Objective: To examine the causes of America’s
advertisement
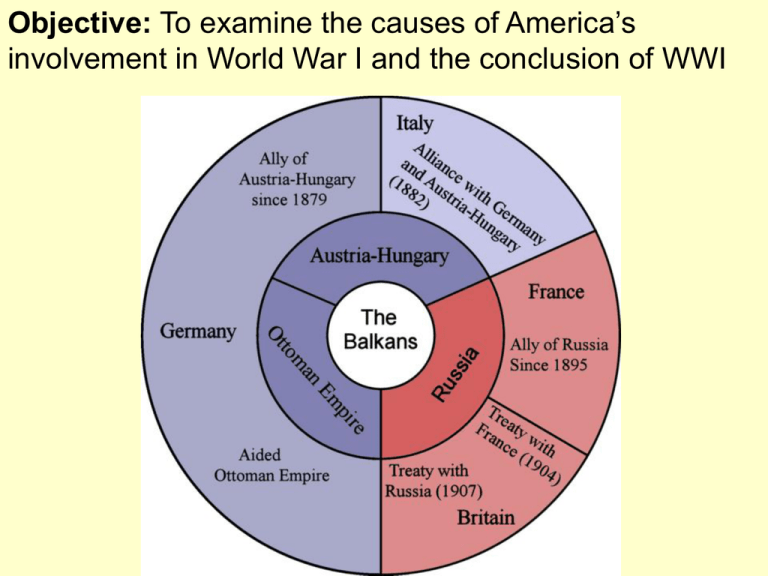
Objective: To examine the causes of America’s involvement in World War I and the conclusion of WWI American Neutrality Officially, the U.S. was a neutral country. However, we traded food, weapons, oil, steel, and other goods far more with the Allied Powers than with the Central Powers. Both the Allied Powers and Central powers used propaganda (one sided information used to persuade) in order to support their cause by making their enemies seem savage. Freedom of the Seas The U.S., as a neutral nation, claimed the right to trade with either side in the war. However, Britain and Germany set up blockades around the British and German coasts. German submarines, called U-boats, torpedoed enemy ships and neutral ships trading with the enemy. A German U-boat Torpedoes a Steamer, circa 1916 · In 1915, a German submarine (U-Boat) torpedoed the Lusitania, a British passenger ship, killing approximately 1,200 people, including 128 Americans. · Americans were infuriated with the destruction of the Lusitania. Moving Toward War Zimmermann telegram: – secret message from Germany to Mexico urging Mexico to attack the U.S. if the U.S. declared war on Germany – Germany promised to help Mexico regain land it lost to the U.S. in the Mexican War. * The U.S. declared war on the Central Powers in 1917. “SWOOPING IN FROM THE WEST” • Russia’s withdrawal from WWI: Russia signs Treaty of Brest-Litovsk w/Germany • This led to increased German troops in Western Front • By late May of 1918 German troops were weakened from their push to claim Paris • Allies sensed weakness, US helped with arrival of 2 million troops • Central Powers began to crumbleGerman soldiers turned on Kaiser Wilhelm II Peace at Last At 11 a.m. on November 11, 1918, Germany agreed to an armistice, ending World War I. * Approximately 13 million people died and 20 million were wounded in the war. Mandate System • During World War I, Great Britain and France agreed to divide large portions of the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East between themselves. • After the war, the “mandate system” gave Great Britain and France control over the lands that became: • Iraq, Transjordan, and Palestine (British controlled) • Syria and Lebanon (French controlled). • The division of the Ottoman Empire through the mandate system planted the seeds for future conflicts in the Middle East Highlight – Britain Highlight – France







