EgYptian Civilization
advertisement

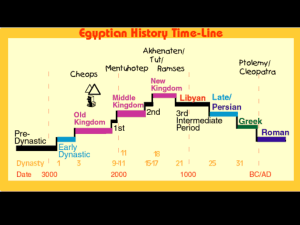
“The Gift of the Nile” EGYPTIAN CIVILIZATION LESSON ESSENTIAL QUESTION What were the main features and acheivements of Egypt’s three kingdoms? GRAPHIC ORGANIZER Old Kingdom Middle Kingdom New Kingdom THE IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY The Nile is the longest river in the world flowing northward from the heart of Africa to the Mediterranean Sea The Nile splits into 2 major branches before reaching the Mediterranean, forming a triangular territory, also known as a delta The Nile Delta is also called Lower Egypt Egypt’s important cities developed The land upstream, to the south, is called Upper Egypt THE IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (CONT) The most important feature of the Nile is its yearly flooding Very predictable Left mud and silt creating an area of rich soil – “Black Land” Served as a unifying factor in Egypt Fastest way to travel Made transportation and communication easier THE IMPACT OF GEOGRAPHY (CONT) Egypt was blessed by natural barriers which lessened the threat of invasion Deserts to the east and west Red Sea to the East Rapids on the southern part of the Nile Mediterranean Sea to the North The regularity of the floods and relative isolation of the Egyptians created a feeling of security and changelessness Confidence in stability and continuity THINK-PAIR-SHARE Explain how flooding patterns of rivers in Egypt and Mesopotamia caused the two civilizations to develop differently. Flooding patterns were regular in Egypt, leading to a feeling of stability. The flooding in Mesopotamia was unpredictable, leading to a belief that the world was at the mercy of harsh and unreliable gods THE IMPORTANCE OF RELIGION Religion helped provide a sense of security polytheistic 2 groups of gods had special importance Sun god- Atum/Re Sun was worshipped as the source of life Ruler was called Son of Re, the sun god in earthly from Land Gods- Osiris and Isis Osiris Led Egyptians to place dead in tombs to await rebirth Isis- important role as a symbol of rebirth symbolized new life brought by the floods each year THE COURSE OF EGYPTIAN HISTORY Historians have divided Egyptian history into three major periods Old Kingdom Middle Kingdom New Kingdom These periods were characterized by long-term stability marked by strong leadership, freedom from invasion, the building of temples and pyramids, and considerable intellectual and cultural activity Between these periods were intermediate periods, periods of chaos and invasion THE COURSE OF EGYPTIAN HISTORY (CONT) Begins around 3100 BC King Menes United the villages of Upper and Lower Egypt into a single kingdom and created the first dynasty- a family of rulers whose right to rule is passed on within the family THE OLD KINGDOM 2700-2200 BC Age of prosperity and splendor Egyptian pharaohs (rulers) possessed absolute powercomplete unlimited power to rule their people However, did have help in ruling Bureaucracy Administrative organization with officials and regular procedures Vizier- “steward of the whole land” Directly responsible to the pharoah In charge of the government bureaucracy THE OLD KINGDOM (CONT) Tombs were well prepared for their residents Egyptians believed humans had two bodies, one physical and one spiritual (ka) Stocked with all necessities for life Believed even though the physical body was dead, the ka could return and continue its life as long as the physical body was properly preserved and tomb was furnished with objects of regular life Mummification- slowly drying a dead body to prevent it from rotting THE PYRAMIDS Building of pyramids occurred during the Old Kingdom Built as part of a larger complex of buildings dedicated to the dead Large pyramid- pharaoh’s burial Smaller pyramids- pharaoh’s family Mastabas ( rectangular structures with flat roofs)pharaoh’s officials THE GREAT PYRAMID Built under King Khufu at Giza around 2540 BC Took more than 20 years to complete Built with incredible precision “Guarded” by the Great Sphinx 240 feet long, 66 feet high Face thought to be of Khafre, Khufu’s son Largest pyramid ever built Could be seen for miles and served to remind people of the glory, might, and wealth of the ruler THE MIDDLE KINGDOM 2050-1652 Egypt began a period of expansion Conquered Nubia; Sent armies to Palestine and Syria Sent traders to Kush, Syria, Mesopotamia, and Crete New concern of the pharaohs for the people Pharaohs portrayed as the shepherd of his people Expected to build public works and provide for the public welfare Pharaohs undertook many helpful projects Drained swampland in Nile Delta Provided thousands of acres of new farmland Dug canal linking Nile River to Red Sea Aided transportation and trade THE MIDDLE KINGDOM (CONT) The Middle Kingdom ended around 1652 BC, when it was invaded by the Hyskos Western Asia Used horse-drawn war chariots Egyptians fought from donkey cart Egyptians learned a great deal from the Hyskos Learned to use bronze in making farm tools and weapons Mastered many of the military skills of the Hyskos Horse-drawn chariots THE NEW KINGDOM 1567-1085 BC Egypt created an empire and became the most powerful state in Southwest Asia Massive wealth boosted the power of the New Kingdom Pharaohs Showed wealth by building new temples Hatshepsut-first woman pharaoh THE NEW KINGDOM (CONT) Amenhotep IV introduced the worship of Aton, god of the sun disk as the sole god Changed his name to Akhenaton (“it is well with Aton) Closed temples of other gods Tutankhamen (Akhenaton’s son) restored the old gods Become pharaoh at age of 9 and ruled for 10 years before his death THE NEW KINGDOM (CONT) Akhenaton’s religious revolution caused upheavals that led to a loss of Egypt’s empire Under Ramses II (1279-1213 BC), the Egyptians regained control of Palestine but were unable to reestablish the borders of their earlier empire New invasions in the thirteenth century BC by the “Sea People” drove the Egyptians back within their old frontier, and ended the Egyptian Empire The New Kingdom collapsed in 1085 BC Egypt was dominated by Libyans, Nubians, Persians, and Macedonians for the next 1000 years THINK-PAIR-SHARE What were the major differences between the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom? Old- divine rulers, built pyramids Middle- pharaohs concerned about people, expanded New- militaristic, created an empire, religious upheavals READING ACTIVITY Read the Section titled Society in Ancient Egypt. After reading make a graphic organizer to list the different social classes and the contributions each made to society. DAILY LIFE IN ANCIENT EGYPT Very positive attitude Married young and monogamous (one wife) Arranged marriages Purpose was to produce children, especially sons The husband was master of the house Wives were respected, in charge of the household and the education of the children Marriages could end in divorce Compensation for the wife WRITING AND EDUCATION Writing emerged around 3000BC Hieroglyphics- “priest-carvings” or “sacred writings” Used for painting on temple walls and in tombs Very complex Used both pictures and abstract forms Took much time to learn Hieratic script- a highly simplified form used fro business transactions, record keeping, and general needs of daily life WRITING AND EDUCATION Hieroglyphs were first carved in stone Hieratic script was written on papyrus Scribes-masters of the art of writing Taught reading and writing At age of 10, boys in upper classes went to schools run by scribes Took many years to become a scribe Learned to read and write by copying texts ACHEIVEMENTS IN ARTS AND SCIENCES Pyramids, temples, and other monuments are some of the artistic achievements of the Egyptians Also made advances in mathematics Developed an accurate 365 day calendar Helped in building massive monuments Able to calculate area and volume and used geometry to calculate flooded area Based on movement of the moon, as well as the bright star Sirius, which rises in the sky just before annual flooding of the Nile Medical advancements Embalming Directions for using splints, bandages, and compresses for treating fractures, wounds, and disease EXIT TICKET Using your notes and the book, answer the following question. What were the main features and achievements of Egypt’s three kingdoms?