File
advertisement

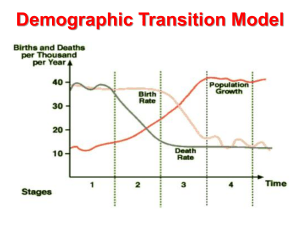
Geography Revision Notes Mr. Kelly Topic: Population November 2012 Lesson Objectives Title: Population Dynamics Today 1. 2. 3. we are going to learn; History of human population growth Reasons why population growth changes Population definitions Thoughts on the video 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What does he predict will happen to future population growth? Why does he think this will happen? What can be done to change this? Why is the highest population growth in the poorest countries? What impacts does having a larger population have on the world? Population distribution and density Population distribution is how people are spread across any given area. There are many factors that affect population distribution such as physical and human factors such as climate, access to jobs, good natural resources and flat low lying land. Population Density Population density is the number of people per square kilometre (km²). Examples 1. 2. 3. Europe 51 people per km² Australia 2 people per km² Singapore 7,148 people per km² High Population Density Website about Japanhttp://www.international.ucla.edu/eas/japan/geography/density1.htm Low Population Density Note! Be able to locate countries on a map which have a high and low population density Be able to explain why these areas have a low or high population density Be able to discuss the problems of low and high population density Important Population Definitions Birth rate- The average number of births per 1,000 people Death rate- The average number of deaths per 1,000 people Life expectancy- The average age you are expected to live in the country you were born in Infant mortality- Is the average number of children per 1,000 born alive but die before the age of one. Natural Increase- When the birth rate is more than the death rate Natural decrease- When the death rate is more than the birth rate Optimal population- When there is a good population level for the natural resources and land of an area Important definitions 1. Dependents are those who rely upon others of working age, e.g. children and old people 2. Economically active are those people who work to receive money, normally people who pay taxes and are between 18-70 Census Demographic information about a country is collected normally every 5 or10 years by using a census. A census is a national record that collects information about everyone in the country during the time of the census. Examples of information collected are; age, gender, education, illnesses and commuter habits. Key point about population How to calculate the natural population growth rate of a country. Subtract the death rate from the birth rate and this will give you the population growth rate per 1,000. E.g. Malta Birth rate= 10.3 Death rate= 8.3 Therefore population growth is 2.0 per 1000 people. Demographic Transition Model Now we will examine the key stages of the Demographic Transition Model (DTM) http://www.ngflcymru.org.uk/vtc/demographic_trans/eng/Intro duction/default.htm Demographic Transition Model (DTM) This shows how changes in birth and death rates can affect population growth These five stages are linked to economic growth which means normally you can determine the population of a country depending on the economic growth of that country. Important things to consider What does the DTM not take into account? Migration Immigration- People moving INTO a country Emigration- People moving OUT of a country Time LEDC’s are developing faster so the time period between each stage may be shorter Important! Remember if you are talking about a country be able to say what stage of the DTM it is in. Test 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What stage of the DTM are the following countries in and why? UAE USA Kenya Brazil Japan Homework 1. Answer questions 3,4+5 on P. 16 of “The New Wider World workbook”. 2. Answer question 1c on P. 133 of “New Key Geography” Census Demographic information about a country is collected normally every 5 or10 years by using a census. A census is a national record that collects information about everyone in the country during the time of the census. Examples of information collected are; age, gender, education, illnesses and commuter habits. Important definitions 1. 2. 3. 4. Life Expectancy is the average number of years a person can expect to live Infant mortality is the average number of children per 1,000 born alive, who die before the age of one year Dependents are those who rely upon others of working age Economically active are those people who work to receive money Population Pyramids Continued…. 1. 2. 3. 4. Population Pyramids show; The population of a country or region divided into five year age groups. The percentage of the total population in each of these age groups The percentage of males and females in each age group Changes in birth and death rate for each age group 5. 6. 7. Life expectancy and infant mortality The proportion of elderly and young people who are dependent on those of a working age- “The economically active group” The effects of people migrating into and out of a country Recap! 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Population density Population distribution Factors that affect population distribution (positive and negative) Areas which are sparsely population and areas which are densely populated Population growth throughout history Population change 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. Demographic transition model Understanding and explaining the demographic transition model Population definitions Census What population pyramids show Please go back over your work or ask me at the end of class if you are still unsure of any of these points! Examples of Population Pyramids Guess the country Homework Draw diagram A p. 8 Answer questions 1-9 on p. 16 Important points to consider 1. 2. Taken from the US Census Bureau! Look beyond census numbers in order to decipher problems in data collection. This involves knowing the history of a country and examining the extent to which past events have affected the population structure. The effects of war in 1963 on males ages 2024, might be apparent in a 2013 population, among males ages 70-74, for example. In many Persian Gulf States, for example, a large proportion of the labour force consists of international migrants, who are predominantly male. Because of this particular feature in Persian Gulf countries, the base population age-sex structures for these countries necessarily include a large maledominant working-age population. A good geographer would see this graph and be able to analyse this by breaking down the key points of this graph. ALWAYS look for possible reasons and back up why you think this is so Examples of Population Pyramids Changing Population http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sc4HxPxNr Z0 Changing Population Structures Too many young people Need more schools Need more food resources for growing population Better health care for the youth Need more recreational facilities, parks, cinemas, sports facilities Better shopping facilities Too many old people Better health care needed for elderly Need more retirement homes Need to ensure there is enough economically active people to look after the dependents. Need more social services for the old people. Population Overpopulation Under population Optimum population Overpopulation If the number of people living in an area is greater than the resources available to support that population, it is overpopulated. E.g. Nigeria in Africa Picture Problems of overpopulation 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Not enough housing Increased water and air pollution Shortage of food and water High crime rates Not enough health care and education Increased traffic Under population If the number of people living in an area is less than is needed to make full use of the resources available then that area can be described as under populated. E.g. Australia has many resources but it is not using them fully. Problems of under population 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Low birth rate Not enough workers to support the growing economy Need to invite people from other countries to help develop the economy. E.g. Australia taking in skilled people from Ireland Less exports as products are not made due to lack of work force Not enough economically active people to support the dependents. Homework 1. 2. Describe some of the impacts of an increasing world population and draw diagram E page 11. Explain how population pyramids can help to plan to the future Optimum Population This is where there is an adequate supply of resources to meet the needs of the population. E.g Germany. China’s one child policy The Chinese government realised in the 1970’s that it was facing a serious issue of over population. In 1979 to try to combat this they introduced population control measures. The main policy introduced was the one child policy which limited one child per family. Main points of policy 1. 2. 3. 4. Couples had to seek permission before marrying and had to seek permission again before having a child Those who followed the policy were given free education, priority housing and family benefits Those who did not follow the policy were not given any benefits and were fined heavily. Women who became pregnant a second time were forced to have an abortion. Successes of the policy By the late 1990’s China estimated that its population is 230 million less because of the ‘one child policy’. The birth rate decreased dramatically from 31 births per 1000 to 19 births per 1000. This has helped to address the severe issues of overpopulation as mentioned previously. Modern changes in the policy However, as mentioned in previous classes every action has a consequence and as geographers it is your job to both notice and comment on these consequences. Consequences of the one child policy The desire for a boy is part of Chinese culture so as a result of the one child policy boys were preferred over girls. The male population increased as a result of more boys, the female population consequently decreased as girls were often abandoned, killed or sold to baby-traffickers. Think about this action on the present day population! 1. 2. 3. Today there is a clear imbalance between the genders as there are more males than females in the 20-35 age group. To help address this the Chinese government changed the policy. Allowing all families in rural areas to have two children Offering women a wider choice in methods of contraception Allowing the option of voluntary family planning in 300 trial districts. IGCSE Question For a country that you have studied, describe policies used by the government to reduce rates of population growth. China’s ageing population An ageing population means that the population is getting older with more and more old people. What would this look like in a population pyramid? This is because the life expectancy of China is increasing. Life expectancy was 40 years old in 1950 it is now over 80 years old https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/theworld-factbook/rankorder/2102rank.html 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. As the population is getting older this means there will be a large amount of elderly dependents. This has problems because; Need money for pensions as there is none set aside strain on working population/higher taxation; need for more money to be spent on care homes/health, more doctors, nurses and medicines needed for old people care/facilities for elderly, etc.; not enough workers for key positions; difficult to defend country; need to attract foreign workers; services for young under utilised/uneconomical, etc. Old age dependency ratio This is the measure of the number of retired people per 100 people in the economically active group. Eg. 20 old people per 100 working people is good 40 old people per 100 working people is bad as this means that the working people have to take care of more elderly people. Russia’s birth incentives Russia’s population is in decline, each year the population is falling by about 700,000. This is threatening economic growth as there will soon not be enough people who are economically active to support the dependents of the country. To address this, Russian President Vladimir Putin offered birth incentives. Russia’s birth incentive policies 1. 2. 3. 4. Women with large families had the title “hero mother” and were given medals and expensive gifts. Monthly child support payments were doubled for the first child Having a second baby received a bonus payment. The state will give women who give up work to have a baby 40% of what they used to earn. Homework 1. 2. 3. 4. Complete population pyramid worksheet China’s one child policy has been highly debated, discuss some of the present day problems that China would experience if this policy wasn’t introduced. Is money the only way to increase population? Think of why money might not be successful in encouraging women to have children. Why is it important to have a balanced population of gender and age? (Min half page answer) Summary 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Population distribution Population density Factors that affect population density and distribution Population growth throughout history and the future population trends Natural increase Birth rate Death rate Infant mortality Life expectancy Dependents Economically active The demographic transition model and each of the 5 stages Continued 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. Population pyramids Changing population structures Population trends Problems of old/young population Problems of under/over population China’s one child policy China’s ageing population Old age dependency ratio Russia’s birth incentives IGCSE Questions Revise population questions from past exam papers. Be aware that questions change every year but you know the basic information you just have to adopt it to be a good geographer and answer the question to the best of your ability using all the information I taught you.