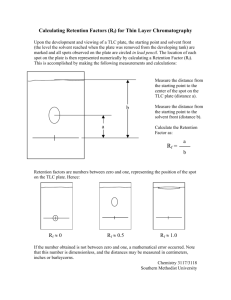
Purity Testing 1. TLC Plate Illustration A TLC (Thin Layer Chromatography) plate is used to separate components of a mixture. It consists of a stationary phase (usually silica gel) coated on a glass or plastic sheet. A sample is applied as a small spot at the baseline, and the mobile phase rises through capillary action. Typical TLC plate regions: I. - Baseline: Where the sample is spotted II. - Solvent front: Final position of the solvent III. - Separated spots: Indicate different components If a substance is pure, it usually shows only one spot on the TLC plate (under UV light or using a staining reagent). 2. Single vs Multiple Spots TLC is a quick method to check purity: - Single Spot: Indicates the substance is likely pure, as only one component is present. - Multiple Spots: Indicates impurities or a mixture of compounds. The Rf value (distance traveled by the compound / distance traveled by solvent) is also compared with a known standard to help verify the identity of the compound. 3. Confirmation Using IR and NMR While TLC gives quick separation information, final confirmation of purity and identity is done using spectroscopic methods: IR Spectroscopy: I. - Identifies functional groups II. - A pure compound shows clean, characteristic absorption peaks NMR Spectroscopy: I. - Gives detailed structural information II. - A pure compound shows well-resolved peaks without unexpected signals Together, TLC, IR, and NMR provide a complete analysis of purity in organic compounds.