel Tilden (D-NY) vs. Rutherford B. Hayes (R-OH) b) Result – Tilden beat Hayes by 250,000 in popular vote Results in four states were disputed (3 were Southern states with split governments) A commission gave the election to Hayes by one electoral vote c) Compromise of 1877 – Democrats accepted Hayes as President in return for Republicans agreeing to pull remaining troops out of South d) Redeemers finished off their takeover of Southern government CHAPTER 13 Reconstruction and the New South SECTION 4 THE NEW SOUTH A. Changing Economies Sharecropping 1. a) b) c) d) Planters faced labor shortages, former slaves needed jobs What was sharecropping? System where a farmer worked a section of land in return for a share of the crop, shelter and tools Problem for sharecroppers – No income during the year until harvest time, keeps them in a cycle of debt Effect of sharecropping – No way out of poverty for sharecroppers, merchants turn huge profit A. Changing Economies 2. Industrial Growth 1. New South – belief that the South should manufacture its own goods to get out of poverty 2. Projects – Build factories, ironworks, textile mills and other businesses Railroads were rebuilt and integrated with the North 3. Effects – Factory owners and investors were the only ones to benefit Industrial workers worked for lower wages than those in North and were almost all white Some workers were stuck in same cycle of debt as sharecroppers B. Black Codes What were they? Laws passed after the Civil War that limited African Americans from achieving social, political and economic equality 2. Examples 3. Re-established white control over African American labor 4. Reaction 1. Today’s Essential Question What were Jim Crow laws and how did they affect America? C. Voting Restrictions 1. Poll tax 2. Property qualifications 3. Literacy test 4. Grandfather clause – groups exempted from a law if they met certain conditions before the law was passed Who would benefit from African Americans not voting? Why? How the colored voter is allowed to cast his ballot in a state where Democrats control the election. (1899) D. Jim Crow Laws Segregation – separation of the races 2. Jim Crow laws – A system of legal segregation that further degraded African Americans 3. Places that were segregated – schools, parks, public buildings, hospitals, transportation, movie theaters 1. Black facilities were always inferior 4. Second class citizens, legitimized anti-black racism Belief – blacks were inferior and should be kept separate Images of Jim Crow - Minstrel Shows Images of Jim Crow - Minstrel Shows Images of Jim Crow Images of Jim Crow Images of Jim Crow Images of Jim Crow Images of Jim Crow What images in the cartoon stand out to you? Was this an accurate portrayal of life in the South at the time? Etiquette norms under Jim Crow A Black male could not offer his hand to a White male – and definitely not to a female Blacks and Whites could not eat together A Black male could not light the cigarette of a White female No PDAs Whites did not use courtesy titles of respect (Mr., Mrs., Miss, Sir, Ma’am, etc.) when referring to Blacks A Black person who rode in a car driven by a white person – rode in the back White motorists had right of way From: Jim Crow Guide Never assert or intimate that a White person is lying Never impute [give away] dishonorable intentions to a White person Never suggest that a White person is from an inferior class Never lay claim to, or demonstrate, superior knowledge Never curse or laugh at a White person Never comment on the appearance of a White female Laws No black barber shall serve white girls or women (GA) Separate buildings/wards for the blind (LA) Buses: separate waiting rooms and ticket windows (ALA) Custody of a white child should not fall to a black adult (SC) Education: separate Laws Libraries: separate (NC) Militia: white and black separately enrolled Nurses: white female nurses could not care for black males (ALA) Prisons: separate sleeping and eating Teaching- fined for teaching in an integrated school (OK) Serving of wine and beer - separate http://www.jimcrowhistory.org/geography/geography.htm Jim Crow quotes "In this perilous world, if a black boy wanted to live a halfway normal life and die a natural death he had to learn early the art of how to get along with white folks." - Benjamin Mays, recalling his childhood in rural South Carolina "My object is to teach the North, the young North, what it has never known—the awful suffering of the white man during the dreadful Reconstruction period. I believe that Almighty God anointed the white men of the South by their suffering during that time immediately after the Civil War to demonstrate to the world that the white man must and shall be supreme." - Thomas Dixon, Jr., author of The Clansman, later became a movie called The Birth of a Nation Questions How did Jim Crow laws affect America? What methods did whites use to keep African Americans separate and inferior? How did African Americans try to fight against segregation? Why were African Americans unable to resist segregation? E. Reinforcing Jim Crow Civil Rights Case of 1883 – 1. Overturned Civil Rights Act of 1875 Supreme Court ruled that 14th Amendment did not prevent private businesses from discriminating a) b) 2. Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) – a) “separate but equal” facilities did not violate 14th Amendment b) c) “We cannot say that a law which authorizes or even requires the separation of the two races in public conveyances is unreasonable.” Henry Brown – Blacks assume they are inferior John Marshall Harlan – Constitution is color-blind F. African American Response 1. Booker T. Washington: economic independence was the key to political and social equality Many African Americans of the time disliked Washington, they thought he gave in to whites too often 2. Ida B. Wells: focused on lynchings and urged African Americans to leave the south G. African American Response 3. WEB DuBois – Niagara Falls – 1905 Booker T. Washington’s greatest black critic a) b) c) denounced all political, civil, and economic discrimination vowed never to accept inferiority formed a nucleus group who joined with concerned whites for a national conference on the “Negro question” H. NAACP 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. National Association for the Advancement of Colored People Formed in 1909 by an interracial group led by W.E.B. DuBois By 1914 – there were 50 branches Worked to achieve equality through the courts 1st victory: Supreme Court declared grandfather clauses unconstitutional