European Exploration & Conquest 1450-1650
advertisement

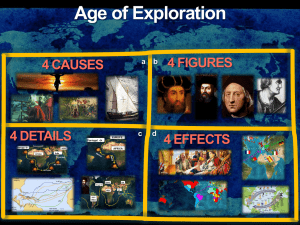
European Exploration & Conquest 1450-1650 Chapter 15 Key Concepts From ancient to medieval times, there was a widespread and thriving network of global trade among East Asia, Southeast Asia, the Mediterranean, the Middle East and Africa. This network was transformed by the intrusion of new groups of Europeans. The Portuguese and the Dutch competed first with Muslim merchants and then with each other in Asia. They joined the British and French in the exploration and colonization of the Americas. Key Concepts Europeans had a variety of motives as well as certain technological advantages that prompted the expansion of their trade in Asia and their exploration of the New World. “Gold, God and Glory” were not only motivators of exploration, but also led Europeans to colonize in ways that fostered economic development and Christianiztion. Key Concepts Among the consequences of the encounter of the Old World with the New was a rapid and thorough decimation of the native population, the transformation of their economic and religious lives, and an enormous expansion of the already existing African slave trade. The Columbian exchange of people, crops and animals led to radical changes in agriculture and diets, as well as in values and technology. As gold and silver infused the European economy, inflation benefited the middle classes while hurting the poor and those on fixed incomes. The increasing wealth of the middle class was an important change in the social structure. Intellectual life saw the introduction of new ideas like skepticism and cultural relativism as well as new forms of racism. AP Tip For those of you interested in world history, the first section of this chapter is very rich with a detailed exploration of centers of wealth and trade around the globe. Although most of this material would not appear on an AP European history exam, it is important to understand it for background and the long-term legacy of colonalism. Pay particular attention to those sections that deal with Europe. World Trade Before the Age of Exploration Global economic network Silk Road – China Silk & porcelains Indian Ocean – Roman Empire Indian jewels; peppers, cloves, textiles, African slaves, gold, ivory Malacca – Malaysia connected Pacific Ocean and Indian Ocean Multinational/Multicultural Euro contribution minimal until mid 1500s China, India, Ottoman Turkey, Safavid Persia and Egypt held dominant roles World Trade Before the Age of Exploration Venice & Genoa During the Medieval period Venice became very wealthy/powerful Excellent navy Dominated the Mediterranean and Asian trade Slaves Luxury goods silks Spices Played important role in exploration of the New World Management of commercial enterprises – Sugar Plantations Decline of dominance Ottomans overtook trade markets Portuguese & Dutch challenges on the other side Atlantic rather than the Mediterranean routes Causes of European Exploration Mid-15thC Recuperation Black Death Population growth Gold Demand for spices & luxury goods More gold/silver sources to pay for goods New routes – bypass Ottoman held Istanbul Direct access to Asia Christian Fervor Victory over last Muslim kingdom in Spain 1492 Convert non-Christians – Asia & Americas Glory Conquest/adventure Renaissance curiosity Thirst for knowledge Natural history Geography cosmology Causes of European Exploration Technology Advances borrowed from the East Caravel – replaced the galley ship Navigational tools Astrolabe Magnetic compass Military weapons Cannons – made exploration & conquest possible Ptolemy’s Geography Inaccurate Encouraged the idea that sailing west from Eur. to Asia was possible Empires Portugal Prince Henry - The Navigator Early voyages of the west coast of Africa Conquered the Arab city of Ceuta – Morocco Initiated Eur. exploration & colonization Madeira Azores Mauritania – NW Africa Cape of Good Hope Bartholomew Diaz 1487 Vasco da Gama 1497 Continued on to Calicut – India Returned laden with spices & textiles Trading Posts estab. India Violent conflicts with rulers Alfonso de Albuquerque defeated Malacca, Goa, and other trading centers – laid foundation of Portuguese empire in Asia Brazil Pedro Alvares Cabral Sighted Brazil - 1500 Rich mineral resources & lucrative sugar plantations 2 million African slaves Most important Portuguese colony Empires Spain Christopher Columbus Genoese – sailed for Spain, Ferdinand & Isabella Hero or villain Experienced in seafaring Trade and circumventing other countries Devote Christian Missionary vision Report to Spain Conversion of natives Gold & silver Believed he reached Asia (until dying day) Contribution had extraordinary impact on world history Empires Spain cont. Columbus Conquest and colonization 2nd voyage Enslaved the people of Hispaniola Forerunner of encomienda system Inept at governing – led to royal control of his conquered areas The Treaty of Tordesillas 1494 Made by Pope Alexander VI Divided New World Spain – everything west Portugal – everything east Imaginary line 370 leagues west of the Cape Verdes Islands Ferdinand Magellan Commissioned by Charles V – further voyages when no gold/silver found in Caribbean Magellan 1st to circumnavigate the globe Route to Asia via the Atlantic Horrific 3 yr voyage Disasters at sea Starvation Mutinies Death of Magellan in the Philippines Demonstrated the vastness of the Pacific Led Spain to abandon its competition win Portugal for the Asian spice trade Empires Spain cont. Ferdinand Magellan Commissioned by Charles V – further voyages when no gold/silver found in Caribbean Magellan 1st to circumnavigate the globe Route to Asia via the Atlantic Horrific 3 yr voyage Disasters at sea Starvation Mutinies Death of Magellan in the Philippines Demonstrated the vastness of the Pacific Led Spain to abandon its competition win Portugal for the Asian spice trade Empires Spain cont. Hernando Cortes’ Conqueror - Mexico Few men – horses & cannons Fortuitous elements beyond his control Dissention w/n the Aztec empire Demoralized population Weakened leadership Aztec Empire – large/wealthy/sophisticated Montezuma & advisors made decisions logical for their culture – paved the way for Spanish victory Francisco Pizarro Incan conquest – Peru 1531 Incans known for engineering & construction Facing internal dissention Executed leader Atahualpa Took until 1570 to gain control Empires Spain cont. New World colonies 200,000 Spaniards immigrated in the 16thC soldiers & drifters Estab large agricultural/ranching estates Sugar plantations Silver mines – Bolivia & Mexico Encomienda system - forced labor Rapid decline of native pop Brutal exploitation Led to the death of 1000s Exposure to Eur disease Land converted from subsistence to cash crops Bartolome’ de Las Casas Empathized with natives – lamented cruetly Argued for the rights of natives Charles V responded by abolishing the worst abuses Empires Holland – Dutch Dominated world maritime trade – 2nd ½ of 17thC Financial center since 16thC 1602 estab Dutch East India Company Expanded their spice markets Ceylon Indonesian archipelago Monopoly – highly profitable Asian spice trade New World trade Briefly held a colony - New York France & England Less dramatic Jon Cabot Genoese Explored Newfoundland & New England for British Jacques Cartier Explored Quebec for France 1st permanent settlement for France in New World