HISTORY-OF-ARCH-20
advertisement
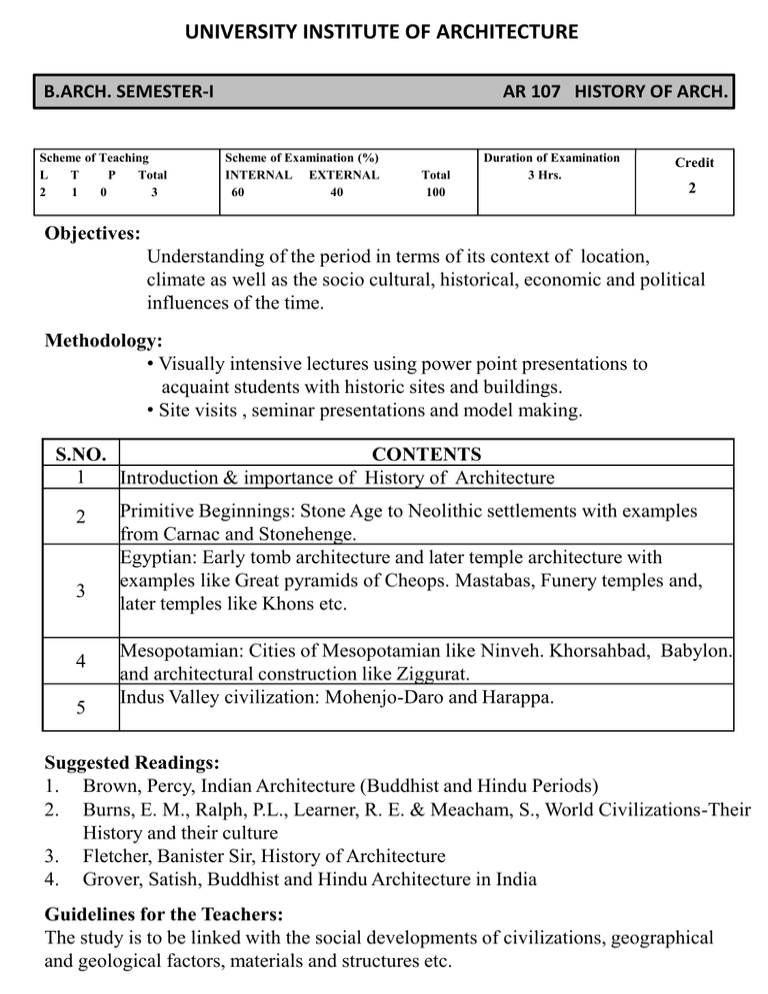
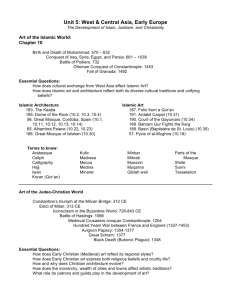
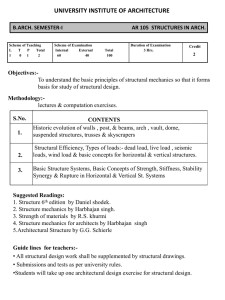
UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF ARCHITECTURE B.ARCH. SEMESTER-I Scheme of Teaching L T P Total 2 1 0 3 AR 107 HISTORY OF ARCH. Scheme of Examination (%) INTERNAL EXTERNAL 60 40 Total 100 Duration of Examination 3 Hrs. Credit 2 Objectives: Understanding of the period in terms of its context of location, climate as well as the socio cultural, historical, economic and political influences of the time. Methodology: • Visually intensive lectures using power point presentations to acquaint students with historic sites and buildings. • Site visits , seminar presentations and model making. S.NO. CONTENTS 1 Introduction & importance of History of Architecture 2 3 4 5 Primitive Beginnings: Stone Age to Neolithic settlements with examples from Carnac and Stonehenge. Egyptian: Early tomb architecture and later temple architecture with examples like Great pyramids of Cheops. Mastabas, Funery temples and, later temples like Khons etc. Mesopotamian: Cities of Mesopotamian like Ninveh. Khorsahbad, Babylon. and architectural construction like Ziggurat. Indus Valley civilization: Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa. Suggested Readings: 1. Brown, Percy, Indian Architecture (Buddhist and Hindu Periods) 2. Burns, E. M., Ralph, P.L., Learner, R. E. & Meacham, S., World Civilizations-Their History and their culture 3. Fletcher, Banister Sir, History of Architecture 4. Grover, Satish, Buddhist and Hindu Architecture in India Guidelines for the Teachers: The study is to be linked with the social developments of civilizations, geographical and geological factors, materials and structures etc. UNIVERSITY INSTITUTE OF ARCHITECTURE B.ARCH. SEMESTER-III Scheme of Teaching L T P Total 2 1 0 3 AR 207 HISTORY OF ARCH. Scheme of Examination (%) INTERNAL EXTERNAL 60 40 Total 100 Duration of Examination 3 Hrs. Credit 2 Objectives:Study of the building ‘types’ and the development of architectural form and character based on the developments in construction and technology. Methodology: • Visually intensive lectures using power point presentations to acquaint students with historic sites and buildings. • Site visits and seminar presentations and model making S.NO. CONTENTS 1 Sources of Islamic Architecture in India 2 The Delhi Imperial Style: Slave, Khalji, Tughlaq, Sayyid, &Lodhi Dynasties. 3 Provincial Architecture: Punjab, Bengal, Gujrat,, Mandu , Chanderi, Jaunpur & Ahmedabad Forts & Tombs: Qutb Shahi Forts , Tombs of Golconda , Architecture of Vijay Nagar, Bijapur & Bidar Mughal Architecture: Babur, Humayun,, Akbar, Jahangir and Shahjahan & Aurangzeb. Sher Shah’s mosque , Fatehpur Sikri & Taj Mahal Architecture of Mughal to Modern Buildings: Lucknow, Agra, Varanasi, Jaipur, Udaipur, & Architecture in Victorian period 4 5 6 Suggested Books: 1. Grover, S., “The Architecture of India: Islamic”, Vikas Publishing House. 1981 2. Parihar, S., “Some Aspects of Indo-Islamic Architecture”, Abhinav Publishers. 1999 3. Brown, Percy, Indian Architecture (Islamic Periods) 4. Burns, E. M., Ralph, P.L., Learner, R. E. & Meacham, S., World CivilizationsTheir History and their culture 5. Fletcher Banister Sir, History of Architecture 6. Maheshwari, Sanjeev & Garg, Rajeev, Ancient Indian Architecture (From Blossom to Boom) 7. Bhartiya kala Parkashan ,Encyclopeadia of Indian Architecture ( islamic)- Vol IV Guidelines for the Teachers: The study is also to be linked with political, geographical factors, materials and structures etc.