Uploaded by
fazaramzy17
Year 8 Chemistry Acids & Alkalis Worksheet | pH Scale & Neutralisation
advertisement

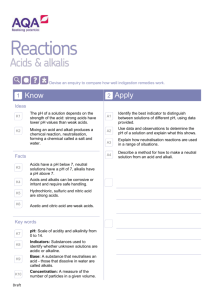
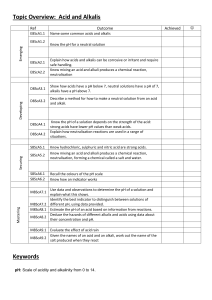
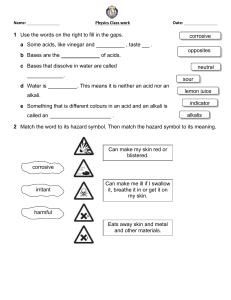
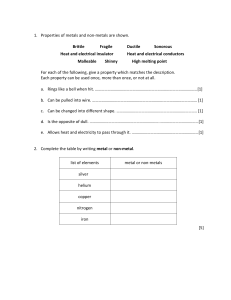
Year 8 Chemistry – Acids and Alkalis Worksheet Learning objectives By the end of this worksheet, you should be able to: - Describe the pH scale and identify acids, alkalis, and neutral substances. - Explain what happens during neutralisation. - Use indicators to test pH. - Apply your knowledge to investigate how indigestion remedies work. Part 1: Recall – Key Knowledge 1. Fill in the blanks: a) Acids have a pH ______ than 7. b) Alkalis have a pH ______ than 7. c) Neutral solutions have a pH of ______. 2. Match the terms to their definitions: Term Definition Indicator A. A substance that neutralises an acid Base B. A measure of how acidic or alkaline a solution is pH scale C. A substance used to show whether a solution is acidic or alkaline 3. Circle the strong acids: Hydrochloric acid, Citric acid, Sulfuric acid, Acetic acid, Nitric acid 4. True or False: a) Acids and alkalis can be corrosive and require safe handling. b) Mixing an acid and an alkali produces only water. c) Neutralisation produces a salt and water. Part 2: Apply – Using Knowledge 5. Devise an enquiry to compare how well different indigestion remedies work. Include: what you will measure, what you will change, what you will keep the same, and how you will ensure safety. 6. Indicators and pH values: You are given four unknown solutions with pH 2, 5, 7, and 11. a) Which are acidic? b) Which are alkaline? c) Which are neutral? d) Suggest the best indicator to distinguish between them and explain why. Part 3: Extend – Challenge Questions 7. Write a general word equation for the reaction between an acid and an alkali. 8. Given these acids and alkalis, write the salt produced when they react: Acid Alkali Hydrochloric acid Sodium hydroxide Sulfuric acid Potassium hydroxide Salt produced Nitric acid Calcium hydroxide 9. Using the data below, deduce which solution is most hazardous and explain why: Substance pH Concentration (mol/dm³) Hydrochloric acid 1 2.0 Ethanoic acid 3 1.0 Sodium hydroxide 13 1.5 10. Estimate the pH of an acid after it reacts completely with an equal amount of alkali and explain your reasoning. Key Terms Acid: Substance with pH < 7 Alkali: Soluble base, pH > 7 Neutralisation: Acid + Alkali → Salt + Water Indicator: Shows whether a substance is acidic, neutral, or alkaline Concentration: Measure of how much solute is in a solution